
The Carnarvon xeric shrublands is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion of Western Australia. The ecoregion is coterminous with the Carnarvon Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) bioregion.

The Murchison is an interim Australian bioregion located within the Mid West of Western Australia. The bioregion is loosely related to the catchment area of the Murchison River and has an area of 281,205 square kilometres (108,574 sq mi). Traditionally the region is known as The Murchison.

The Central Kimberley, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the central Kimberley region of Western Australia, comprising an area of 7,675,587 hectares.
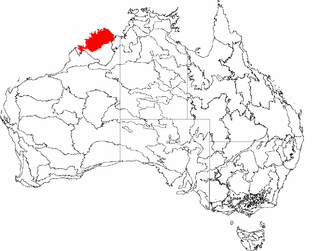
The Northern Kimberley, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the northern Kimberley region of Western Australia, comprising 8,420,100 hectares.

The Victoria Bonaparte, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Northern Territory and Western Australia, comprising 7,301,242 hectares.

Yalgoo is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of 5,087,577 hectares. The bioregion, together with the Avon Wheatbelt and Geraldton Sandplains bioregions, is part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion as classified by the World Wildlife Fund.

Central Ranges is an Australian bioregion, with an area of 101,640.44 square kilometres spreading across two states and one territory: South Australia, Western Australia, and the Northern Territory. It forms a large part of the World Wide Fund for Nature Central Ranges xeric scrub ecoregion.

New England Tablelands, an interim Australian bioregion, is located mainly in New South Wales, comprising 3,002,213 hectares, of which 2,860,758 hectares or 95.23 per cent of the bioregion lies within New South Wales; and the residual within Queensland. This bioregion is one of the smaller bioregions in NSW, occupying 3.57 per cent of the state.

New South Wales North Coast or NSW North Coast, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in New South Wales, comprising 3,996,591 hectares.

The Pine Creek biogeographic region, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Northern Territory, and comprises 2,851,777 hectares.

The Gulf Coastal, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Northern Territory, comprising 2,711,718 hectares.

The Gulf Fall and Uplands, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Northern Territory and Queensland, comprising 11,847,909 hectares.

Burt Plain, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Northern Territory, and comprises 7,379,719 hectares.

The Simpson Strzelecki Dunefields, an interim Australian bioregion, comprises 27,984,283 hectares, and is part of four state/territories of Australia: the Northern Territory, South Australia, New South Wales and Queensland

Mount Isa Inlier, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Queensland, and comprises 6,778,263 hectares.
The Pacific Subtropical Islands is an interim Australian bioregion which includes Norfolk Island and Lord Howe Island. Its IBRA code is PSI.

Central Mackay Coast, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in Queensland, and comprises 1,464,208 hectares.
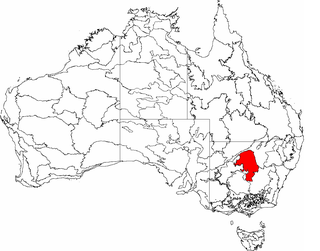
Cobar Peneplain, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in New South Wales, and comprises 7,385,346 hectares.

Finke, an interim Australian bioregion, comprises 7,267,416 hectares, and is part of two state/territories of Australia: the Northern Territory and South Australia. It is part of the Central Ranges xeric scrub ecoregion.

Stony Plains, an interim Australian bioregion, comprises 13,166,372 hectares, and is part of two state/territories of Australia: the Northern Territory and South Australia.



















