
The Braconidae are a family of parasitoid wasps. After the closely related Ichneumonidae, braconids make up the second-largest family in the order Hymenoptera, with about 17,000 recognized species and many thousands more undescribed. One analysis estimated a total between 30,000 and 50,000, and another provided a narrower estimate between 42,000 and 43,000 species.

Microgastrinae is a subfamily of braconid wasps, encompassing almost 3,000 described species, with an estimated 30,000–50,000 total species. This makes it one of the richest subfamilies with the most species of parasitoid wasps.

The Doryctinae or doryctine wasps are a large subfamily of braconid parasitic wasps (Braconidae). Numerous genera and species formerly unknown to science are being described every year. This subfamily is presumably part of a clade containing otherwise any or all of the Alysiinae, Braconinae, Gnamptodontinae, Opiinae and Ypsistocerinae, and might be most closely related to the last one of these. Whether the Rogadinae are also part of this group is not known.

Bracon is a genus of wasps in the Braconidae, a family of parasitoid wasps. There are several hundred described species but there are thousands still undescribed. The genus is cosmopolitan, distributed throughout the world, with most of the described species occurring in the Palearctic realm.

The Alysiinae are a subfamily of braconid parasitoid wasps with over 1000 described species. Several species have been used in biocontrol programs. They are closely related to the Opiinae.

Blacini is a tribe of braconid Parasitoid wasps. Formerly the subfamily Blacinae, this group was demoted to a tribe and placed within the Brachistinae based on molecular evidence in 2011.

Alabagrus is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are at least 100 described species in Alabagrus.

Brachistinae is a subfamily of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae.

Heerz is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are at least four described species in Heerz, found in Mexico and Central America.
Sathon is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are more than 20 described species in Sathon, found throughout the world.
Deuterixys is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are about 18 described species in Deuterixys, found throughout most of the world.
Fornicia is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are more than 30 described species in Fornicia, found mainly in Asia, Africa, and the Neotropics.

Hygroplitis is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are about nine described species in Hygroplitis, found in the Holarctic.
Iconella is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are about 38 described species in Iconella, found throughout most of the world.
Illidops is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are more than 30 described species in Illidops, found throughout most of the world.
Paroplitis is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are about five described species in Paroplitis.
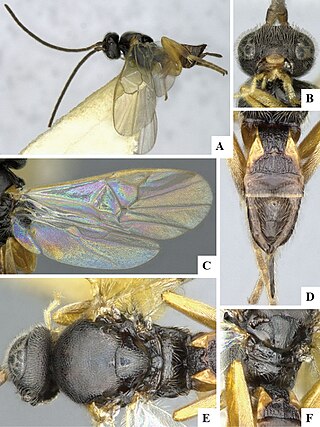
Pholetesor is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are more than 50 described species in Pholetesor, found mainly in the Holarctic.

Protapanteles is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are more than 20 described species in Protapanteles, found mainly in the Holarctic.
Rasivalva is a genus of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae. There are about 12 described species in Rasivalva. They are found mainly in the Holarctic, although one species is found in Africa.
Hormius is a genus of parasitoid wasp in the subfamily Hormiinae first described by Christian Gottfried Daniel Nees von Esenbeck in 1818.











