
Oscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. The term vibration is precisely used to describe mechanical oscillation. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current.

The bass drum, or kick drum, is a large drum that produces a note of low definite or indefinite pitch. The instrument is typically cylindrical, with the drum's diameter much greater than the drum's depth, with a struck head at both ends of the cylinder. The heads may be made of calfskin or plastic and there is normally a means of adjusting the tension either by threaded taps or by strings. Bass drums are built in a variety of sizes, but size does not dictate the volume produced by the drum. The pitch and the sound can vary much with different sizes, but the size is also chosen based on convenience and aesthetics. Bass drums are percussion instruments and vary in size and are used in several musical genres. Three major types of bass drums can be distinguished.
In Western musical notation, the staff (US) or stave (UK) is a set of five horizontal lines and four spaces that each represent a different musical pitch or in the case of a percussion staff, different percussion instruments. Appropriate music symbols, depending on the intended effect, are placed on the staff according to their corresponding pitch or function. Musical notes are placed by pitch, percussion notes are placed by instrument, and rests and other symbols are placed by convention.

Straightedge and compass construction, also known as ruler-and-compass construction or classical construction, is the construction of lengths, angles, and other geometric figures using only an idealized ruler and a pair of compasses.

An engineering drawing is a type of technical drawing that is used to convey information about an object. A common use is to specify the geometry necessary for the construction of a component and is called a detail drawing. Usually, a number of drawings are necessary to completely specify even a simple component. The drawings are linked together by a master drawing or assembly drawing which gives the drawing numbers of the subsequent detailed components, quantities required, construction materials and possibly 3D images that can be used to locate individual items. Although mostly consisting of pictographic representations, abbreviations and symbols are used for brevity and additional textual explanations may also be provided to convey the necessary information.
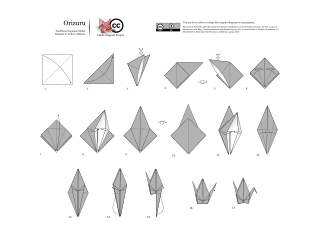
The Yoshizawa–Randlett system is a diagramming system used to describe the folds of origami models. Many origami books begin with a description of basic origami techniques which are used to construct the models. There are also a number of standard bases which are commonly used as a first step in construction. Models are typically classified as requiring low, intermediate or high skill depending on the complexity of the techniques involved in the construction.

A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground noises and shaking such as caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The output of such a device—formerly recorded on paper or film, now recorded and processed digitally—is a seismogram. Such data is used to locate and characterize earthquakes, and to study the Earth's internal structure.

The discipline of origami or paper folding has received a considerable amount of mathematical study. Fields of interest include a given paper model's flat-foldability, and the use of paper folds to solve up-to cubic mathematical equations.

A theodolite is a precision optical instrument for measuring angles between designated visible points in the horizontal and vertical planes. The traditional use has been for land surveying, but they are also used extensively for building and infrastructure construction, and some specialized applications such as meteorology and rocket launching.

An alidade or a turning board is a device that allows one to sight a distant object and use the line of sight to perform a task. This task can be, for example, to triangulate a scale map on site using a plane table drawing of intersecting lines in the direction of the object from two or more points or to measure the angle and horizontal distance to the object from some reference point Polar measurement. Angles measured can be horizontal, vertical or in any chosen plane.

A folding machine is a machine used primarily for the folding of paper. Folding is the sharp-edged bending of paper webs or sheets under pressure at a prepared or unprepared bending point along a straight line according to specified dimensions and folding layouts. Paper can be folded with either a buckle or a knife; thus, there are generally three types of folding machines: buckle folders, knife folders or a combination of these two types. Whilst buckle folding is the more popular of the two methods, knife folding is sometimes preferable. Folding machine models vary in sophistication, with high-end machines capable of processing more complex folding jobs and unusual paper forms. Organizations required to undertake mass mail-out campaigns often employ folding machines to improve efficiency. However it is very commonly used finishing process across the printing industry.
The dynamic stability of an aircraft refers to how the aircraft behaves after it has been disturbed following steady non-oscillating flight.

A raster scan, or raster scanning, is the rectangular pattern of image capture and reconstruction in television. By analogy, the term is used for raster graphics, the pattern of image storage and transmission used in most computer bitmap image systems. The word raster comes from the Latin word rastrum, which is derived from radere ; see also rastrum, an instrument for drawing musical staff lines. The pattern left by the lines of a rake, when drawn straight, resembles the parallel lines of a raster: this line-by-line scanning is what creates a raster. It is a systematic process of covering the area progressively, one line at a time. Although often a great deal faster, it is similar in the most general sense to how one's gaze travels when one reads lines of text. The data to be drawn is stored in an area of memory called the refresh buffer or frame buffer. This memory area holds the values for each pixel on the screen. These values are retrieved from the refresh buffer and painted onto the screen one row at a time.

A circumferentor, or surveyor's compass, is an instrument used in surveying to measure horizontal angles. It was superseded by the theodolite in the early 19th century.
T2K is a particle physics experiment studying the oscillations of the accelerator neutrinos. The experiment is conducted in Japan by the international cooperation of about 500 physicists and engineers with over 60 research institutions from several countries from Europe, Asia and North America and it is a recognized CERN experiment (RE13).

An exercise book or composition book is a notebook that is used in schools to copy down schoolwork and notes. A student will usually have a different exercise book for each separate lesson or subject.

Kawasaki's theorem is a theorem in the mathematics of paper folding that describes the crease patterns with a single vertex that may be folded to form a flat figure. It states that the pattern is flat-foldable if and only if alternatingly adding and subtracting the angles of consecutive folds around the vertex gives an alternating sum of zero. Crease patterns with more than one vertex do not obey such a simple criterion, and are NP-hard to fold.

In geometry, a pentagon is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540°.

In surveying, a gyrotheodolite is an instrument composed of a gyrocompass mounted to a theodolite. It is used to determine the orientation of true north. It is the main instrument for orientation in mine surveying and in tunnel engineering, where astronomical star sights are not visible and GPS does not work.

In mathematics, Lill's method is a visual method of finding the real roots of a univariate polynomial of any degree. It was developed by Austrian engineer Eduard Lill in 1867. A later paper by Lill dealt with the problem of complex roots.


















