
An octopus is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda. The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. The soft body can radically alter its shape, enabling octopuses to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their eight appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used both for respiration and for locomotion, by expelling a jet of water. Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse of all invertebrates.

A squid is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.

A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology.

Bobtail squid are a group of cephalopods closely related to cuttlefish. Bobtail squid tend to have a rounder mantle than cuttlefish and have no cuttlebone. They have eight suckered arms and two tentacles and are generally quite small.

Oegopsida is one of the two orders of squid in the superorder Decapodiformes, in the class Cephalopoda. Together with the Myopsina, it was formerly considered to be a suborder of the order Teuthida, in which case it was known as Oegopsina. This reclassification is due to Oegopsina and Myopsina not being demonstrated to form a clade.

Belemnoids are an extinct group of marine cephalopod, very similar in many ways to the modern squid. Like them, the belemnoids possessed an ink sac, but, unlike the squid, they possessed ten arms of roughly equal length, and no tentacles. The name "belemnoid" comes from the Greek word βέλεμνον, belemnon meaning "a dart or arrow" and the Greek word είδος, eidos meaning "form".
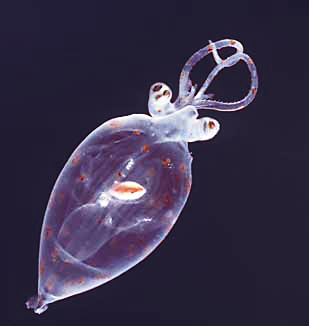
Decapodiformes is a superorder of Cephalopoda comprising all cephalopod species with ten limbs, specifically eight short arms and two long tentacles. It is hypothesized that the ancestral coleoid had five identical pairs of limbs, and that one branch of descendants evolved a modified arm pair IV to become the Decapodiformes, while another branch of descendants evolved and then eventually lost its arm pair II, becoming the Octopodiformes.

Cirrina or Cirrata is a suborder and one of the two main divisions of octopuses. Cirrate octopuses have a small, internal shell and two fins on their head, while their sister suborder Incirrina has neither. The fins of cirrate octopods are associated with a unique cartilage-like shell in a shell sac. In cross-section, the fins have distinct proximal and distal regions, both of which are covered by a thin surface sheath of muscle.

Incirrata is a suborder of the order Octopoda. The suborder contains the classic "benthic octopuses," as well as many pelagic octopus families, including the paper nautiluses. The incirrate octopuses are distinguished from the cirrate octopuses by the absence in the former of the "cirri" filaments for which the cirrates are named, as well as by the lack of paired swimming fins on the head, and lack of a small internal shell.

Octopodiformes is a superorder of the subclass Coleoidea, comprising the octopuses and the vampire squid. All living members of Octopodiformes have eight arms, either lacking the two tentacles of squid or modifying the tentacles into thin filaments. Octopodiformes is often considered the crown group of octopuses and vampire squids, including all descendants of their common ancestor. Some authors use the term Vampyropoda for the same general category, though others use "Vampyropoda" to refer to the total group. Another term is Octobranchia, referring to cephalopods without prominent tentacles.

All cephalopods possess flexible limbs extending from their heads and surrounding their beaks. These appendages, which function as muscular hydrostats, have been variously termed arms, legs or tentacles.

Neocoleoidea is a large group of marine cephalopods. This cohort contains two extant groups: Decapodiformes and Octopodiformes. Species within this group exist in all major habitats in the ocean, in both the southern and northern polar regions, and from intertidal zones to great depths. Whilst conventionally held to be monophyletic, the only morphological character for the group is the presence of suckers: although the presence of these features in the belemnites suggests that they do not support the Neocoleoidea, and hence that the group may be paraphyletic.

Orthoceratoidea is a major subclass of nautiloid cephalopods. Members of this subclass usually have orthoconic (straight) to slightly cyrtoconic (curved) shells, and central to subcentral siphuncles which may bear internal deposits. Orthoceratoids are also characterized by dorsomyarian muscle scars, extensive cameral deposits, and calciosiphonate connecting rings with a porous and calcitic inner layer.
The cephalopods have a long geological history, with the first nautiloids found in late Cambrian strata.

Phragmoteuthida is an order of extinct coleoid cephalopods characterized by a fan-like teuthoid pro-ostracum attached to a belemnoid-like phragmocone.

Belemnitida is an extinct order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most to the tip: the tongue-shaped pro-ostracum, the conical phragmocone, and the pointy guard. The calcitic guard is the most common belemnite remain. Belemnites, in life, are thought to have had 10 hooked arms and a pair of fins on the guard. The chitinous hooks were usually no bigger than 5 mm (0.20 in), though a belemnite could have had between 100 and 800 hooks in total, using them to stab and hold onto prey.
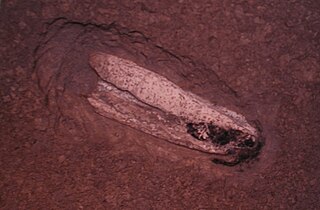
The gladius, or pen, is a hard internal bodypart found in many cephalopods of the superorder Decapodiformes and in a single extant member of the Octopodiformes, the vampire squid. It is so named for its superficial resemblance to the Roman short sword of the same name, and is a vestige of the ancestral mollusc shell, which was external. The gladius is located dorsally within the mantle and usually extends for its entire length. Composed primarily of chitin, it lies within the shell sac, which is responsible for its secretion. Some species, like the bigfin reef squid, still has a gladius with some degree of mineralization.

Argonautoidea is a superfamily of the suborder Incirrata containing all known argonautoids.

Syllipsimopodi is an extinct member of the cephalopod subclass Coleoidea originally interpreted to belong to the clade Vampyropoda, which includes octopuses (Octopoda) and vampire squids (Vampyromorphida). The type and only known species is Syllipsimopodi bideni, named in honor of US President Joe Biden, and to raise awareness of his climate change policies. The holotype fossil was found in the Bear Gulch Limestone deposit in the US state of Montana in 1988, and donated that year to the Royal Ontario Museum by B. Hawes, designated ROMIP 64897. The species lived during the (Carboniferous) Mississippian subperiod, 330.3 to 323.4 million years ago, pushing back the group of cephalopods by 81.9 million years.


















