
The Twelfth Amendment to the United States Constitution provides the procedure for electing the President and Vice President. It replaced the procedure provided in Article II, Section 1, Clause 3, by which the Electoral College originally functioned. The amendment was proposed by the Congress on December 9, 1803, and was ratified by the requisite three-fourths of state legislatures on June 15, 1804. The new rules took effect for the 1804 presidential election and have governed all subsequent presidential elections.

The United States presidential election of 1796 was the third quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, November 4 to Wednesday, December 7, 1796. It was the first contested American presidential election, the first presidential election in which political parties played a dominant role, and the only presidential election in which a president and vice president were elected from opposing tickets. Incumbent Vice President John Adams of the Federalist Party defeated former Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson of the Democratic-Republican Party.

The election of president and vice president of the United States is an indirect election in which citizens of the United States who are registered to vote in one of the 50 U.S. states or in Washington, D.C. cast ballots not directly for those offices, but instead for members of the U.S. Electoral College, known as electors. These electors then in turn cast direct votes, known as electoral votes, for president, and for vice president. The candidate who receives an absolute majority of electoral votes is then elected to that office. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of the votes for President, the House of Representatives chooses the winner; if no one receives an absolute majority of the votes for Vice President, then the Senate chooses the winner.
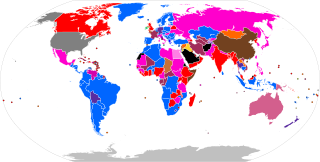
An electoral system is a set of rules that determine how elections and referendums are conducted and how their results are determined. Political electoral systems are organized by governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations.

The 1824 United States elections elected the members of the 19th United States Congress. It marked the end of the Era of Good Feelings and the First Party System. Members of the Democratic-Republican Party continued to maintain a dominant role in federal politics, but the party became factionalized between supporters of Andrew Jackson and supporters of John Quincy Adams. The Federalist Party ceased to function as a national party, having fallen into irrelevance following a relatively strong performance in 1812.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1864. The Liberal Party was the only party to nominate candidates, and the result was a victory for Manuel Murillo Toro.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in February 1866. The result was a victory for Tomás Cipriano de Mosquera of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1868. The result was a victory for Santos Gutiérrez of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1870. The result was a victory for Eustorgio Salgar of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1872. The result was a victory for Manuel Murillo Toro of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1874. The result was a victory for Santiago Pérez de Manosalbas of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1876. The result was a victory for Aquileo Parra of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1878. The result was a victory for Julián Trujillo Largacha of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1880. The result was a victory for Rafael Núñez of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1882. The result was a victory for Francisco Javier Zaldúa of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in the United States of Colombia in 1884. The result was a victory for Rafael Núñez of the Liberal Party.

Presidential elections were held in Colombia on 1 February 1898. The result was a victory for Manuel Antonio Sanclemente of the National Party.

Presidential elections were held in Colombia in 1904. The result was a victory for Rafael Reyes of the Conservative Party.

Presidential elections were held in Gran Colombia in 1825, with Congress certifying the results the following year. The result was a victory for Simón Bolívar, who received 582 of the 608 votes. Francisco de Paula Santander was elected Vice President.
In the United States, a contingent election is the procedure used in presidential elections in the case where no candidate wins an absolute majority of votes in the Electoral College, the constitutional mechanism for electing the President and the Vice President of the United States. A contingent election for the president is decided by a vote of the United States House of Representatives, and the contingent election for the vice president is decided by a vote of the United States Senate. The contingent election procedure, along with the other parts of the presidential election process, was first established in Article Two, Section 1, Clause 3 of the United States Constitution, and then modified by the 12th Amendment in 1804.







