
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively.
In molecular biology, biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.
A heptose is a monosaccharide with seven carbon atoms.
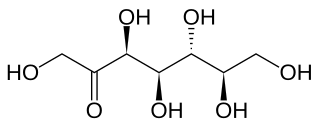
Sedoheptulose or pseudoheptulose or D-altro-heptulose is a ketoheptose—a monosaccharide with seven carbon atoms and a ketone functional group. It is one of the few heptoses found in nature, and is found in various fruits and vegetables ranging from carrots and leeks to figs, mangos and avocados.

Succinyl coenzyme A synthetase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible reaction of succinyl-CoA to succinate. The enzyme facilitates the coupling of this reaction to the formation of a nucleoside triphosphate molecule from an inorganic phosphate molecule and a nucleoside diphosphate molecule. It plays a key role as one of the catalysts involved in the citric acid cycle, a central pathway in cellular metabolism, and it is located within the mitochondrial matrix of a cell.

Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, often just aldolase, is an enzyme catalyzing a reversible reaction that splits the aldol, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, into the triose phosphates dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). Aldolase can also produce DHAP from other (3S,4R)-ketose 1-phosphates such as fructose 1-phosphate and sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate. Gluconeogenesis and the Calvin cycle, which are anabolic pathways, use the reverse reaction. Glycolysis, a catabolic pathway, uses the forward reaction. Aldolase is divided into two classes by mechanism.
Pantothenate kinase (EC 2.7.1.33, PanK; CoaA) is the first enzyme in the Coenzyme A (CoA) biosynthetic pathway. It phosphorylates pantothenate (vitamin B5) to form 4'-phosphopantothenate at the expense of a molecule of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of CoA.

Amidophosphoribosyltransferase (ATase), also known as glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase (GPAT), is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) into 5-phosphoribosyl-1-amine (PRA), using the amine group from a glutamine side-chain. This is the committing step in de novo purine synthesis. In humans it is encoded by the PPAT gene. ATase is a member of the purine/pyrimidine phosphoribosyltransferase family.

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.
In enzymology, an ADP-L-glycero-D-manno-heptose 6-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In molecular biology, the protein domain SAICAR synthase is an enzyme which catalyses a reaction to create SAICAR. In enzymology, this enzyme is also known as phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.47) catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a nicotinate-nucleotide-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose-7-phosphate kinase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 7-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-alpha-D-manno-heptose-7-phosphate kinase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:D-glycero-alpha-D-manno-heptose 7-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate adenylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-alpha-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate guanylyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name GTP:D-glycero-alpha-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate guanylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-β-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate 7-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.82) is an enzyme with systematic name D-glycero-β-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate 7-phosphohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-α-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate 7-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.83) is an enzyme with systematic name D-glycero-α-D-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate 7-phosphohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
TDP-4-oxo-6-deoxy-alpha-D-glucose-3,4-oxoisomerase (dTDP-3-dehydro-6-deoxy-alpha-D-galactopyranose-forming) is an enzyme with systematic name dTDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranose:dTDP-3-dehydro-6-deoxy-alpha-D-galactopyranose isomerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction









