Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the binding of Ca2+ is required for the activation of calmodulin. Once bound to Ca2+, calmodulin acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins such as kinases or phosphatases.
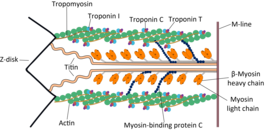
Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-specific troponins I and T are extensively used as diagnostic and prognostic indicators in the management of myocardial infarction and acute coronary syndrome. Blood troponin levels may be used as a diagnostic marker for stroke or other myocardial injury that is ongoing, although the sensitivity of this measurement is low.

Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state.

Troponin I, cardiac muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNNI3 gene. It is a tissue-specific subtype of troponin I, which in turn is a part of the troponin complex.
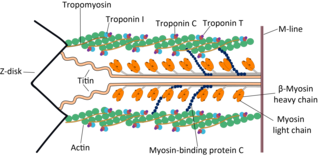
Cardiac muscle troponin T (cTnT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNNT2 gene. Cardiac TnT is the tropomyosin-binding subunit of the troponin complex, which is located on the thin filament of striated muscles and regulates muscle contraction in response to alterations in intracellular calcium ion concentration.

Ryanodine receptor 2 (RYR2) is one of a class of ryanodine receptors and a protein found primarily in cardiac muscle. In humans, it is encoded by the RYR2 gene. In the process of cardiac calcium-induced calcium release, RYR2 is the major mediator for sarcoplasmic release of stored calcium ions.

Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TPM1 gene. This gene is a member of the tropomyosin (Tm) family of highly conserved, widely distributed actin-binding proteins involved in the contractile system of striated and smooth muscles and the cytoskeleton of non-muscle cells.

ACTC1 encodes cardiac muscle alpha actin. This isoform differs from the alpha actin that is expressed in skeletal muscle, ACTA1. Alpha cardiac actin is the major protein of the thin filament in cardiac sarcomeres, which are responsible for muscle contraction and generation of force to support the pump function of the heart.

The myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYBPC3 gene. This isoform is expressed exclusively in heart muscle during human and mouse development, and is distinct from those expressed in slow skeletal muscle (MYBPC1) and fast skeletal muscle (MYBPC2).

Troponin C, also known as TN-C or TnC, is a protein that resides in the troponin complex on actin thin filaments of striated muscle and is responsible for binding calcium to activate muscle contraction. Troponin C is encoded by the TNNC1 gene in humans for both cardiac and slow skeletal muscle.

Telethonin, also known as Tcap, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TCAP gene. Telethonin is expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle at Z-discs and functions to regulate sarcomere assembly, T-tubule function and apoptosis. Telethonin has been implicated in several diseases, including limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy and idiopathic cardiomyopathy.

Myosin regulatory light chain 2, ventricular/cardiac muscle isoform (MLC-2) also known as the regulatory light chain of myosin (RLC) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYL2 gene. This cardiac ventricular RLC isoform is distinct from that expressed in skeletal muscle (MYLPF), smooth muscle (MYL12B) and cardiac atrial muscle (MYL7).

Slow skeletal muscle troponin T (sTnT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNNT1 gene.

Myosin heavy chain, α isoform (MHC-α) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYH6 gene. This isoform is distinct from the ventricular/slow myosin heavy chain isoform, MYH7, referred to as MHC-β. MHC-α isoform is expressed predominantly in human cardiac atria, exhibiting only minor expression in human cardiac ventricles. It is the major protein comprising the cardiac muscle thick filament, and functions in cardiac muscle contraction. Mutations in MYH6 have been associated with late-onset hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, atrial septal defects and sick sinus syndrome.

Myosin essential light chain (ELC), ventricular/cardiac isoform is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYL3 gene. This cardiac ventricular/slow skeletal ELC isoform is distinct from that expressed in fast skeletal muscle (MYL1) and cardiac atrial muscle (MYL4). Ventricular ELC is part of the myosin molecule and is important in modulating cardiac muscle contraction.
Calcium buffering describes the processes which help stabilise the concentration of free calcium ions within cells, in a similar manner to how pH buffers maintain a stable concentration of hydrogen ions. The majority of calcium ions within the cell are bound to intracellular proteins, leaving a minority freely dissociated. When calcium is added to or removed from the cytoplasm by transport across the cell membrane or sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium buffers minimise the effect on changes in cytoplasmic free calcium concentration by binding calcium to or releasing calcium from intracellular proteins. As a result, 99% of the calcium added to the cytosol of a cardiomyocyte during each cardiac cycle becomes bound to calcium buffers, creating a relatively small change in free calcium.
ParvE101Q is an experimental modification of parvalbumin, designed to delay calcium sequestration in heart muscles to enhance contraction. The protein parvalbumin has EF hand motifs used for calcium binding. EF hands are structural helix-loop-helix protein subunits that have a high affinity for calcium ions, and a moderate affinity for magnesium ions. In muscle, the binding of Ca2+ by parvalbumin efficiently sequesters it following contraction. This increases the speed of muscle relaxation, allowing the muscle to contract again sooner. Although parvalbumin is classified as a delayed calcium buffer, it quickly sequesters Ca2+, usually before the muscle is done fully contracting. Large amounts of parvalbumin allow rapid contractions of muscles at a high contractile speed with the trade-off of having relatively lower contraction force. This decreased force of contraction is due to the rapid sequestration of Ca2+, preventing prolonged contraction which is required for greater force.
Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling (CardiacEC coupling) describes the series of events, from the production of an electrical impulse (action potential) to the contraction of muscles in the heart. This process is of vital importance as it allows for the heart to beat in a controlled manner, without the need for conscious input. EC coupling results in the sequential contraction of the heart muscles that allows blood to be pumped, first to the lungs (pulmonary circulation) and then around the rest of the body (systemic circulation) at a rate between 60 and 100 beats every minute, when the body is at rest. This rate can be altered, however, by nerves that work to either increase heart rate (sympathetic nerves) or decrease it (parasympathetic nerves), as the body's oxygen demands change. Ultimately, muscle contraction revolves around a charged atom (ion), calcium (Ca2+), which is responsible for converting the electrical energy of the action potential into mechanical energy (contraction) of the muscle. This is achieved in a region of the muscle cell, called the transverse tubule during a process known as calcium induced calcium release.
A8V is point mutation on Troponin C (cTNC) that leads to a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The coordinated cardiac muscle contraction is regulated by the troponin complex on thin filament (troponin C which is calcium binding, troponin T that plays the role with tropomyosin, and troponin I which has an inhibitory action annulating the S1 ATPase activity in the presence of tropomyosin and troponin and absence of Ca2+). This mutation is determined by the change of Alanine to Valine at nucleotide 23 from C to T. Patients with this type of mutation shows thickness on the left ventricle wall of around 18 mm, compared to the normal this thickness would be 12 mm. Also, A8V affects the Ca2+ binding affinity compared to normal genotype and increased sensitivity on force development.
D145E is a point mutation on troponin C that leads to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy disease. This mutation is caused by the change of nucleotide C to A at nucleotide 435, switching the amino acid aspartic acid to glutamic acid, which is located at the C-terminal tail. Patients with this mutation have different structure on the thin filament and alter the binding of Ca2+ at the troponin C site IV. Further, D145E causes increase in development of force and activation of ATPase in the presence of Ca2+.