Monomethylhydrazine is a highly toxic, volatile hydrazine derivative with the chemical formula CH3NHNH2. It is used as a rocket propellant in bipropellant rocket engines because it is hypergolic with various oxidizers such as nitrogen tetroxide and nitric acid. As a propellant, it is described in specification MIL-PRF-27404.
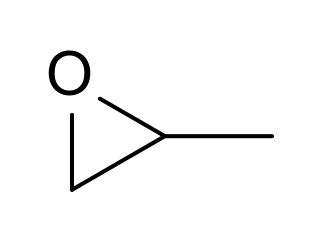
Propylene oxide is an acutely toxic and carcinogenic organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CHCH2O. This colourless volatile liquid with an odour similar to ether, is produced on a large scale industrially. Its major application is its use for the production of polyether polyols for use in making polyurethane plastics. It is a chiral epoxide, although it is commonly used as a racemic mixture.

Bromoform is an organic compound with the chemical formula CHBr3. It is a colorless liquid at room temperature, with a high refractive index and a very high density. Its sweet odor is similar to that of chloroform. It is one of the four haloforms, the others being fluoroform, chloroform, and iodoform. It is a brominated organic solvent. Currently its main use is as a laboratory reagent. It is very slightly soluble in water and is miscible with alcohol, benzene, chloroform, ether, petroleum ether, acetone and oils.
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base.

Hydrogen selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula H2Se. This hydrogen chalcogenide is the simplest and most commonly encountered hydride of selenium. H2Se is a colorless, flammable gas under standard conditions. It is the most toxic selenium compound with an exposure limit of 0.05 ppm over an 8-hour period. Even at extremely low concentrations, this compound has a very irritating smell resembling that of decayed horseradish or 'leaking gas', but smells of rotten eggs at higher concentrations.

Diethylenetriamine (abbreviated Dien or DETA) and also known as 2,2’-Iminodi(ethylamine)) is an organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CH2NH2)2. This colourless hygroscopic liquid is soluble in water and polar organic solvents, but not simple hydrocarbons. Diethylenetriamine is structural analogue of diethylene glycol. Its chemical properties resemble those for ethylene diamine, and it has similar uses. It is a weak base and its aqueous solution is alkaline. DETA is a byproduct of the production of ethylenediamine from ethylene dichloride.

Allyl alcohol is an organic compound with the structural formula CH2=CHCH2OH. Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a raw material for the production of glycerol, but is also used as a precursor to many specialized compounds such as flame-resistant materials, drying oils, and plasticizers. Allyl alcohol is the smallest representative of the allylic alcohols.

Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) is an organic compound in the class known as isocyanates. More specifically, it is an aliphatic diisocyanate. It is produced in relatively small quantities, accounting for only 3.4% of the global diisocyanate market in the year 2000. Aliphatic diisocyanates are used, not in the production of polyurethane foam, but in special applications, such as enamel coatings which are resistant to abrasion and degradation from ultraviolet light. These properties are particularly desirable in, for instance, the exterior paint applied to aircraft.

Dimethoxymethane, also called methylal, is a colorless flammable liquid with a low boiling point, low viscosity and excellent dissolving power. It has a chloroform-like odor and a pungent taste. It is the dimethyl acetal of formaldehyde. Dimethoxymethane is soluble in three parts water and miscible with most common organic solvents.

2-Ethoxyethanol, also known by the trademark Cellosolve or ethyl cellosolve, is a solvent used widely in commercial and industrial applications. It is a clear, colorless, nearly odorless liquid that is miscible with water, ethanol, diethyl ether, acetone, and ethyl acetate.

2-Methoxyethanol, or methyl cellosolve, is an organic compound with formula C
3H
8O
2 that is used mainly as a solvent. It is a clear, colorless liquid with an ether-like odor. It is in a class of solvents known as glycol ethers which are notable for their ability to dissolve a variety of different types of chemical compounds and for their miscibility with water and other solvents. It can be formed by the nucleophilic attack of methanol on protonated ethylene oxide followed by proton transfer:
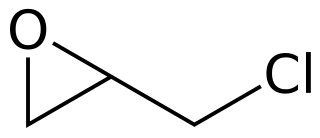
Epichlorohydrin is an organochlorine compound and an epoxide. Despite its name, it is not a halohydrin. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor, moderately soluble in water, but miscible with most polar organic solvents. It is a chiral molecule generally existing as a racemic mixture of right-handed and left-handed enantiomers. Epichlorohydrin is a highly reactive electrophilic compound and is used in the production of glycerol, plastics, epoxy glues and resins, epoxy diluents and elastomers.

Bromochloromethane or methylene bromochloride and Halon 1011 is a mixed halomethane. It is a heavy low-viscosity liquid with refractive index 1.4808.

Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether is an organic compound and is a liquid epoxy resin. The compound is a colorless viscous liquid. It is a key component of many epoxy resin formulations. Addition of further Bisphenol A and a catalyst and heat can produce Bisphenol A glycidyl ether epoxy resins of higher molecular weight that are solid.
4,4′-Methylenedianiline (MDA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2(C6H4NH2)2. It is a colorless solid, although commercial samples can appear yellow or brown. It is produced on an industrial scale, mainly as a precursor to polyurethanes.

m-Xylylenediamine is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CH2NH2)2. A colorless oily liquid, it is produced by hydrogenation of isophthalonitrile.
n-Butyl glycidyl ether is an industrial chemical used in adhesives, sealants, and as a paint or coating additive. It is principally used to reduce the viscosity of epoxy resin systems.
1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether (B14DODGE) is an organic chemical in the glycidyl ether family. It is aliphatic and a colorless liquid. It has two epoxide (oxirane) groups per molecule. Its main use is in modifying epoxy resins especially viscosity reduction.

Diglycidyl resorcinol ether, also called Resorcinol diglycidyl ether (RDGE) is a liquid aromatic organic chemical compound and chemically a glycidyl ether.

Phenyl glycidyl ether, is a liquid aromatic organic chemical in the glycidyl ether class of compounds. It has the formula C9H10O2. It has the CAS Registry Number 122-60-1 and the IUPAC name of 2-(phenoxymethyl)oxirane. A key use is in the viscosity reduction of epoxy resin systems. It is REACH registered and on EINECS under the name 2,3-epoxypropyl phenyl ether.

















