
Trillium is a genus of about fifty flowering plant species in the family Melanthiaceae. Trillium species are native to temperate regions of North America and Asia, with the greatest diversity of species found in the southern Appalachian Mountains in the southeastern United States.

Coreopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. Common names include calliopsis and tickseed, a name shared with various other plants.

Constantine Samuel Rafinesque-Schmaltz was a French early 19th-century polymath born near Constantinople in the Ottoman Empire and self-educated in France. He traveled as a young man in the United States, ultimately settling in Ohio in 1815, where he made notable contributions to botany, zoology, and the study of prehistoric earthworks in North America. He also contributed to the study of ancient Mesoamerican linguistics, in addition to work he had already completed in Europe.

Clintonia is a genus of flowering plants in the lily family Liliaceae. Plants of the genus are distributed across the temperate regions of North America and eastern Asia, in the mesic understory of deciduous or coniferous forests. The genus, first described by Constantine Samuel Rafinesque in 1818, was named for DeWitt Clinton (1769–1828), a naturalist and politician from the U.S. state of New York. For this reason, plants of the genus are commonly known as Clinton's lily. The common name bluebead refer to the distinctive fruit of members of the genus. Since fruit color varies somewhat across species, the common name bead lily is used as well.
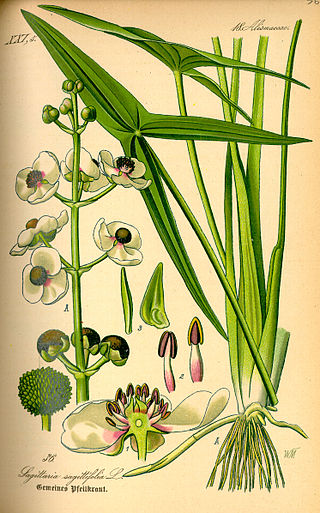
Sagittaria is a genus of about 30 species of aquatic plants whose members go by a variety of common names, including arrowhead, duck potato, swamp potato, tule potato, and wapato. Most are native to South, Central, and North America, but there are also some from Europe, Africa, and Asia.

Peltandra, the arrow arums, is a genus of plants in the family Araceae. It is native to the eastern United States, eastern Canada, and Cuba.
- Peltandra sagittifolia - (Michx.) Morong - Spoon flower or the white arrow arum - southeastern US from eastern Louisiana to Virginia
- Peltandra virginica(L.) Schott - Arum arrow - Cuba, Quebec, Ontario, Oregon, California, Washington; eastern US from Maine to Florida, west to Texas, Kansas, and Minnesota
- †Peltandra primaeva – Eocene, Golden Valley Formation, North Dakota, USA

Spiranthes is a genus of orchids in the subfamily Orchidoideae. They are known commonly as ladies tresses, ladies'-tresses, or lady's tresses. The genus is distributed in the Americas, Eurasia, and Australia. The genus name Spiranthes is derived from the Greek speira ("coil") and anthos ("flower"), and was inspired by the spirally arranged inflorescence.

Arnoglossum is a North American genus of plants in the family Asteraceae, described as a genus in 1817. They have the common name Indian plantain because they resemble the unrelated common plantain.

Heliopsis is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, native to dry prairies in North and South America. The sunflower-like composite flowerheads are usually yellow, up to 8 cm (3 in) in diameter, and are borne in summer. Species are commonly called ox-eye or oxeye.

Galearis is a genus of the orchid family (Orchidaceae) native to North America and eastern Asia. It contains about ten recognized species. The family name comes from the Greek word orchis ('testicle'), in reference to the shape of the root.

Trillium cuneatum, the little sweet betsy, also known as whip-poor-will flower, large toadshade, purple toadshade, and bloody butcher, is a species of flowering plant in the family Melanthiaceae. It is a member of the Trillium cuneatum complex, a subgroup of the sessile-flowered trilliums. It is native to the southeastern United States but is especially common in a region that extends from southern Kentucky through central Tennessee to northern Alabama. In its native habitat, this perennial plant flowers from early March to late April. It is the largest of the eastern sessile-flowered trilliums.
The World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD) is a biogeographical system developed by the international Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG) organization, formerly the International Working Group on Taxonomic Databases. The WGSRPD standards, like other standards for data fields in botanical databases, were developed to promote "the wider and more effective dissemination of information about the world's heritage of biological organisms for the benefit of the world at large". The system provides clear definitions and codes for recording plant distributions at four scales or levels, from "botanical continents" down to parts of large countries. The codes may be referred to as TDWG geographical codes. Current users of the system include the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), and Plants of the World Online (POWO).

Packera glabella is one of several plants with the common name butterweed, this one has also been called cressleaf groundsel and yellowtop. It is native to central and southeastern North America but spreads so aggressively, overtaking other native plants, that it is considered invasive. Further, when eaten, it is toxic to humans and highly toxic to horses & cattle. Authorities recommend eradicating it, conventionally with 2,4-D.

Engelmannia peristenia, called Engelmann daisy or cutleaf daisy, is a North American species of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the south-central United States, primarily from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and southeastern Colorado, but with more isolated populations in Arizona, Louisiana, Arkansas, Missouri, Nebraska, and South Dakota.

Trillium maculatum, the spotted wakerobin or spotted trillium, is a species of flowering plant in the family Melanthiaceae. It is a member of the Trillium cuneatum complex, a closely related group of sessile-flowered trilliums. The species is endemic to the southeastern United States, ranging across Alabama, Georgia, South Carolina, and northern Florida.
Croptilon rigidifolium, called the stiff-leaf scratchdaisy, is a North American species of flowering plants in the tribe Astereae within the family Asteraceae. It has been found in the US State of Texas and also in the Mexican State of Nuevo León.
Croptilon hookerianum, called Hooker's scratchdaisy, is a North American species of flowering plants in the tribe Astereae within the family Asteraceae. It has been found in the US states of Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Arkansas.

Croptilon divaricatum, called the slender scratchdaisy, is a North American species of flowering plants in the tribe Astereae within the family Asteraceae. It is native to the southeastern and south-central United States, in the states of Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Virginia, and the Carolinas.

Krigia cespitosa, known as common dwarf-dandelion, opposite-leaved dwarf-dandelion, or weedy dwarfdandelion, is a North American species of plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to northeastern Mexico and to the southeastern and south-central United States, from Florida to Texas and north as far as southeastern Nebraska, southern Illinois, and central West Virginia

Hypericum virginicum, the marsh St. Johns-wort or Virginia marsh St. Johnswort, is a species of flowering plant in the family Hypericaceae. It is native to the central and eastern United States and eastern Canada.

















