Kim Eric Drexler is an American engineer best known for introducing molecular nanotechnology (MNT), and his studies of its potential from the 1970s and 1980s. His 1991 doctoral thesis at Massachusetts Institute of Technology was revised and published as the book Nanosystems: Molecular Machinery Manufacturing and Computation (1992), which received the Association of American Publishers award for Best Computer Science Book of 1992. He has been called the "godfather of nanotechnology".

Molecular nanotechnology (MNT) is a technology based on the ability to build structures to complex, atomic specifications by means of mechanosynthesis. This is distinct from nanoscale materials. Based on Richard Feynman's vision of miniature factories using nanomachines to build complex products, this advanced form of nanotechnology would make use of positionally-controlled mechanosynthesis guided by molecular machine systems. MNT would involve combining physical principles demonstrated by biophysics, chemistry, other nanotechnologies, and the molecular machinery of life with the systems engineering principles found in modern macroscale factories.
Nanotechnology was defined by the National Nanotechnology Initiative as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. The definition of nanotechnology is inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is therefore common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to the broad range of research and applications whose common trait is size. An earlier description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology.

"There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom: An Invitation to Enter a New Field of Physics" was a lecture given by physicist Richard Feynman at the annual American Physical Society meeting at Caltech on December 29, 1959. Feynman considered the possibility of direct manipulation of individual atoms as a more robust form of synthetic chemistry than those used at the time. Although versions of the talk were reprinted in a few popular magazines, it went largely unnoticed until the 1980s.

Richard Errett Smalley was an American chemist who was the Gene and Norman Hackerman Professor of Chemistry, Physics, and Astronomy at Rice University. In 1996, along with Robert Curl, also a professor of chemistry at Rice, and Harold Kroto, a professor at the University of Sussex, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of a new form of carbon, buckminsterfullerene, also known as buckyballs. He was an advocate of nanotechnology and its applications.
Gray goo is a hypothetical global catastrophic scenario involving molecular nanotechnology in which out-of-control self-replicating machines consume all biomass on Earth while building many more of themselves, a scenario that has been called ecophagy(the literal consumption of the ecosystem). The original idea assumed machines were designed to have this capability, while popularizations have assumed that machines might somehow gain this capability by accident.

A molecular assembler, as defined by K. Eric Drexler, is a "proposed device able to guide chemical reactions by positioning reactive molecules with atomic precision". A molecular assembler is a kind of molecular machine. Some biological molecules such as ribosomes fit this definition. This is because they receive instructions from messenger RNA and then assemble specific sequences of amino acids to construct protein molecules. However, the term "molecular assembler" usually refers to theoretical human-made devices.
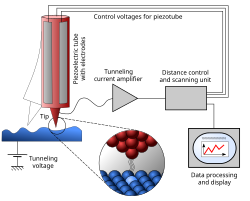
Mechanosynthesis is a term for hypothetical chemical syntheses in which reaction outcomes are determined by the use of mechanical constraints to direct reactive molecules to specific molecular sites. There are presently no non-biological chemical syntheses which achieve this aim. Some atomic placement has been achieved with scanning tunnelling microscopes.

Engines of Creation: The Coming Era of Nanotechnology is a 1986 molecular nanotechnology book written by K. Eric Drexler with a foreword by Marvin Minsky. An updated version was released in 2007. The book has been translated into Japanese, French, Spanish, Italian, Russian, and Chinese.

Nanoid robotics, or for short, nanorobotics or nanobotics, is an emerging technology field creating machines or robots, which are called nanorobots or simply nanobots, whose components are at or near the scale of a nanometer. More specifically, nanorobotics refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building nanorobots with devices ranging in size from 0.1 to 10 micrometres and constructed of nanoscale or molecular components. The terms nanobot, nanoid, nanite, nanomachine and nanomite have also been used to describe such devices currently under research and development.
Supramolecular chemistry refers to the branch of chemistry concerning chemical systems composed of a discrete number of molecules. The strength of the forces responsible for spatial organization of the system range from weak intermolecular forces, electrostatic charge, or hydrogen bonding to strong covalent bonding, provided that the electronic coupling strength remains small relative to the energy parameters of the component. While traditional chemistry concentrates on the covalent bond, supramolecular chemistry examines the weaker and reversible non-covalent interactions between molecules. These forces include hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, pi–pi interactions and electrostatic effects.

Molecular machines are a class of molecules typically described as an assembly of a discrete number of molecular components intended to produce mechanical movements in response to specific stimuli, mimicking macromolecular devices such as switches and motors. Naturally occurring or biological molecular machines are responsible for vital living processes such as DNA replication and ATP synthesis. Kinesins and ribosomes are examples of molecular machines, and they often take the form of multi-protein complexes. For the last several decades, scientists have attempted, with varying degrees of success, to miniaturize machines found in the macroscopic world. The first example of an artificial molecular machine (AMM) was reported in 1994, featuring a rotaxane with a ring and two different possible binding sites. In 2016 the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jean-Pierre Sauvage, Sir J. Fraser Stoddart, and Bernard L. Feringa for the design and synthesis of molecular machines.
The use of nanotechnology in fiction has attracted scholarly attention. The first use of the distinguishing concepts of nanotechnology was "There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom", a talk given by physicist Richard Feynman in 1959. K. Eric Drexler's 1986 book Engines of Creation introduced the general public to the concept of nanotechnology. Since then, nanotechnology has been used frequently in a diverse range of fiction, often as a justification for unusual or far-fetched occurrences featured in speculative fiction.
The history of nanotechnology traces the development of the concepts and experimental work falling under the broad category of nanotechnology. Although nanotechnology is a relatively recent development in scientific research, the development of its central concepts happened over a longer period of time. The emergence of nanotechnology in the 1980s was caused by the convergence of experimental advances such as the invention of the scanning tunneling microscope in 1981 and the discovery of fullerenes in 1985, with the elucidation and popularization of a conceptual framework for the goals of nanotechnology beginning with the 1986 publication of the book Engines of Creation. The field was subject to growing public awareness and controversy in the early 2000s, with prominent debates about both its potential implications as well as the feasibility of the applications envisioned by advocates of molecular nanotechnology, and with governments moving to promote and fund research into nanotechnology. The early 2000s also saw the beginnings of commercial applications of nanotechnology, although these were limited to bulk applications of nanomaterials rather than the transformative applications envisioned by the field.

Molecular biophysics is a rapidly evolving interdisciplinary area of research that combines concepts in physics, chemistry, engineering, mathematics and biology. It seeks to understand biomolecular systems and explain biological function in terms of molecular structure, structural organization, and dynamic behaviour at various levels of complexity. This discipline covers topics such as the measurement of molecular forces, molecular associations, allosteric interactions, Brownian motion, and cable theory. Additional areas of study can be found on Outline of Biophysics. The discipline has required development of specialized equipment and procedures capable of imaging and manipulating minute living structures, as well as novel experimental approaches.

David Alan Leigh FRS FRSE FRSC is a British chemist, Royal Society Research Professor and, since 2014, the Sir Samuel Hall Chair of Chemistry in the Department of Chemistry at the University of Manchester. He was previously the Forbes Chair of Organic Chemistry at the University of Edinburgh (2001–2012) and Professor of Synthetic Chemistry at the University of Warwick (1998–2001).
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to nanotechnology:
Wet nanotechnology involves working up to large masses from small ones.
In molecular nanotechnology, chemosynthesis is any chemical synthesis where reactions occur due to random thermal motion, a class which encompasses almost all of modern synthetic chemistry. The human-authored processes of chemical engineering are accordingly represented as biomimicry of the natural phenomena above, and the entire class of non-photosynthetic chains by which complex molecules are constructed is described as chemo-.
This glossary of nanotechnology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to nanotechnology, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.