
Fine Gael is a liberal-conservative political party in Ireland. Fine Gael is currently the governing and largest party in Ireland in terms of members of the Oireachtas and Irish members of European Parliament. The party has a membership of 35,000, and is the senior partner governing in a minority coalition with several independent politicians, with party leader Leo Varadkar serving as Taoiseach. Varadkar succeeded Enda Kenny as party leader on 2 June 2017 and as Taoiseach on 14 June; Kenny had been leader since 2002, and Taoiseach since 2011.

Referendums in the United Kingdom are occasionally held at a national, regional or local level. National referendums can be permitted by an Act of Parliament and regulated through the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000, but they are by tradition extremely rare due to the principle of parliamentary sovereignty meaning that they cannot be constitutionally binding on either the Government or Parliament, although they usually have a persuasive political effect.

Latvia elects on national level a legislature. The Saeima has 100 members, elected for a four-year term by proportional representation with a 5% threshold. An unmodified Sainte-Laguë method is used to allocate seats. The parliamentary elections are held on the first Saturday of October. Locally, Latvia elects municipal councils, consisting of 7 to 60 members, depending on the size of the municipality, also by proportional representation for a four-year term.
A constitutional referendum was held in Abkhazia on 3 October 1999, alongside presidential elections. Voters were asked whether they approved of the constitution that had been approved by the Supreme Soviet on 26 November 1994, together with an amendment abolishing the life term for appointed judges and replacing it with five year terms. It was approved by 97.7% of voters. However, ethnic Georgians who had been expelled from Abkhazia during the conflict of 1992–93 did not participate in the referendum and the results were not recognised internationally.

A constitutional referendum was held in Kyrgyzstan on 21 October 2007, following the constitutional crisis caused by amendments passed since the Tulip Revolution in 2005 being invalidated by the Constitutional Court of Kyrgyzstan on 14 September 2007. Voters were asked whether questions on a new constitution and electoral law. Both were approved by over 95% of voters.

An independence referendum was held in the Republic of Georgia on 31 March 1991. It was approved by 99.5% of voters.
Parliamentary elections were held in Abkhazia on 23 November 1996, with a second round on 7 December. There was also a simultaneous referendum held amongst Abkhazian refugees.

A referendum on electing a Constitutional Assembly was held in Colombia on 27 May 1990 alongside presidential elections. The proposal was approved by 96% of voters. A Constitutional Assembly was later elected in December 1990 and produced the 1991 constitution.

Parliamentary elections were held in Colombia on 11 March 1990 alongside local elections and an unofficial referendum on electing a Constitutional Assembly.

Constitutional Assembly elections were held in Colombia on 9 December 1990 alongside a referendum on the Assembly itself. The Assembly sat from February to July 1991 and drew up the 1991 constitution.

This national electoral calendar for the year 2016 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2016 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

A fifteen-part constitutional referendum was held in Colombia on 25 October 2003. Whilst all fifteen proposals were approved by voters, only one question had a sufficient numbers of votes to pass the 25% quorum requirement.

An independence referendum was held on Anjouan, an island in the Comoros, on 26 October 1997. Over 99% of voters voted in favour of independence. However, the vote was not recognised and the island returned to the control of the Comorian government in 2001.

A constitutional referendum was held in Tajikistan on 22 May 2016. A total of 41 constitutional amendments were proposed. The changes included:

The Colombian peace plebiscite to ratify the final agreement on the termination of the Colombian conflict between the Colombian government and the FARC guerillas was held on October 2, 2016. It failed with 50.2% voting against it and 49.8% voting in favor.
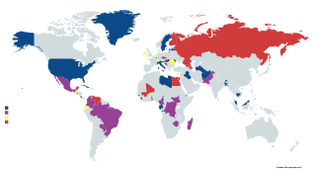
This national electoral calendar for the year 2018 lists the national/federal direct elections to be held in 2018 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included. Specific dates are given where they have been known.

The Common Alternative Revolutionary Force is a communist political party in Colombia, established in 2017 as the political successor of the former rebel group the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC). The peace accords agreed upon by the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia and the Colombian government in 2016 provided for the FARC's participation in politics as a legal, registered political party following its successful disarmament.

The Thirty-seventh Amendment of the Constitution of Ireland is an amendment to the constitution of Ireland which removed the offence of publishing or uttering blasphemous matter. An amendment to the constitution must be proposed in Dáil Éireann, passed by both Houses of the Oireachtas, and approved in a referendum.

A referendum on anti-corruption measures was held in Colombia on 26 August 2018. Voters were asked whether they approve of seven proposals aimed at reducing corruption: limiting the number of terms for politicians at all levels to three; requiring election candidates disclose their assets and those of their relatives; elected politicians being required to disclose their activities and private interests; a requirement for public hearings on budgets; a requirement for all public sector contracts to go out to tender; the removal of the right to parole for people convicted of corruption; and reducing the maximum salary of public officials and politicians from forty times the minimum wage to twenty-five times.














