Related Research Articles

Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of muscle diseases that results in increasing weakening and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ in which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin. Many people will eventually become unable to walk. Some types are also associated with problems in other organs.
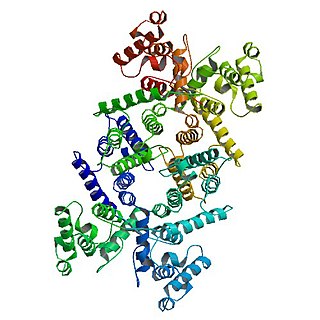
Dystrophin is a rod-shaped cytoplasmic protein, and a vital part of a protein complex that connects the cytoskeleton of a muscle fiber to the surrounding extracellular matrix through the cell membrane. This complex is variously known as the costamere or the dystrophin-associated protein complex (DAPC). Many muscle proteins, such as α-dystrobrevin, syncoilin, synemin, sarcoglycan, dystroglycan, and sarcospan, colocalize with dystrophin at the costamere.

Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy. The symptom of muscle weakness usually begins around the age of four in boys and worsens quickly. Typically muscle loss occurs first in the thighs and pelvis followed by those of the arms. This can result in trouble standing up. Most are unable to walk by the age of 12. Affected muscles may look larger due to increased fat content. Scoliosis is also common. Some may have intellectual disability. Females with a single copy of the defective gene may show mild symptoms.

Becker muscular dystrophy is an X-linked recessive inherited disorder characterized by slowly progressing muscle weakness of the legs and pelvis. It is a type of dystrophinopathy. This is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene, which encodes the protein dystrophin. Becker muscular dystrophy is related to Duchenne muscular dystrophy in that both result from a mutation in the dystrophin gene, but has a milder course.
The sarcoglycans are a family of transmembrane proteins involved in the protein complex responsible for connecting the muscle fibre cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix, preventing damage to the muscle fibre sarcolemma through shearing forces.
The dystrophin-associated protein complex is a multiprotein complex that includes dystrophin and the dystrophin-associated proteins.

Dystroglycan is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DAG1 gene.

Utrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UTRN gene.

The costamere is a structural-functional component of striated muscle cells which connects the sarcomere of the muscle to the cell membrane.
Syncoilin is a muscle-specific intermediate filament, first isolated as a binding partner to α-dystrobrevin, as determined by a yeast two-hybrid assay.
Originally identified as Kirsten ras associated gene (krag), Sarcospan (SSPN) (is a 25-kDa transmembrane protein located in the dystrophin-associated protein complex of skeletal muscle cells, where it is most abundant. It contains four transmembrane spanning helices with both N- and C-terminal domains located intracellularly. Loss of SSPN expression occurs in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dystrophin is required for proper localization of SSPN. SSPN is also an essential regulator of Akt signaling pathways. Without SSPN, Akt signaling pathways will be hindered and muscle regeneration will not occur.
The syntrophins are a family of five 60-kiloDalton proteins that are associated with dystrophin, the protein associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and Becker muscular dystrophy. The name comes from the Greek word syntrophos, meaning "companion." The five syntrophins are encoded by separate genes and are termed α, β1, β2, γ1, and γ2. Syntrophin was first identified as a dystrophin-associated protein present in the Torpedo electric organ. Subsequently, α-syntrophin was shown to be the predominant isoform in skeletal muscle where it is localized on the sarcolemma and enriched at the neuromuscular junction. The β-syntrophins and γ2-syntrophin are also present in skeletal muscle but also are in most other tissues. The expression of γ1-syntrophin is mostly confined to brain. The syntrophins are adaptor proteins that use their multiple protein interaction domains to localize a variety of signaling proteins to specific intracellular locations. α-Syntrophin binds to nNOS in the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex in skeletal muscle cells. There it produces NO upon muscle contraction leading to dilation of the arteries in the local area.
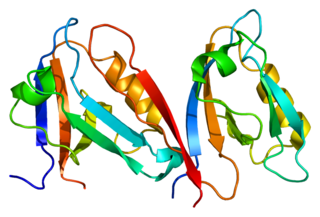
Alpha-1-syntrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNTA1 gene. Alpha-1 syntrophin is a signal transducing adaptor protein and serves as a scaffold for various signaling molecules. Alpha-1 syntrophin contains a PDZ domain, two Pleckstrin homology domain and a 'syntrophin unique' domain.

Beta-sarcoglycan is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SGCB gene.

Beta-2-syntrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNTB2 gene.

Beta-1-syntrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNTB1 gene.

Dystrobrevin alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DTNA gene.

Beta dystrobrevin also known as DTNB is a protein which in humans is encoded by the DTNB gene.
In molecular biology, exon skipping is a form of RNA splicing used to cause cells to “skip” over faulty or misaligned sections of genetic code, leading to a truncated but still functional protein despite the genetic mutation.
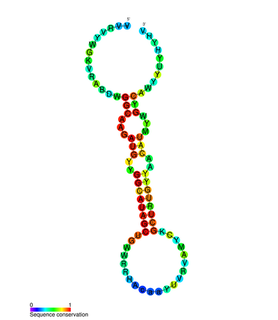
miR-31 has been characterised as a tumour suppressor miRNA, with its levels varying in breast cancer cells according to the metastatic state of the tumour. From its typical abundance in healthy tissue is a moderate decrease in non-metastatic breast cancer cell lines, and levels are almost completely absent in mouse and human metastatic breast cancer cell lines. There has also been observed a strong encapsulation of tumour cells expressing miR-31, as well as a reduced cell survival rate. miR-31's antimetastatic effects therefore make it a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer. However, these two papers were formally retracted by the authors in 2015.
References
- ↑ Dystrophin-Associated Proteins at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |