
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea to the south in the Atlantic Ocean. It covers an area of 923,769 square kilometres (356,669 sq mi), and with a population of over 230 million, it is the most populous country in Africa, and the world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in the north, Chad in the northeast, Cameroon in the east, and Benin in the west. Nigeria is a federal republic comprising 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory, where the capital, Abuja, is located. The largest city in Nigeria is Lagos, one of the largest metropolitan areas in the world and the largest in Africa.

Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa and the sixth in the world. It is also one of the most densely populated countries in Africa, with approximately 218.5 million people in an area of 923,768 km2 (356,669 sq mi).

Biafra (/biˈɑfɹə/), officially the Republic of Biafra, was a partially recognised secessionist state in West Africa that declared independence from Nigeria and existed from 1967 until 1970. Its territory consisted of the former Eastern Region of Nigeria, predominantly inhabited by the Igbo ethnic group. Biafra was established on 30 May 1967 by Igbo military officer and Eastern Region governor C. Odumegwu Ojukwu under his presidency, following a series of ethnic tensions and military coups after Nigerian independence in 1960 that culminated in the 1966 anti-Igbo pogrom. The military of Nigeria proceeded to invade Biafra shortly after its declaration of independence, resulting in the start of the Nigerian Civil War.

The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people is an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown, due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 30 million people worldwide.

Chief Obafemi Jeremiah Oyeniyi Awolowo was a Nigerian nationalist and statesman who played a key role in Nigeria's independence movement (1957-1960). Awolowo founded the Yoruba nationalist group Egbe Omo Oduduwa, and was the first Leader of Government Business and Minister of Local Government and Finance, and first Premier of the Western Region under Nigeria's parliamentary system, from 1952 to 1959. He was the official Leader of the Opposition in the federal parliament to the Balewa government from 1959 to 1963.

The city of Warri is an oil hub within South-South Nigeria and houses an annex of the Delta State Government House. Warri City is one of the major hubs of the petroleum industry in Nigeria. Warri and her twin city, Uvwie are the commercial capital of Delta State with a population of over 311,970 people in 2006. The city is the indigenous territory of Urhobo, itsekiri and Ijaw people.

Lagos State is a state in southwestern Nigeria. Of the 36 states, it is both the most populous and smallest in area. Bounded to the south by the Bight of Benin and to the west by the international border with Benin, Lagos State borders Ogun State to the northeast making it the only Nigerian state to border only one other state. Named for the city of Lagos—the most populous city in Africa—the state was formed from the Western Region and the former Federal Capital Territory on 27 May 1967.

Adamawa state is a state in the North-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria, bordered by Borno to the northwest, Gombe to the west, and Taraba to the southwest, while its eastern border forms part of the national border with Cameroon. It takes its name from the historic emirate of Adamawa, with the emirate's old capital of Yola, serving as the capital city of Adamawa state. The state is one of the most heterogeneous in Nigeria, with over 100 indigenous ethnic groups. It was formed in 1991, when the former Gongola state was divided into Adamawa and Taraba states. Since it was carved out of the old Gongola State in 1991 by the General Ibrahim Badamsi Babangida military regime, Adamawa State has had 10 men, both military and civilian, controlling the levers of power, who played crucial roles in transforming the state into what it is today.

Cross River State is a state in the Eastern part of Nigeria. Named for the Cross River, the state was formed from the eastern part of the Eastern Region on 27 May 1967. Its capital is Calabar, it borders to the north through Benue state, to the west through Ebonyi state and Abia state, and to the southwest through Akwa Ibom state, while its eastern border forms part of the national border with Cameroon. Originally known as the South-Eastern State before being renamed in 1976, Cross River state formerly included the area that is now Akwa Ibom state, which became a distinct state in 1987.

The culture of Nigeria is shaped by Nigeria's multiple ethnic groups. The country has 527 languages, seven of which are extinct. Nigeria also has over 1150 dialects and ethnic groups. The three largest ethnic groups are the Hausas that are predominantly in the north, the Yorubas who predominate in the southwest, and the Igbos in the southeast. There are many other ethnic groups with sizeable populations across the different parts of the country. The Kanuri people are located in the northeast part of Nigeria, the Tiv people of north central and the Efik-Ibibio are in the south south. The Bini people are most frequent in the region between Yorubaland and Igboland.
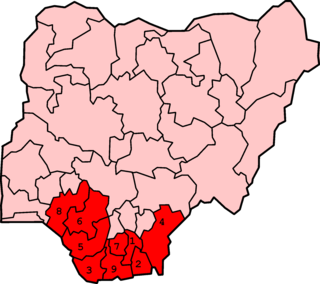
The Niger Delta is the delta of the Niger River sitting directly on the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean in Nigeria. It is located within nine coastal southern Nigerian states, which include: all six states from the South South geopolitical zone, one state (Ondo) from South West geopolitical zone and two states from South East geopolitical zone.

Borno State is a state in the North-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria, bordered by Yobe to the west, Gombe to the southwest, and Adamawa to the south while its eastern border forms part of the national border with Cameroon, its northern border forms part of the national border with Niger, and its northeastern border forms all of the national border with Chad, being the only Nigerian state to border three foreign countries. It takes its name from the historic emirate of Borno, with the emirate's old capital of Maiduguri serving as the capital city of Borno State. The state was formed in 1976 when the former North-Eastern State was broken up. It originally included the area that is now Yobe State, which became a distinct state in 1991.

The Itsekiri are one of the Yoruboid subgroup of Nigeria's Niger Delta area, They speak a Yoruboid language and can be found in Delta State. The Itsekiris presently number 2.7 million people and live mainly in the Warri South, Warri North and Warri South West local government districts of Delta State on the Atlantic coast of Nigeria. Significant communities of Itsekiris can be found in parts of Edo and Ondo states and in various other Nigerian cities including Lagos, Benin City, Port Harcourt and Abuja. Many people of Itsekiri descent also reside in the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada. The Itsekiris are closely related to the Yoruba of South Western Nigeria and also close to the Okpe people and Edo peoples. The Itsekiris traditionally refer to their land as the Kingdom of Warri or 'Iwere' as its proper name – which is geographically contiguous to the area covered by the three Warri local government districts. The area is a key centre of Nigeria's crude oil and natural gas production and petroleum refining and the main town Warri forms the industrial and commercial nucleus of the Delta State region.
The Middle Belt or Central Nigeria is a term used in human geography to designate a belt region stretching across central Nigeria longitudinally and forming a transition zone between Northern and Southern Nigeria. It is composed of the southern half of the defunct Northern Region of Nigeria, now comprising mostly the North Central and parts of the North East and North West geopolitical zones, and is characterised by its lack of a clear majority ethnic group. It is also the location of Nigeria's Federal Capital Territory.

The Hausa are a native ethnic group in West Africa. They speak the Hausa language, which is the second most spoken language after Arabic in the Afro-Asiatic language family. The Hausa are a culturally homogeneous people based primarily in the Sahelian and the sparse savanna areas of southern Niger and northern Nigeria respectively, numbering around 76 million people with significant indigenized populations in Benin, Cameroon, Ivory Coast, Chad, Sudan, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Togo, Ghana, Eritrea, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Senegal and the Gambia.
Nigerians or the Nigerian people are citizens of Nigeria or people with ancestry from Nigeria. The name Nigeria was taken from the Niger River running through the country. This name was allegedly coined in the late 19th century by British journalist Flora Shaw, who later married Baron Frederick Lugard, a British colonial administrator. Nigeria is composed of various ethnic groups and cultures and the term Nigerian refers to a citizenship-based civic nationality. Nigerians derive from over 250 ethno-linguistic groups. Though there are multiple ethnic groups in Nigeria, economic factors result in significant mobility of Nigerians of multiple ethnic and religious backgrounds to reside in territories in Nigeria that are outside their ethnic or religious background, resulting in the mixing of the various ethnic and religious groups, especially in Nigeria's cities. The English language is the lingua franca of Nigerians. Nigeria is divided roughly in half between Muslims, who live mostly in the north, and Christians, who live mostly in the south; indigenous religions, such as those native to the Igbo and Yoruba ethnicities, are in the minority.
Ijaw Youth Council is a civil rights organization in Nigeria, founded in 1998, which supports the interests of the Ijaw ethnic group of the Niger Delta. At the point of the establishment of the IYC, leadership of the organization spread across the Nigerian states where the Ijaw people resides. Hence, in the South-South Nigeria, Pronto Douglass led the IYC while Pere Camfo was the leader of the IYC in Ondo State From 2001 to 2004, it was headed by Mujahid Dokubo-Asari, until Asari split from the movement to found the Niger Delta People's Volunteer Force.
Eddalands administratively designated by Nigeria formerly as Afikpo South and changed to Edda LGA as part of the 16 constitutional amendment acts signed by President Muhammadu Buhari on 17th March, 2023 covers an entire local government area in Ebonyi State, Nigeria. It is the most homogeneous LGA in Nigeria with people of one language, one culture and one tradition across the entire LGA.
Herder–farmer conflicts in Nigeria are a series of disputes over arable land resources across Nigeria between the mostly-Muslim Fulani herders and the mostly-Christian non-Fulani farmers. The conflicts have been especially prominent in the Middle Belt since the return of democracy in 1999. More recently, they have deteriorated into attacks on farmers by Fulani herdsmen.













