
The national flag of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a sky blue flag, adorned with a yellow star in the upper left canton and cut diagonally by a red stripe with a yellow fimbriation. It was adopted on 18 February 2006. A new constitution, ratified in December 2005 and which came into effect in February 2006, promoted a return to a flag similar to that flown between 1963 and 1971, with a change from a royal blue to sky blue background. Blue represents peace. Red stands for "the blood of the country's martyrs", yellow the country's wealth; and the star symbol the future for the country. It is one of the few national flags incorporating a diagonal line, with other examples including Tanzania, Namibia, Trinidad and Tobago, and Brunei.

Xanthosoma is a genus of flowering plants in the arum family, Araceae. The genus is native to tropical America but widely cultivated and naturalized in other tropical regions. Several are grown for their starchy corms, an important food staple of tropical regions, known variously as malanga, otoy, otoe, cocoyam, tannia, tannier, yautía, macabo, ocumo, macal, taioba, dasheen, quequisque, ʻape and as Singapore taro. Many other species, including especially Xanthosoma roseum, are used as ornamental plants; in popular horticultural literature these species may be known as ‘ape due to resemblance to the true Polynesian ʻape, Alocasia macrorrhizos, or as elephant ear from visual resemblance of the leaf to an elephant's ear. Sometimes the latter name is also applied to members in the closely related genera Caladium, Colocasia (taro), and Alocasia.
Cyttaranthus is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1955. It contains only one known species, Cyttaranthus congolensis, native to tropical Africa.

Ancistrocladus is a genus of woody lianas in the monotypic family Ancistrocladaceae. The branches climb by twining other stems or by scrambling with hooked tips. They are found in the tropics of the Old World.

Aneilema is a genus of monocotyledonous plants of approximately 60 species. The vast majority of the species are native to sub-Saharan Africa, but a few are found in Oceania and one, Aneilema brasiliense, is from South America. It is the third largest genus in the family Commelinaceae after Commelina and Tradescantia, and it is one of only six genera in the family to occur in both the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere.

Angraecopsis is a genus of plants in the family Orchidaceae. It was first described by Fritz Kraenzlin in 1900 and given its name on account with the genus' similarity to Angraecum species. Angraecopsis are native to Africa, Madagascar, Réunion, Mauritius and the Comoros. The growth habit is rather small and the leaves emerge from a woody stem.

Palisota is a genus of plant in family Commelinaceae, first described in 1828. It is native to sub-Saharan Africa.
Eremospatha is a genus of climbing flowering plants in the palm family found in tropical Africa. These rattans are uncommon in cultivation and poorly understood by taxonomists. Closely related to Laccosperma, they are differentiated by the near complete absence of bracts and bracteoles. The name is from Greek meaning "without a spathe".

Hyparrhenia is a genus of grasses. Many species are known commonly as thatching grass.

Democratic Republic of the Congo–Russia relations are the bilateral foreign relations between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Russia. The Democratic Republic of the Congo has an embassy in Moscow and an honorary consulate in Yekaterinburg. Russia has an embassy in Kinshasa. The relations between the two countries were established on July 7, 1960, and restored since November 30, 1967.

Aerangis luteoalba is a species of epiphytic orchid native to eastern and central Africa. This species includes 2 currently recognized varieties:

Amorphophallus titanum, the titan arum, is a flowering plant in the family Araceae. It has the largest unbranched inflorescence in the world. The inflorescence of the talipot palm, Corypha umbraculifera, is larger, but it is branched rather than unbranched. A. titanum is endemic to rainforests on the Indonesian island of Sumatra.

Ancistrorhynchus is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family Orchidaceae. It contains 16 species native to tropical Africa.
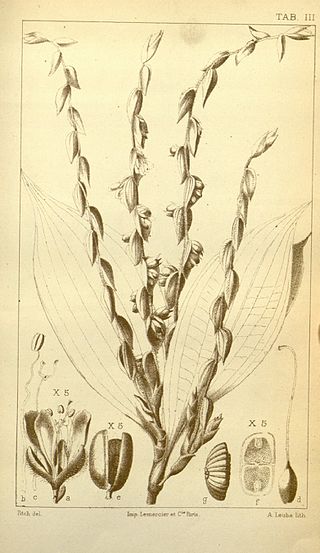
Polyspatha is a genus of perennial monocotyledonous flowering plants in the family Commelinaceae. It is restricted to tropical Africa consists of three recognized species.
Cuviera is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae native to tropical Africa. It was originally described by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1807 and is named after the French naturalist Georges Cuvier.
Amphiasma is a genus of 7 species of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It was described by Cornelis Bremekamp in 1952. The genus is found from southern Tanzania to Namibia.
Aulacocalyx is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is found in tropical Africa.

Craterispermum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It contains 16 species that occur in tropical Africa and Seychelles. It is the only genus in the tribe Craterispermeae, of which the divergence time is estimated at 34.8 million years ago.

Kabuyea is a plant genus in the family Tecophilaeaceae, first described as a genus in 1998. It has one known species, Kabuyea hostifolia, native to Tanzania and Mozambique.

Marantochloa purpurea is a species of plant in the family Marantaceae. It is found in tropical Africa, where its natural habitat is moist lowland forest. The leaf stems are used for various purposes including making string, baskets, mats and traps and the leaves are used for thatching, and for wrapping objects.















