In computer science, an array data structure, or simply an array, is a data structure consisting of a collection of elements, each identified by at least one array index or key. An array is stored such that the position of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called one-dimensional array.
Relative molecular mass or molecular weight is the mass of a molecule. It is calculated as the sum of the relative atomic masses of each constituent element multiplied by the number of atoms of that element in the molecular formula. The molecular mass of small to medium size molecules, measured by mass spectrometry, determines stoichiometry. For large molecules such as proteins, methods based on viscosity and light-scattering can be used to determine molecular mass when crystallographic data are not available.
In object-oriented programming and software engineering, the visitor design pattern is a way of separating an algorithm from an object structure on which it operates. A practical result of this separation is the ability to add new operations to existent object structures without modifying the structures. It is one way to follow the open/closed principle.
Relative atomic mass or atomic weight is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a given sample to the atomic mass constant. The atomic mass constant is defined as being 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Since both quantities in the ratio are masses, the resulting value is dimensionless; hence the value is said to be relative.
Market segmentation is the activity of dividing a broad consumer or business market, normally consisting of existing and potential customers, into sub-groups of consumers based on some type of shared characteristics. In dividing or segmenting markets, researchers typically look for common characteristics such as shared needs, common interests, similar lifestyles or even similar demographic profiles. The overall aim of segmentation is to identify high yield segments – that is, those segments that are likely to be the most profitable or that have growth potential – so that these can be selected for special attention.
A weight function is a mathematical device used when performing a sum, integral, or average to give some elements more "weight" or influence on the result than other elements in the same set. The result of this application of a weight function is a weighted sum or weighted average. Weight functions occur frequently in statistics and analysis, and are closely related to the concept of a measure. Weight functions can be employed in both discrete and continuous settings. They can be used to construct systems of calculus called "weighted calculus" and "meta-calculus".
Ethical consumerism is a type of consumer activism that is based on the concept of dollar voting. It is practiced through 'positive buying' in that ethical products are favoured, or 'moral boycott', that is negative purchasing and company-based purchasing.
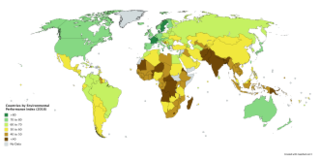
The Environmental Performance Index (EPI) is a method of quantifying and numerically marking the environmental performance of a state's policies. This index was developed from the Pilot Environmental Performance Index, first published in 2002, and designed to supplement the environmental targets set forth in the United Nations Millennium Development Goals.
Marketing ethics is an area of applied ethics which deals with the moral principles behind the operation and regulation of marketing. Some areas of marketing ethics overlap with media ethics.
Ethical marketing refers to the application of marketing ethics into the marketing process. Briefly, marketing ethics refers to the philosophical examination, from a moral standpoint, of particular marketing issues that are matters of moral judgment. Ethical marketing generally results in a more socially responsible and culturally sensitive business community. The establishment of marketing ethics has the potential to benefit society as a whole, both in the short- and long-term. Ethical marketing should be part of business ethics in the sense that marketing forms a significant part of any business model. Study of Ethical marketing should be included in applied ethics and involves examination of whether or not an honest and factual representation of a product or service has been delivered in a framework of cultural and social values.
The graphical control element inspector window is a type of dialog window that shows a list of the current attributes of a selected object and allows these parameters to be changed on the fly. A common use is in Integrated Development Environments, where the window shows the changing values of variables associated to an object during a debugging session.
Global marketing is “marketing on a worldwide scale reconciling or taking commercial advantage of global operational differences, similarities and opportunities in order to meet global objectives".
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to marketing:
The Economist Intelligence Unit’s where-to-be-born index attempts to measure which country will provide the best opportunities for a healthy, safe and prosperous life in the years ahead. It is based on a method that links the results of subjective life-satisfaction surveys to the objective determinants of quality of life across countries along with a forward-looking element.
Organizational ethics is the ethics of an organization, and it is how an organization responds to an internal or external stimulus. Organizational ethics is interdependent with the organizational culture. Although it is akin to both organizational behavior (OB) and industrial and organizational psychology as well as business ethics on the micro and macro levels, organizational ethics is neither OB or I/O psychology, nor is it solely business ethics. Organizational ethics express the values of an organization to its employees and/or other entities irrespective of governmental and/or regulatory laws.
Language support for array types may include certain built-in array data types, some syntactic constructions that the programmer may use to define such types and declare array variables, and special notation for indexing array elements. For example, in the Pascal programming language, the declaration type MyTable = array [1..4,1..2] of integer, defines a new array data type called MyTable. The declaration var A: MyTable then defines a variable A of that type, which is an aggregate of eight elements, each being an integer variable identified by two indices. In the Pascal program, those elements are denoted A[1,1], A[1,2], A[2,1],… A[4,2]. Special array types are often defined by the language's standard libraries.

A stock index or stock market index is a measurement of a section of the stock market. It is computed from the prices of selected stocks. It is a tool used by investors and financial managers to describe the market, and to compare the return on specific investments.
The EF English Proficiency Index attempts to rank countries by the average level of English language skills amongst those adults who took the EF test. It is the product of EF Education First, an international education company, and draws its conclusions from data collected via English tests available for free over the internet. The index is an online survey first published in 2011 based on test data from 1.7 million test takers. The most recent, eighth edition was released in October, 2018.
In computer science, the median of medians is an approximate (median) selection algorithm, frequently used to supply a good pivot for an exact selection algorithm, mainly the quickselect, that selects the kth largest element of an initially unsorted array. Median of medians finds an approximate median in linear time only, which is limited but an additional overhead for quickselect. When this approximate median is used as an improved pivot, the worst-case complexity of quickselect reduces significantly from quadratic to linear, which is also the asymptotically optimal worst-case complexity of any selection algorithm. In other words, the median of medians is an approximate median-selection algorithm that helps building an asymptotically optimal, exact general selection algorithm, by producing good pivot elements.
Pitch quantification is the attempt to describe the quality of a pitch using a single numeric value based on quantifiable aspects of an individual baseball pitch. There are two main kinds of pitch quantification. The first is outcome oriented. This means that the result of a given pitch is a component used to calculate the overall numeric value that describes the quality of the pitch. The other kind of pitch quantification does not consider the outcome of a pitch when calculating quality. Rather, it is batter independent. Its quality can be assessed without regard to what the batter does with the pitch.


