
Azara is a genus of eleven species of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. They are native to temperate to subtropical regions of South America, from southern Brazil and Bolivia to southern Argentina and Chile. They are most often found at woodland margins and lakesides. Azara was formerly classed in the family Flacourtiaceae.

Embothrium is a genus of two to eight species in the plant family Proteaceae, native to southern South America, in Chile and adjacent western Argentina; the genus occurs as far south as Tierra del Fuego. Common names include Chilean firebush in English, notro in Argentina, ciruelillo, fosforito or notro chileno in Chilean Spanish.

Escallonia is a genus of shrubs and trees in the family Escalloniaceae. They are native to North and South America.
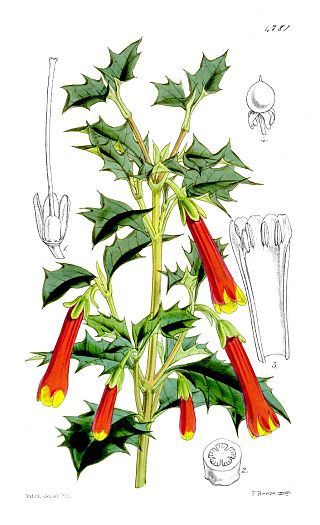
Desfontainia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Columelliaceae, though it was placed formerly in Loganiaceae, Potaliaceae, or a family of its own, Desfontainiaceae.

Citronella mucronata, the huillipatagua, naranjillo, or Chilean citronella tree, is an evergreen tree in the family Cardiopteridaceae. It is endemic to Chile and grows in the Chilean matorral region of central Chile from 30º to 40° south latitude.

Salvia cuspidata is a species of perennial shrub in the family Lamiaceae. It is native to the Andes mountains in Bolivia, Chile, and Peru, growing at elevations up to 10,000 ft (3,000 m).

Salvia oppositiflora is a species of perennial flowering plant in the famiily Lamiaceae. It is native to Peru, growing at high elevations—7,000 to 12,000 feet. It was collected in 1798 by Hipólito Ruiz López and José Antonio Pavón Jiménez and later described in Flora of Peru.

Salvia sagittata is a species of herbaceous perennial plant in the family Lamiaceae. It is native to the Andes Mountains, growing at elevations from 9,500 to 10,500 ft. The specific epithet refers to the arrow-shaped leaves. The plant was collected and named in 1798 by Hipólito Ruiz López and José Antonio Pavón Jiménez, two Spanish botanists who spent ten years in Peru and Chile on a commission by the government of Spain to go to the New World in search of new medicinal and agricultural plants.

Tillandsia capillaris is a species of flowering plant in the family Bromeliaceae. This species is native to southern and western South America.

Tillandsia virescens is a species of flowering plant in the family Bromeliaceae. This species is native to Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Peru. It was first described in 1802.

Acaena pinnatifida, known by the common names Argentinian biddy-biddy and California sheepbur, is a species of plant. It is known from California and in Argentina and Chile. The population from California is sometimes considered to be a distinct species or variety from the population in South America.

Clinanthus is a genus of bulbous plants in the family Amaryllidaceae. It is found in western South America, including Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, north Chile and north west Argentina.

Gaiadendron is a genus of parasitic shrubs or trees in the family Loranthaceae. It solely comprises the species Gaiadendron punctatum, which is found in North and South America.

Escallonia 'Iveyi' is a hybrid cultivar planted as a garden ornamental. The cultivar originated as a natural hybrid seedling discovered in the garden of Caerhays Castle in Cornwall. The cultivar was named for the Caerhays estate's gardener, David Ivey, by Edgar Thurston in his book British & foreign trees and shrubs in Cornwall. Thurston believed it to be a hybrid of E. montevidensis and E. × exonensis(E. rosea × E. rubra)., whereas others later adjudged the female parent to be E. bifida. The shrub was accorded the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Merit in 1926, and the Award of Garden Merit in 1993.

Escallonia resinosa is a species of evergreen shrub or tree in the family Escalloniaceae. It is native to the Andean forests of Peru, Bolivia and southern Ecuador from 2600 to 4200 meters above sea level. A component of high Andean forests, it is regarded as an important source of raw materials for the Andean peoples.

Escallonia pulverulenta is a species of evergreen shrub in the family Escalloniaceae. It is endemic to the coastal and inner valleys of Central Chile, from 5–1,200 metres (16–3,937 ft) above sea level.

Fuchsia denticulata is a species of shrub in the family Onagraceae. It is native to Bolivia and Peru.

Escallonia paniculata is a species of tree in the family Escalloniaceae. It is native to Costa Rica, Panama and South America.
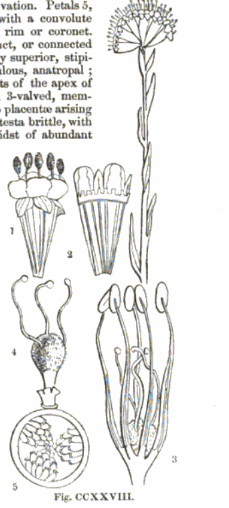
Malesherbia fasciculata is a subshrub that is native to the subtropics of Northern and Central Chile.
Malesherbia lirana is a perennial herb whose native range is from Argentina and Chile. The species has racemose inflorescences that are 2 - 3.9 cm in size and cream colored petals. It flowers in spring to late summer.



















