
The nuclear lamina is a dense fibrillar network inside the nucleus of eukaryote cells. It is composed of intermediate filaments and membrane associated proteins. Besides providing mechanical support, the nuclear lamina regulates important cellular events such as DNA replication and cell division. Additionally, it participates in chromatin organization and it anchors the nuclear pore complexes embedded in the nuclear envelope.
Lamina-associated polypeptide 2 (LAP2), isoforms beta/gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMPO gene. LAP2 is an inner nuclear membrane (INM) protein.

Laminopathies are a group of rare genetic disorders caused by mutations in genes encoding proteins of the nuclear lamina. They are included in the more generic term nuclear envelopathies that was coined in 2000 for diseases associated with defects of the nuclear envelope. Since the first reports of laminopathies in the late 1990s, increased research efforts have started to uncover the vital role of nuclear envelope proteins in cell and tissue integrity in animals.

Prelamin-A/C, or lamin A/C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNA gene. Lamin A/C belongs to the lamin family of proteins.

Lamin-B receptor is a protein, and in humans, it is encoded by the LBR gene.

LEM domain-containing protein 3 (LEMD3), also known as MAN1, is an integral protein in the inner nuclear membrane (INM) of the nuclear envelope. It is encoded by the LEMD3 gene and was first identified after it was isolated from the serum of a patient with a collagen vascular disease.

Chromobox protein homolog 3 is a protein that is encoded by the CBX3 gene in humans.

Nuclear pore glycoprotein-210 (gp210) is an essential trafficking regulator in the eukaryotic nuclear pore complex. Gp-210 anchors the pore complex to the nuclear membrane. and protein tagging reveals its primarily located on the luminal side of double layer membrane at the pore. A single polypeptide motif of gp210 is responsible for sorting to nuclear membrane, and indicate the carboxyl tail of the protein is oriented toward the cytoplasmic side of the membrane.
G2/mitotic-specific cyclin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNB1 gene.

M-phase inducer phosphatase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDC25B gene.

WEE1 homolog , also known as WEE1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the WEE1 gene.

Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUMA1 gene.

Matrix metalloproteinase-16 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP16 gene.

A kinase anchor protein 1, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKAP1 gene.

A-kinase anchor protein 8 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the AKAP8 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase PLK2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PLK2 gene.

Protein unc-84 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UNC84A gene.

Torsin-1A-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TOR1AIP1 gene. More commonly known as lamina associated polypeptide 1 (LAP1), it is a type II integral membrane protein that resides in the inner nuclear membrane. The luminal domain of LAP1 interacts with Torsin A and is necessary for the ATPase activity of Torsin A. LAP1 plays a critical role in skeletal and heart muscle. Mutations in TOR1AIP1 have been linked to muscular dystrophy and cardiomyopathy. It's deletion from mouse hepatocytes leads to defected very-low density lipoprotein secretion and causes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis

Nuclear prelamin A recognition factor, also known as NARF, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NARF gene.
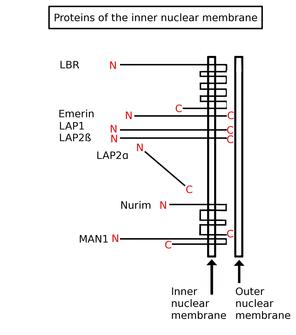
Inner nuclear membrane proteins are membrane proteins that are embedded in or associated with the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope. There are about 60 INM proteins, most of which are poorly characterized with respect to structure and function. Among the few well-characterized INM proteins are lamin B receptor (LBR), lamina-associated polypeptide 1 (LAP1), lamina-associated polypeptide-2 (LAP2), emerin and MAN1.























