Scoring
In Divertimento, the instrumentation for each movement is different, as many parts are tacet in some movements. The suite is scored for two flutes, two piccolos (piccolo 2 doubling flute 3), two oboes, a cor anglais, an E-flat clarinet, two clarinets in B-flat and in A, a bass clarinet in B-flat, two bassoons, a contrabassoon, four French horns in F, three trumpets in C, three trombones, a tuba (doubling a baritone euphonium), a large percussion section consisting of timpani, four differently-sized snare drums, a bass drum, a pair of cymbals, a pair of large cymbals, a suspended cymbal, a gong, a triangle, a tambourine, a woodblock, two differently-sized Cuban cowbells, sandpaper blocks, a güiro, a pair of maracas, three bongos, two congas, four temple blocks, a drum kit, a glockenspiel, a xylophone, a vibraphone, and chimes; a piano, a harp, and a standard string section. [2] [3]
Movements
The first movement, Sennets and Tuckets, was initially planned to be the Divertimento itself, a short piece with no further ambitions. The hendiadic title refers to two terms William Shakespeare used to describe fanfares in stage direction: a sennet announces the entrance of a king on stage, while a tucket is used as musical flourishing. It is in C major and 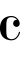 , marked "Allegro non troppo, ma con brio" at the beginning. The B-C relationship is much more conspicuous than in other movements, especially in the last few chords, which feature a strongly dissonant B-C clash. Igor Stravinsky's Dumbarton Oaks concerto is quoted in the movement. [1] [2] The piece features many of the composition styles Bernstein explored in his professional career. [7]
, marked "Allegro non troppo, ma con brio" at the beginning. The B-C relationship is much more conspicuous than in other movements, especially in the last few chords, which feature a strongly dissonant B-C clash. Igor Stravinsky's Dumbarton Oaks concerto is quoted in the movement. [1] [2] The piece features many of the composition styles Bernstein explored in his professional career. [7]
The second movement, Waltz, is a string-only movement where the typical waltz time is replaced with a 7
8 (3
8+2
8+2
8). This is because Bernstein attempted to evoke the waltz from Tchaikovsky's Pathétique Symphony, which is in 5
4, and which was a favorite of Sergei Koussevitzky, a long-time friend and collaborator of Bernstein's, and conductor of the BSO. The movement would later become a song dedicated to Bernstein's daughter Jamie for her 28th birthday. [1] [2] [5]
The third movement, Mazurka, is scored for woodwinds and harp. A slow-moving piece in 3
4 (the time signature only changes for one bar to 5
4), it is marked Mesto (sad) in the score and is in C minor. At the end, the oboe performs a short cadenza where Bernstein quotes the oboe cadenza used by Beethoven in his Fifth Symphony. [1] [2]
The fourth movement, Samba, is colorful, using Latin rhythms and orchestration. Somewhat reminiscent of the music he wrote in other Latino-related works such as West Side Story, the time signature is 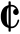 , but frequently changing. It is a fast and lively piece with a few tempo shifts, scored for the whole orchestra. [1] [2]
, but frequently changing. It is a fast and lively piece with a few tempo shifts, scored for the whole orchestra. [1] [2]
The fifth movement, Turkey Trot, has an uncommon time signature: 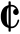 +3
+3
4. [8] It is a dance that is meant to sound odd, almost limping. The composer uses subito dynamic extreme changes and some advanced techniques, such as col legno for the strings. The piece was taken from the discarded Coppola movie project. [1] [2] [5]
The sixth movement, Sphinxes, is the shortest and slowest one. Spanning only 11 bars (with one bar in the middle that acts as a grand pause), the piece features a twelve-tone row. This movement also shares its title with a small movement in Schumann's Carnaval — a piece so simple Schumann was uncertain it was going to be played. The movement ends with an attacca, jumping directly into the next movement. [1] [2]
The seventh movement, Blues, is a slow blues featuring brass and percussion instruments. This movement includes a solo fragment by the baritone euphonium and a short cadenza at the end by the first trumpet. Time signatures are variable, but they generally shift from 12
8 to 9
8. Bernstein specifically requests the drum kit to largely ad lib his part with the brass while encouraging "spontaneous invention". The movement is a reference to Bernstein's boyhood visits to Boston nightclubs, and bears some resemblance to Bernstein's own Prelude, Fugue and Riffs . [1] [2] [5]
The final movement, In Memoriam; March: "The BSO Forever" is a movement in two parts. The first part, In Memoriam is a slow "Andante" section with a solemn canon scored for three flutes. According to Jack Gottlieb, this section is meant to serve as remembrance to "the conductors and members of the Boston Symphony Orchestra no longer with us". After a long trill, the segment segues into the march. The march, a lively and fast dance, is loosely based on the Radetzky March , which was a regular feature of Arthur Fiedler's Boston Pops concerts. The march is followed by a Trio I which features a different theme. This is, in turn, followed by a Trio II, only to come back to the main march. After a long pause, the Trio II theme and the ending are reprised. Near the end, Bernstein's score asks the two main flutists and, later, the entire brass section to stand up, which was typical of traditional Sousa marches, especially The Stars and Stripes Forever , which is where the title comes from. [1] [2]
