The urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle) is a cycle of biochemical reactions that produces urea (NH2)2CO from ammonia (NH3). Animals that use this cycle, mainly amphibians and mammals, are called ureotelic.

Argininosuccinate synthase or synthetase is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of argininosuccinate from citrulline and aspartate. In humans, argininosuccinate synthase is encoded by the ASS gene located on chromosome 9.

Cyanophycin, also known as CGP or multi-L-arginyl-poly, is a non-protein, non-ribosomally produced amino acid polymer composed of an aspartic acid backbone and arginine side groups.

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).

In enzymology, an arginine—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aspartate—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-alanine—alanyl-poly(glycerolphosphate) ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-aspartate ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an indoleacetate—lysine synthetase (EC 6.3.2.20) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

o-Succinylbenzoate—CoA ligase, encoded from the menE gene in Escherichia coli, catalyzes the fifth reaction in the synthesis of menaquinone. This pathway is called 1, 4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoate biosynthesis I. Vitamin K is a quinone that serves as an electron transporter during anaerobic respiration. This process of anaerobic respiration allows the bacteria to generate the energy required to survive.
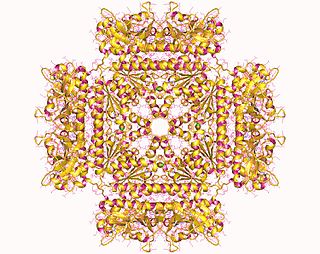
In molecular biology, the protein domain SAICAR synthase is an enzyme which catalyses a reaction to create SAICAR. In enzymology, this enzyme is also known as phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a trypanothione synthase (EC 6.3.1.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [glutamate—ammonia-ligase] adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The bacterial cell wall provides strength and rigidity to counteract internal osmotic pressure, and protection against the environment. The peptidoglycan layer gives the cell wall its strength, and helps maintain the overall shape of the cell. The basic peptidoglycan structure of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria comprises a sheet of glycan chains connected by short cross-linking polypeptides. Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan is a multi-step process comprising three main stages:
- formation of UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid (UDPMurNAc) from N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc).
- addition of a short polypeptide chain to the UDPMurNAc.
- addition of a second GlcNAc to the disaccharide-pentapeptide building block and transport of this unit through the cytoplasmic membrane and incorporation into the growing peptidoglycan layer.
CPHA or CPhA may refer to:
Acetoin dehydrogenase (EC 2.3.1.190, acetoin dehydrogenase complex, acetoin dehydrogenase enzyme system, AoDH ES) is an enzyme with systematic name acetyl-CoA:acetoin O-acetyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

(ADP-ribosyl)hydrolase 1, also termed [Protein ADP-ribosylarginine] hydrolase and protein-Nω-(ADP-D-ribosyl)-L-arginine ADP-ribosylhydrolase (EC 3.2.2.19), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADPRH gene. This enzyme is a specific mono(ADP-ribosyl)hydrolase that catalyses the removal of an ADP-ribosyl modification from target arginine residues of protein substrates. The chemical reactions can formally be described as follows:

Cyanophycinase (EC 3.4.15.6, cyanophycin degrading enzyme, beta-Asp-Arg hydrolysing enzyme, CGPase, CphB, CphE, cyanophycin granule polypeptidase, extracellular CGPase) is an enzyme. It catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cyanophycin synthase (L-aspartate-adding) is an enzyme with systematic name cyanophycin:L-aspartate ligase (ADP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction









