In abstract algebra, an alternative algebra is an algebra in which multiplication need not be associative, only alternative. That is, one must have
In mathematics, a Clifford algebra is an algebra generated by a vector space with a quadratic form, and is a unital associative algebra with the additional structure of a distinguished subspace. As K-algebras, they generalize the real numbers, complex numbers, quaternions and several other hypercomplex number systems. The theory of Clifford algebras is intimately connected with the theory of quadratic forms and orthogonal transformations. Clifford algebras have important applications in a variety of fields including geometry, theoretical physics and digital image processing. They are named after the English mathematician William Kingdon Clifford (1845–1879).
In mathematics, the octonions are a normed division algebra over the real numbers, a kind of hypercomplex number system. The octonions are usually represented by the capital letter O, using boldface O or blackboard bold . Octonions have eight dimensions; twice the number of dimensions of the quaternions, of which they are an extension. They are noncommutative and nonassociative, but satisfy a weaker form of associativity; namely, they are alternative. They are also power associative.
In mathematics, hypercomplex number is a traditional term for an element of a finite-dimensional unital algebra over the field of real numbers. The study of hypercomplex numbers in the late 19th century forms the basis of modern group representation theory.
In mathematics, the Cayley–Dickson construction, sometimes also known as the Cayley–Dickson process or the Cayley–Dickson procedure produces a sequence of algebras over the field of real numbers, each with twice the dimension of the previous one. It is named after Arthur Cayley and Leonard Eugene Dickson. The algebras produced by this process are known as Cayley–Dickson algebras, for example complex numbers, quaternions, and octonions. These examples are useful composition algebras frequently applied in mathematical physics.
In mathematics, and more specifically in abstract algebra, a *-algebra is a mathematical structure consisting of two involutive ringsR and A, where R is commutative and A has the structure of an associative algebra over R. Involutive algebras generalize the idea of a number system equipped with conjugation, for example the complex numbers and complex conjugation, matrices over the complex numbers and conjugate transpose, and linear operators over a Hilbert space and Hermitian adjoints. However, it may happen that an algebra admits no involution.
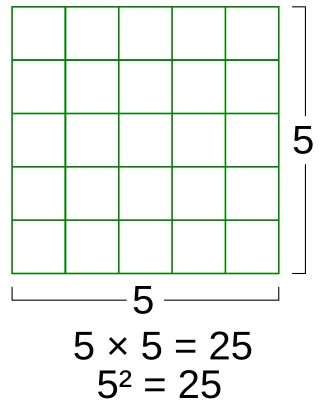
In mathematics, a square is the result of multiplying a number by itself. The verb "to square" is used to denote this operation. Squaring is the same as raising to the power 2, and is denoted by a superscript 2; for instance, the square of 3 may be written as 32, which is the number 9. In some cases when superscripts are not available, as for instance in programming languages or plain text files, the notations x^2 (caret) or x**2 may be used in place of x2. The adjective which corresponds to squaring is quadratic.
In algebra, a split-complex number is based on a hyperbolic unitj satisfying A split-complex number has two real number components x and y, and is written The conjugate of z is Since the product of a number z with its conjugate is an isotropic quadratic form.
In abstract algebra, the biquaternions are the numbers w + xi + yj + zk, where w, x, y, and z are complex numbers, or variants thereof, and the elements of {1, i, j, k} multiply as in the quaternion group and commute with their coefficients. There are three types of biquaternions corresponding to complex numbers and the variations thereof:
In mathematics, given a vector space X with an associated quadratic form q, written (X, q), a null vector or isotropic vector is a non-zero element x of X for which q(x) = 0.
In abstract algebra, the split-quaternions or coquaternions form an algebraic structure introduced by James Cockle in 1849 under the latter name. They form an associative algebra of dimension four over the real numbers.
In mathematics, a quaternion algebra over a field F is a central simple algebra A over F that has dimension 4 over F. Every quaternion algebra becomes a matrix algebra by extending scalars, i.e. for a suitable field extension K of F, is isomorphic to the 2 × 2 matrix algebra over K.
In mathematics, the split-octonions are an 8-dimensional nonassociative algebra over the real numbers. Unlike the standard octonions, they contain non-zero elements which are non-invertible. Also the signatures of their quadratic forms differ: the split-octonions have a split signature (4,4) whereas the octonions have a positive-definite signature (8,0).
In abstract algebra, a bicomplex number is a pair (w, z) of complex numbers constructed by the Cayley–Dickson process that defines the bicomplex conjugate , and the product of two bicomplex numbers as
A non-associative algebra (or distributive algebra) is an algebra over a field where the binary multiplication operation is not assumed to be associative. That is, an algebraic structure A is a non-associative algebra over a field K if it is a vector space over K and is equipped with a K-bilinear binary multiplication operation A × A → A which may or may not be associative. Examples include Lie algebras, Jordan algebras, the octonions, and three-dimensional Euclidean space equipped with the cross product operation. Since it is not assumed that the multiplication is associative, using parentheses to indicate the order of multiplications is necessary. For example, the expressions (ab)(cd), (a(bc))d and a(b(cd)) may all yield different answers.
In mathematics, an octonion algebra or Cayley algebra over a field F is a composition algebra over F that has dimension 8 over F. In other words, it is a 8-dimensional unital non-associative algebra A over F with a non-degenerate quadratic form N such that
In mathematics, Hurwitz's theorem is a theorem of Adolf Hurwitz (1859–1919), published posthumously in 1923, solving the Hurwitz problem for finite-dimensional unital real non-associative algebras endowed with a nondegenerate positive-definite quadratic form. The theorem states that if the quadratic form defines a homomorphism into the positive real numbers on the non-zero part of the algebra, then the algebra must be isomorphic to the real numbers, the complex numbers, the quaternions, or the octonions, and that there are no other possibilities. Such algebras, sometimes called Hurwitz algebras, are examples of composition algebras.
In the field of mathematics called abstract algebra, a division algebra is, roughly speaking, an algebra over a field in which division, except by zero, is always possible.
In algebra, an Okubo algebra or pseudo-octonion algebra is an 8-dimensional non-associative algebra similar to the one studied by Susumu Okubo. Okubo algebras are composition algebras, flexible algebras (A(BA) = (AB)A), Lie admissible algebras, and power associative, but are not associative, not alternative algebras, and do not have an identity element.
In mathematics, a bioctonion, or complex octonion, is a pair (p,q) where p and q are biquaternions.








