
A tunicate is an exclusively marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata. This grouping is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords. The subphylum was at one time called Urochordata, and the term urochordates is still sometimes used for these animals. They are the only chordates that have lost their myomeric segmentation, with the possible exception of the seriation of the gill slits. However, doliolids still display segmentation of the muscle bands.

Thaliacea is a class of marine animals within the subphylum Tunicata, comprising the salps, pyrosomes and doliolids. Unlike their benthic relatives the ascidians, from which they are believed to have emerged, thaliaceans are free-floating (pelagic) for their entire lifespan. The group includes species with complex life cycles, with both solitary and colonial forms.

Ascidiacea, commonly known as the ascidians or sea squirts, is a paraphyletic class in the subphylum Tunicata of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders. Ascidians are characterized by a tough outer "tunic" made of a polysaccharide.

Botrylloides leachii is a colonial tunicate of the family Styelidae. Its unique methods of propagation and regeneration make it an ideal model organism for use in biological study of development, immunology, stem cells, and regeneration.

Clavelina picta, common name the painted tunicate, is a species of tunicate, in the genus Clavelina. These animals, like all ascidians, are sessile filter feeders.

Ecteinascidia turbinata, commonly known as the mangrove tunicate, is a species of tunicate in the family Perophoridae. It was described to science in 1880 by William Abbott Herdman. The cancer drug trabectedin can be isolated from this species.

Atriolum robustum is a colonial tunicate or sea squirt in the family Didemnidae. It is native to the western and central Indo-Pacific where it is usually found anchored to a hard surface in shallow water.

Didemnum vexillum is a species of colonial tunicate in the family Didemnidae. It is commonly called sea vomit, marine vomit, pancake batter tunicate, or carpet sea squirt. It is thought to be native to Japan, but it has been reported as an invasive species in a number of places in Europe, North America and New Zealand. It is sometimes given the nickname "D. vex" because of the vexing way in which it dominates marine ecosystems when introduced into new locations; however, the species epithet vexillum actually derives from the Latin word for flag, and the species was so named because of the way colonies' long tendrils appear to wave in the water like a flag.

Ciona savignyi is a marine animal sometimes known as the Pacific transparent sea squirt or solitary sea squirt. It is a species of tunicates in the family Cionidae. It is found in shallow waters around Japan and has spread to the west coast of North America where it is regarded as an invasive species.
Perophora viridis, the honeysuckle tunicate, is a species of colonial sea squirt in the genus Perophora found in the tropical western Atlantic Ocean.
Perophora multiclathrata is a species of colonial sea squirt in the genus Perophora. It is native to the tropical Indo-Pacific and the western Atlantic Ocean.
Molgula citrina is a species of solitary tunicate in the family Molgulidae. It is found on both sides of the northern Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. In 2008 it was found in Kachemak Bay in Alaska, the first time it had been detected in the Pacific Ocean.

Morchellium argus, the red-flake ascidian, is a species of colonial sea squirt, a tunicate in the family Polyclinidae. It is native to shallow water in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, especially round the coasts of Britain.

Polyclinum planum is a compound ascidian commonly known as the elephant ear tunicate. It is an ascidian tunicate in the family Polyclinidae. Ascidians are also known as sea squirts.

Polycarpa pomaria is a species of tunicate or sea squirt in the family Styelidae. It is native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean where it lives on the seabed at depths down to about 450 metres (1,500 ft).

Dendrodoa grossularia is a species of tunicate or sea squirt in the family Styelidae, commonly known as the baked bean ascidian. It is native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean where it is common in shallow water and on the lower shore in exposed rocky sites.

Distomus variolosus is a species of tunicate or sea squirt in the family Styelidae. It is native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean where it lives on the seabed, typically on the stems and fronds of kelp.
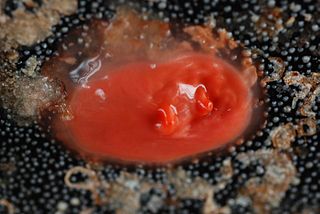
Cnemidocarpa finmarkiensis is a species of solitary ascidian tunicate in the family Styelidae. Common names include broad base sea squirt, orange sea squirt, red sea squirt, shiny orange sea squirt, shiny red tunicate and Finmark's tunicate. It is native to shallow waters in the northern and northeastern Pacific Ocean.

Halocynthia igaboja, commonly known as sea hedgehog, bristly tunicate or spiny sea squirt, is a species of tunicate in the family Pyuridae. It is native to the northeastern Pacific Ocean. This species was first described in 1906 by the Japanese marine biologist Asajiro Oka, who gave it the name Cynthia ritteri. It was later transferred to the genus Halocynthia.

Clavelina ossipandae, the skeleton panda sea squirt or skeleton panda ascidian, is a species of colonial ascidian, a group of sessile, marine filter-feeding invertebrates. Originally discovered near Kume Island in Japan by local divers, pictures of the animal attracted attention in the media for its appearance prior to its formal taxonomic description in 2024.

















