
The Murchison is a loosely defined area of Western Australia located within the interior of the Mid West region. It was the subject of a major gold rush in the 1890s and remains a significant mining district. The Murchison is also included as an interim Australian bioregion. The bioregion is loosely related to the catchment area of the Murchison River and has an area of 281,205 square kilometres (108,574 sq mi).
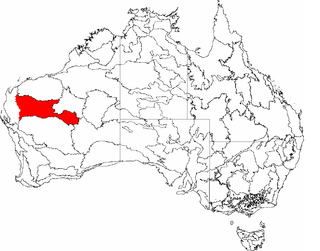
Gascoyne is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of 180,752.57 square kilometres (69,788.96 sq mi). Together with Murchison bioregion to the south, it constitutes the Western Australian Mulga shrublands ecoregion, as assessed by the World Wildlife Fund.

Yalgoo is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of 5,087,577 hectares. The bioregion, together with the Avon Wheatbelt and Geraldton Sandplains bioregions, is part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion as classified by the World Wildlife Fund.

The Brigalow Belt is a wide band of acacia-wooded grassland that runs between tropical rainforest of the coast and the semi-arid interior of Queensland and northern New South Wales, Australia. The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) divides the Brigalow Belt into two IBRA regions, or bioregions, Brigalow Belt North (BBN) and Brigalow Belt South (BBS). The North and South Brigalow Belt are two of the 85 bioregions across Australia and the 15 bioregions in Queensland. Together they form most of the Brigalow tropical savanna ecoregion.
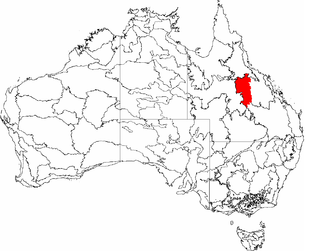
The Desert Uplands is an interim Australian bioregion located in north and central western Queensland which straddles the Great Dividing Range between Blackall and Pentland.

New England Tablelands, an interim Australian bioregion, is located mainly in New South Wales, comprising 3,002,213 hectares, of which 2,860,758 hectares or 95.23 per cent of the bioregion lies within New South Wales; and the residual within Queensland. This bioregion is one of the smaller bioregions in NSW, occupying 3.57 per cent of the state.

New South Wales North Coast or NSW North Coast, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in New South Wales, comprising 3,996,591 hectares.

The Tasmanian South East is an interim Australian bioregion located in the south-eastern region of Tasmania, comprising 1,131,822 hectares.
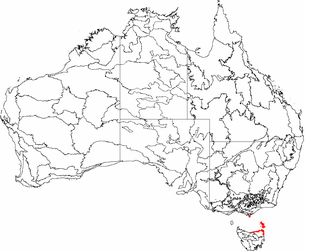
Furneaux is an interim Australian bioregion that includes the Furneaux Group of more than one hundred islands off the northeast coast of Tasmania, as well as the northeast corner of Tasmania and Wilson's Promontory on the Australian mainland. It covers an area of 537,543 hectares.

Nandewar, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in New South Wales and Queensland, and comprises an area of 2,701,977 hectares, surrounded by the Brigalow Belt South to the west, south-west and north-west, and to the east by the New England Tablelands. This is a region of hills on Palaeozoic sediments and lithosols and of Eucalyptus albens woodlands and summer rainfall.

Burt Plain, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Northern Territory, and comprises 7,379,719 hectares.

The Simpson Strzelecki Dunefields, an interim Australian bioregion, comprises 27,984,283 hectares, and is part of four state/territories of Australia: the Northern Territory, South Australia, New South Wales and Queensland

Mount Isa Inlier, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the Queensland, and comprises 6,778,263 hectares.

Central Mackay Coast, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in Queensland, and comprises 1,464,208 hectares.
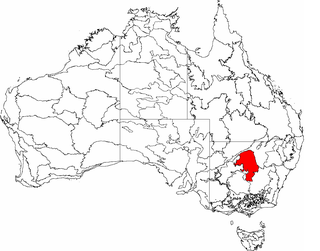
Cobar Peneplain, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in New South Wales, and comprises 7,385,346 hectares.

Finke, an interim Australian bioregion, comprises 7,267,416 hectares, and is part of two state/territories of Australia: the Northern Territory and South Australia. It is part of the Central Ranges xeric scrub ecoregion.

Davenport Murchison Ranges is an interim Australian bioregion located in the Northern Territory. It has an area of 5,805,108 hectares. The bioregion is part of the larger Great Sandy-Tanami desert ecoregion.

Gawler is an interim Australian bioregion located in South Australia. It has an area of 12,002,883 hectares. Gawler bioregion is part of the Tirari–Sturt stony desert ecoregion.

The Darling Riverine Plains is an interim Australian bioregion located in southern Queensland and northern New South Wales. It has an area of 10,699,769 hectares. South Eastern Queensland bioregion is part of the Southeast Australia temperate savanna ecoregion.

The South East Corner is an interim Australian bioregion located in eastern Victoria and south-eastern New South Wales. It has an area of 2,532,053 hectares. The South East Corner bioregion is part of the Southeast Australia temperate forests ecoregion, and it also features the Lowland Grassy Woodland.





















