An aldose is a monosaccharide with a carbon backbone chain with a carbonyl group on the endmost carbon atom, making it an aldehyde, and hydroxyl groups connected to all the other carbon atoms. Aldoses can be distinguished from ketoses, which have the carbonyl group away from the end of the molecule, and are therefore ketones.
In biochemistry, isomerases are a general class of enzymes that convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:
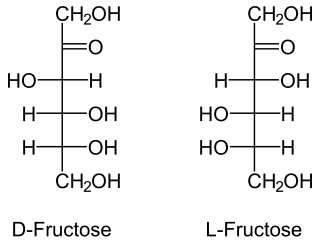
In organic chemistry, a ketose is a monosaccharide containing one ketone group per molecule. The simplest ketose is dihydroxyacetone, which has only three carbon atoms. It is the only ketose with no optical activity. All monosaccharide ketoses are reducing sugars, because they can tautomerize into aldoses via an enediol intermediate, and the resulting aldehyde group can be oxidised, for example in the Tollens' test or Benedict's test. Ketoses that are bound into glycosides, for example in the case of the fructose moiety of sucrose, are nonreducing sugars.
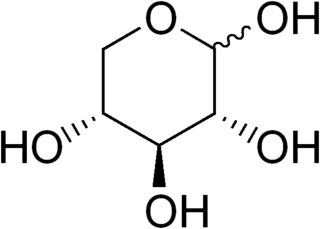
D-Xylose is a five-carbon aldose that can be catabolized or metabolized into useful products by a variety of organisms.
In enzymology, a 4-deoxy-L-threo-5-hexosulose-uronate ketol-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arabinose-5-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arabinose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a corticosteroid side-chain-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a galactose-6-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucuronate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a hydroxypyruvate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-arabinose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-fucose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-rhamnose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mannose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase (PRAI) is an enzyme that catalyzes the third step of the synthesis of the amino acid tryptophan.
In enzymology, a ribose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a S-methyl-5-thioribose-1-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-( methylideneamino)imidazole-4-carboxamide isomerase is an enzyme with systematic name 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-( methylideneamino)imidazole-4-carboxamide aldose-ketose-isomerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

In enzymology, a xylose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of D-xylose and D-xylulose. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those intramolecular oxidoreductases interconverting aldoses and ketoses. The isomerase has now been observed in nearly a hundred species of bacteria. Xylose-isomerases are also commonly called fructose-isomerases due to their ability to interconvert glucose and fructose. The systematic name of this enzyme class is D-xylose aldose-ketose-isomerase. Other names in common use include D-xylose isomerase, D-xylose ketoisomerase, and D-xylose ketol-isomerase.







