Related Research Articles
Deamination is the removal of an amino group from a molecule. Enzymes that catalyse this reaction are called deaminases.

In biochemistry, a nuclease is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides of nucleic acids. Nucleases variously effect single and double stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of DNA repair. Defects in certain nucleases can cause genetic instability or immunodeficiency. Nucleases are also extensively used in molecular cloning.

Exodeoxyribonuclease V is an enzyme of E. coli that initiates recombinational repair from potentially lethal double strand breaks in DNA which may result from ionizing radiation, replication errors, endonucleases, oxidative damage, and a host of other factors. The RecBCD enzyme is both a helicase that unwinds, or separates the strands of DNA, and a nuclease that makes single-stranded nicks in DNA. It catalyses exonucleolytic cleavage in either 5′- to 3′- or 3′- to 5′-direction to yield 5′-phosphooligonucleotides.
In molecular biology, endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically, while many, typically called restriction endonucleases or restriction enzymes, cleave only at very specific nucleotide sequences. Endonucleases differ from exonucleases, which cleave the ends of recognition sequences instead of the middle (endo) portion. Some enzymes known as "exo-endonucleases", however, are not limited to either nuclease function, displaying qualities that are both endo- and exo-like. Evidence suggests that endonuclease activity experiences a lag compared to exonuclease activity.
DNA glycosylases are a family of enzymes involved in base excision repair, classified under EC number EC 3.2.2. Base excision repair is the mechanism by which damaged bases in DNA are removed and replaced. DNA glycosylases catalyze the first step of this process. They remove the damaged nitrogenous base while leaving the sugar-phosphate backbone intact, creating an apurinic/apyrimidinic site, commonly referred to as an AP site. This is accomplished by flipping the damaged base out of the double helix followed by cleavage of the N-glycosidic bond.

In biochemistry and molecular genetics, an AP site, also known as an abasic site, is a location in DNA that has neither a purine nor a pyrimidine base, either spontaneously or due to DNA damage. It has been estimated that under physiological conditions 10,000 apurinic sites and 500 apyrimidinic may be generated in a cell daily.
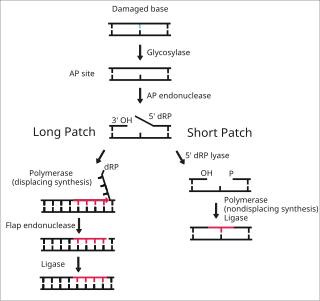
Base excision repair (BER) is a cellular mechanism, studied in the fields of biochemistry and genetics, that repairs damaged DNA throughout the cell cycle. It is responsible primarily for removing small, non-helix-distorting base lesions from the genome. The related nucleotide excision repair pathway repairs bulky helix-distorting lesions. BER is important for removing damaged bases that could otherwise cause mutations by mispairing or lead to breaks in DNA during replication. BER is initiated by DNA glycosylases, which recognize and remove specific damaged or inappropriate bases, forming AP sites. These are then cleaved by an AP endonuclease. The resulting single-strand break can then be processed by either short-patch or long-patch BER.

DNA polymerase II is a prokaryotic DNA-dependent DNA polymerase encoded by the PolB gene.

Activation-induced cytidine deaminase, also known as AICDA, AID and single-stranded DNA cytosine deaminase, is a 24 kDa enzyme which in humans is encoded by the AICDA gene. It creates mutations in DNA by deamination of cytosine base, which turns it into uracil. In other words, it changes a C:G base pair into a U:G mismatch. The cell's DNA replication machinery recognizes the U as a T, and hence C:G is converted to a T:A base pair. During germinal center development of B lymphocytes, error-prone DNA repair following AID action also generates other types of mutations, such as C:G to A:T. AID is a member of the APOBEC family.
A nick is a discontinuity in a double stranded DNA molecule where there is no phosphodiester bond between adjacent nucleotides of one strand typically through damage or enzyme action. Nicks allow DNA strands to untwist during replication, and are also thought to play a role in the DNA mismatch repair mechanisms that fix errors on both the leading and lagging daughter strands.
Deoxyribonuclease IV (phage-T4-induced) is catalyzes the degradation nucleotides in DsDNA by attacking the 5'-terminal end.
Uracil-DNA glycosylase is an enzyme. Its most important function is to prevent mutagenesis by eliminating uracil from DNA molecules by cleaving the N-glycosidic bond and initiating the base-excision repair (BER) pathway.

Cyclin-O is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNO gene.

G/T mismatch-specific thymine DNA glycosylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TDG gene. Several bacterial proteins have strong sequence homology with this protein.

DNA-3-methyladenine glycosylase also known as 3-alkyladenine DNA glycosylase (AAG) or N-methylpurine DNA glycosylase (MPG) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MPG gene.

Single-strand selective monofunctional uracil DNA glycosylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMUG1 gene. SMUG1 is a glycosylase that removes uracil from single- and double-stranded DNA in nuclear chromatin, thus contributing to base excision repair.

Very short patch (VSP) repair is a DNA repair system that removes GT mismatches created by the deamination of 5-methylcytosine to thymine. This system exists because the glycosylases which normally target deaminated bases cannot target thymine.
The RecF pathway, also called the RecFOR pathway, is a pathway of homologous recombination that repairs DNA in bacteria. It repairs breaks that occur on only one of DNA's two strands, known as single-strand gaps. The RecF pathway can also repair double-strand breaks in DNA when the RecBCD pathway, another pathway of homologous recombination in bacteria, is inactivated by mutations. Like the RecBCD pathway, the RecF pathway requires RecA for strand invasion. The two pathways are also similar in their phases of branch migration, in which the Holliday junction slides in one direction, and resolution, in which the Holliday junctions are cleaved apart by enzymes.

The FPG IleRS zinc finger domain represents a zinc finger domain found at the C-terminal in both DNA glycosylase/AP lyase enzymes and in isoleucyl tRNA synthetase. In these two types of enzymes, the C-terminal domain forms a zinc finger.
DNA-deoxyinosine glycosylase is an enzyme with systematic name DNA-deoxyinosine deoxyribohydrolase. This enzyme is involved in DNA damage repair and targets hypoxanthine bases.
References
- ↑ Barrett TE, Schärer OD, Savva R, Brown T, Jiricny J, Verdine GL, Pearl LH (December 1999). "Crystal structure of a thwarted mismatch glycosylase DNA repair complex". The EMBO Journal. 18 (23): 6599–609. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.23.6599. PMC 1171723 . PMID 10581234.
- ↑ Sung JS, Mosbaugh DW (August 2000). "Escherichia coli double-strand uracil-DNA glycosylase: involvement in uracil-mediated DNA base excision repair and stimulation of activity by endonuclease IV". Biochemistry. 39 (33): 10224–35. doi:10.1021/bi0007066. PMID 10956012.
- ↑ Mokkapati SK, Fernández de Henestrosa AR, Bhagwat AS (September 2001). "Escherichia coli DNA glycosylase Mug: a growth-regulated enzyme required for mutation avoidance in stationary-phase cells". Molecular Microbiology. 41 (5): 1101–11. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02559.x. PMID 11555290.