
Publius Servilius Casca Longus was one of the assassins of Julius Caesar and plebeian tribune in 43 BC. He and several other senators conspired to kill him, a plan which they carried out on 15 March 44 BC. Afterward, Casca fought with the liberators during the Liberators' civil war. He is believed to have died at the Battle of Phillipi either by suicide or at the hands of Octavian's forces.

Nyctereutes is a genus of canid which includes only two extant species, both known as raccoon dogs: the common raccoon dog and the Japanese raccoon dog. Nyctereutes first entered the fossil record 5.5 million years ago (Mya) in northern China. It was one of the earliest canines to arrive in the Old World. All but two species became extinct before the end of the Pleistocene. A study suggests that the evolution of Nyctereutes was influenced by environmental and climatic changes, such as the expansion and contraction of forests and the fluctuations of temperature and precipitation.

Antilocapra is a genus of the family Antilocapridae, which contains only a single living species, the pronghorn (Antilocapra americana). Another species, the Pacific pronghorn, lived in California during the Late Pleistocene and survived as recently as 12,000 BP. The name means "antelope-goat".

Viverravidae is an extinct monophyletic family of mammals from extinct superfamily Viverravoidea within the clade Carnivoramorpha, that lived from the early Palaeocene to the late Eocene in North America, Europe and Asia. They were once thought to be the earliest carnivorans and ancestral to extant ones, but now are placed outside the order Carnivora based on cranial morphology as relatives to extant carnivorans.
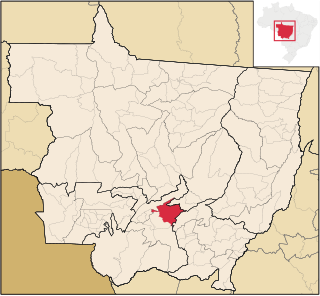
Chapada dos Guimarães is a municipality located in central Brazil, 62 km from the city of Cuiabá, the capital of Mato Grosso State. It is home to the Chapada dos Guimarães National Park. Outside this town is the geographic center of South America.

Pantolambda is an extinct genus of Paleocene pantodont mammal. Pantolambda lived during the middle Paleocene, and has been found both in Asia and North America.

Ailuravus is a genus of prehistoric rodents in the family Ischyromyidae.

Fossilworks was a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world.

Rio Casca is a Brazilian municipality located in the state of Minas Gerais. The city belongs to the mesoregion of Zona da Mata and to the microregion of Ponte Nova. As of 2020, the population was 13,473 in a total area of 384 km².
Brachypsalis is an extinct genus of mustelids, which existed during the Miocene period.
Eocaiman is an extinct genus of caiman containing species living from the Early Paleocene to Miocene in what is now Argentina, Itaboraí Formation of Brazil and Colombia. Eocaiman contains three described species: E. cavernensis, E. palaeocenicus, and E. itaboraiensis, and is typically recovered as one of the more basal members of Caimaninae. Notocaiman was synonymized with Eocaiman paleocenicus in 2022.
Macrocephalochelys is an extinct genus of turtles in the family Chelydridae. It was first described from a partial skull from the Pliocene found in Ukraine by Piboplichko and Taraschchuk in 1960. It was assigned to the family Chelydridae by R. L. Carroll in 1988 although it had been hypothesised to belong in Chelydridae by Chkhikvadze in 1971.

Lystrosauridae is a family of dicynodont therapsids from the Permian and Triassic time periods. It includes two genera, Lystrosaurus and Kwazulusaurus. Kwazulusaurus includes a single species, K. shakai, from the Late Permian of South Africa and Lystrosaurus includes many species from the Late Permian and Early Triassic of South Africa, India, and Antarctica.

Saghacetus is an extinct genus of basilosaurid early whale, fossils of which have been found in the Upper Eocene Qasr el Sagha Formation, Egypt.
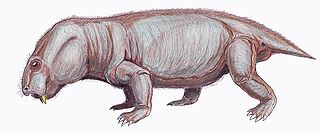
Kingoriidae is an extinct family of dicynodont therapsids. It includes the Late Permian Niassodon, Thliptosaurus, Dicynodontoides and the Triassic Kombuisia.
Scaglia is an extinct genus of South American astrapotherid land mammal that lived during the Eocene.

Masracetus is an extinct genus of basilosaurid ancient whale known from the Late Eocene of Egypt.

The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms.

Tasbacka is an extinct genus of sea turtle containing several species.
Alligator mcgrewi is an extinct species of alligator described by K.P. Schmidt in 1941. They lived in the Early Miocene period, and their range was principally in what is now Nebraska, United States. It is a small alligator with an estimated body length of 1.6 metres (5.2 ft). The Alligator mcgrewi has a unique snout, distinguishing it from other alligator species. This special feature suggests that A. mcgrewi evolved from specific environmental adaptations.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.















