This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

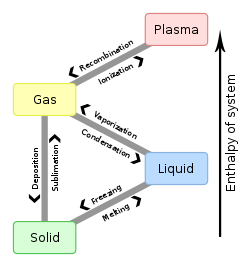
Deposition is the phase transition in which gas transforms into solid without passing through the liquid phase. Deposition is a thermodynamic process. The reverse of deposition is sublimation and hence sometimes deposition is called desublimation.