
Cynanchum is a genus of about 300 species including some swallowworts, belonging to the family Apocynaceae. The taxon name comes from Greek kynos and anchein, hence the common name for several species is dog-strangling vine. Most species are non-succulent climbers or twiners. There is some evidence of toxicity.

Robert Wight MD FRS FLS was a Scottish surgeon in the East India Company, whose professional career was spent entirely in southern India, where his greatest achievements were in botany – as an economic botanist and leading taxonomist in south India. He contributed to the introduction of American cotton. As a taxonomist he described 110 new genera and 1267 new species of flowering plants. He employed Indian botanical artists to illustrate many plants collected by himself and Indian collectors he trained. Some of these illustrations were published by William Hooker in Britain, but from 1838 he published a series of illustrated works in Madras including the uncoloured, six-volume Icones Plantarum Indiae Orientalis (1838–53) and two hand-coloured, two-volume works, the Illustrations of Indian Botany (1838–50) and Spicilegium Neilgherrense (1845–51). By the time he retired from India in 1853 he had published 2464 illustrations of Indian plants. The standard author abbreviation Wight is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.

Elaeocarpus munroi is a species of flowering plant in the Elaeocarpaceae family and is endemic to India. It was first formally described in 1838 by Robert Wight who gave it the name Monocera munroii in his book Illustrations of Indian Botany. In 1874, Maxwell T. Masters changed the name to Elaeocarpus munroi in the Hooker's Flora of British India. The specific epithet (munroi) honours the botanist, William Munro.

Eriolaena is a genus of flowering plants. Traditionally included in the family Sterculiaceae, it is included now in the recently expanded Malvaceae. The genus is distributed in Asia, from southern China through Indochina to India, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, and in coastal Mozambique.

The genus Brachystelma is represented by over a hundred species in the world, chiefly distributed in South Africa, South-East Asia and Australasia. In India, 17 species are known to occur, of which nine are endemic.

Vincetoxicum is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae. Although the species in Vincetoxicum have sometimes been included in Cynanchum, chemical and molecular evidence shows that Vincetoxicum is more closely related to Tylophora. The generic name means "poison-beater" in Botanical Latin because of the plants' supposed antidotal effects against snakebite.

Kobresia is a genus of plants in the sedge family. They are sometimes called bog sedges. These perennial sedges are quite similar to Carex species in appearance. The genus is widespread across much of Europe, Asia and North America, with many species native to the Himalayas.
Sphaerocaryum is a genus of Asian plants in the grass family. The only known species is Sphaerocaryum malaccense, native to southern China, Indochina, the Indian Subcontinent, Peninsular Malaysia, Philippines, and Sumatra.

Stenotaphrum is a widespread genus of plants in the grass family.
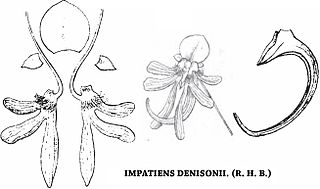
Impatiens denisonii is a scapigerous herb species of the family Balsaminaceae, which is found only in the Western Ghats in South India. It is among the rarest of the eighteen Impatiens species which are endemic to the Nilgiri Hills. It was very abundant and considered among the most beautiful plants in the Nilgiri Hills.
Vincetoxicum auriculatum, synonym Cynanchum auriculatum, is a species of climbing vine. Its Chinese name is niu pi xiao [ 牛皮消 ]. V. auriculatum flowers between June and August; fruiting from August all the way to December.

Periploca is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described for modern science by Linnaeus in 1753. It is native to Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- Periploca aphyllaDecne. - Middle East from Sinai to Pakistan
- Periploca calophylla(Wight) Falc. - S China, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam, E Himalayas, Vietnam
- Periploca chevalieriBrowicz - Cape Verde Islands
- Periploca chrysanthaD.S. Yao, X.D. Chen & J.W. Ren - Gansu Province in China
- Periploca floribundaTsiang - Yunnan, Vietnam
- Periploca forrestiiSchltr. - Guangxi, Guizhou, Qinghai, Sichuan, Tibet, Yunnan, India, Kashmir, Myanmar, Nepal
- Periploca graecaL. - Mediterranean
- Periploca hydaspidisFalc. - Kashmir
- Periploca laevigataAiton - Canary Islands, Savage Islands
- Periploca linearifoliaQuart.-Dill. & A. Rich - Ethiopia
- Periploca nigrescensAfzel. - W Africa
- Periploca refractifoliaGilli - Tanzania
- Periploca sepiumBunge - widespread across much of China
- Periploca tsiangiiD. Fang & H.Z. Ling - Guangxi Province in China
- Periploca visciformis(Vatke) K. Schum. - Somalia

Cynanchum acutum is a species of climbing vine swallowworts native to Europe, Africa, and Asia.

Dregea is a genus of vines in the Apocynaceae, first described as a genus with this name in 1838. It is native to Africa and southern Asia.

Genianthus is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1883. It is native to southern China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.
Lygisma is a plant genus in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1883. It is native to southern China, Indochina, Malaysia, and the Himalayas.
- Lygisma angustifolia(Wight) Hook.f. - Himalayas
- Lygisma flavum(Ridl.) Kerr - Peninsular Malaysia
- Lygisma inflexum(Costantin) Kerr - Vietnam, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan
- Lygisma nervosumKerr - Thailand

Oxystelma is a genus of flowering plants of the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1810. It is native to Africa and Asia.
Pentatropis is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1834. It is native to Africa and southern Asia.
Pentasachme is a species of plants in the Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1834. It contains only one recognized species, Pentasachme caudatum, native to southern China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.

Hypericum hookerianum, or Hooker's St. John's Wort, is a perennial shrub in the flowering plant family Hypericaceae native to eastern and southern Asia. The specific name hookerianum is named for William Jackson Hooker.














