
Boraginaceae, the borage or forget-me-notfamily, includes about 2,000 species of shrubs, trees, and herbs in 146 to 154 genera with a worldwide distribution.

Echium plantagineum, commonly known as purple viper's-bugloss or Patterson's curse, is a species of the genus Echium native to western and southern Europe, northern Africa, and southwestern Asia. It has also been introduced to Australia, South Africa, and United States, where it is an invasive weed. Due to a high concentration of pyrrolizidine alkaloids, it is poisonous to grazing livestock, especially those with simple digestive systems, such as horses.
Salvation Jane may refer to:

Echium vulgare, known as viper's bugloss and blueweed, is a species of flowering plant in the borage family Boraginaceae. It is native to most of Europe and western and central Asia and it occurs as an introduced species in north-eastern North America, south-western South America and the South and North Island of New Zealand. The plant root was used in ancient times as a treatment for snake or viper bites. If eaten, the plant is toxic to horses and cattle through the accumulation of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in the liver.

Salvation Jane is the fourth studio album by New Zealand singer Jenny Morris. It was released in July 1995 on the rooArt label, after a four-year gap from her last album. The album was produced by Andrew Farriss and Mark Moffatt, together with Electric Hippies' duo Steve Balbi and Justin Stanley. The album featured songs from a songwriting retreat held at Miles Copeland's castle, Chateau de Marouatte, in Bordeaux, France. Here, Morris co-wrote a number of songs with other international songwriters, including Jud Friedman, Rich Wayland, Mark Cawley and Dennis Greaves.

Echium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Boraginaceae that contains about 70 species and several subspecies.
Bugloss is a name used for several plants in the borage family (Boraginaceae):

Stearidonic acid (SDA: C18H28O2; 18:4, n-3) is an ω-3 fatty acid, sometimes called moroctic acid.
Viper's grass most commonly refers to many species in the genus Scorzonera, and can be occasionally styled as viper's-grass.

Paterson's curse or Salvation Jane is an invasive plant species in Australia. There are a number of theories regarding where the name Salvation Jane originated, and it is mostly used in South Australia. These explanations include "salvation jane" referring to the flower which looks similar to the bonnets of Salvation Army ladies, its “salvation” to beekeepers because it is often in flower when the honeyflow is down, and due to its use as a source of emergency food for grazing animals when the less drought-tolerant grazing pastures die off. Other names are blueweed, Lady Campbell weed, Riverina bluebell, and purple viper's bugloss.

Arnoglossum plantagineum also known as tuberous Indian-plantain, groovestem Indian plantain or prairie Indian plantain, is a North American species of Arnoglossum in the sunflower family. The Latin specific epithet plantagineum refers to the leaves of the plant which are similar to those of a plantain.

Utetheisa pulchelloides, the heliotrope moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in the Indo-Australian region including Borneo, Hong Kong, New Zealand, Papua, Seychelles, most of Australia,Tenerife and La Línea de la Concepción [Cádiz]. The species was first described by George Hampson in 1907.
Dialectica aemula is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Australia, India (Bihar) and Nepal.

Singularia alternaria is a moth of the family Pterophoridae. It is found in Argentina, Chile and Ecuador.
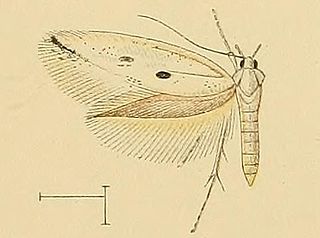
Perittia echiella is a moth of the family Elachistidae. It is found on the Iberian Peninsula, Sardinia and Sicily and in Greece.

Doronicum plantagineum, the plantain-leaved leopard's-bane or plantain false leopardbane, is a European plant species in the sunflower family. It is native to southeastern Europe from Greece and Italy to Ukraine and the Czech Republic. There are reports of the species being naturalized in the State of Oregon in the northwestern United States.

Craterostigma plantagineum, is a resurrection plant species in the genus Craterostigma. It is a dwarf growing plant and can be found to make a 'carpet' across the ground, with blooms in shades of blue and purple. It is a well-studied desiccation-tolerant species known for its extreme vegetative tolerance against dehydration and desiccation. It is native to parts of Africa and to India. It is known as a resurrection plant.

Craterostigma is a genus of shrub-like flowering plants in the family Linderniaceae, found in Africa, Madagascar, Socotra, the Arabian Peninsula, the Indian Subcontinent, Sri Lanka, China, Southeast Asia and Java. The best studied species is the resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum, known for its unique drought tolerance.














