
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, industrial buildings, for vector control, and control of insect parasites of animals and humans.

Pesticide resistance describes the decreased susceptibility of a pest population to a pesticide that was previously effective at controlling the pest. Pest species evolve pesticide resistance via natural selection: the most resistant specimens survive and pass on their acquired heritable changes traits to their offspring. If a pest has resistance then that will reduce the pesticide's efficacy – efficacy and resistance are inversely related.
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward.

Spider mites are members of the family Tetranychidae, which includes about 1,200 species. They are part of the subclass Acari (mites). Spider mites generally live on the undersides of leaves of plants, where they may spin protective silk webs, and can cause damage by puncturing the plant cells to feed. Spider mites are known to feed on several hundred species of plants.

Varroa destructor, the Varroa mite, is an external parasitic mite that attacks and feeds on honey bees and is one of the most damaging honey bee pests in the world. A significant mite infestation leads to the death of a honey bee colony, usually in the late autumn through early spring. Without management for Varroa mite, honey bee colonies typically collapse within 2 to 3 years in temperate climates. These mites can infest Apis mellifera, the western honey bee, and Apis cerana, the Asian honey bee. Due to very similar physical characteristics, this species was thought to be the closely related Varroa jacobsoni prior to 2000, but they were found to be two separate species after DNA analysis.

The Russian wheat aphid is an aphid that can cause significant losses in cereal crops. The species was introduced to the United States in 1986 and is considered an invasive species there. This aphid is pale green and up to 2 mm long. Cornicles are very short, rounded, and appear to be lacking. There is an appendage above the cauda giving the aphid the appearance of having two tails. The saliva of this aphid is toxic to the plant and causes whitish striping on cereal leaves. Feeding by this aphid will also cause the flag leaf to turn white and curl around the head causing incomplete head emergence. Its host plants are cereal grain crops including wheat and barley and to a lesser extent, wild grasses such as wheatgrasses, brome-grasses, ryegrasses and anything in the grass family.
Cydia pomonella granulovirus (CpGV) is a granulovirus belonging to the family Baculoviridae. It has a double-stranded DNA genome that is approximately 123,500 base pairs in length with 143 ORFs. The virus forms small bodies called granules containing a single virion. CpGV is a virus of invertebrates – specifically Cydia pomonella, commonly known as the Codling moth. CpGV is highly pathogenic, it is known as a fast GV – that is, one that will kill its host in the same instar as infection; thus, it is frequently used as a biological pesticide.

Benzoylureas (BPUs) are chemical derivatives of N-benzoyl-N′-phenylurea, which are used as insecticides. They do not directly kill the insect, but disrupt moulting and egg hatch, and thus act as insect growth regulators. They act by inhibiting chitin synthase, preventing the formation of chitin in the insect's body.

Spinosad is an insecticide based on chemical compounds found in the bacterial species Saccharopolyspora spinosa. The genus Saccharopolyspora was discovered in 1985 in isolates from crushed sugarcane. The bacteria produce yellowish-pink aerial hyphae, with bead-like chains of spores enclosed in a characteristic hairy sheath. This genus is defined as aerobic, Gram-positive, nonacid-fast actinomycetes with fragmenting substrate mycelium. S. spinosa was isolated from soil collected inside a nonoperational sugar mill rum still in the Virgin Islands. Spinosad is a mixture of chemical compounds in the spinosyn family that has a generalized structure consisting of a unique tetracyclic ring system attached to an amino sugar (D-forosamine) and a neutral sugar (tri-Ο-methyl-L-rhamnose). Spinosad is relatively nonpolar and not easily dissolved in water.

Indoxacarb is an oxadiazine pesticide developed by DuPont that acts against lepidopteran larvae. It is marketed under the names Indoxacarb Technical Insecticide, Steward Insecticide and Avaunt Insecticide. It is also used as the active ingredient in the Syngenta line of commercial pesticides: Advion and Arilon.
An insect growth regulator (IGR) is a chemical insecticide that kills insects indirectly by disrupting their life cycles. The term was initially proposed to describe the effects of juvenile hormone analogs. Although the term "insect growth disruptor" more accurately describes the actions of IGRs, it did not become widely used. IGRs encompass chemical classes with three modes of action : juvenile hormone analogs, chitin synthesis inhibitors, and ecdysone receptor agonists.

Diamide insecticides are a class of insecticides, active mainly against lepidoptera (caterpillars), which act on the insect ryanodine receptor. They are diamides of either phthalic acid or anthranilic acid, with various appropriate further substitutions.

Phorodon humuli, the hop aphid, or damson-hop aphid, is an aphid in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap.
The Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) was formed in 1984 and works as a specialist technical group of the industry association CropLife to be able to provide a coordinated industry response to prevent or delay the development of insecticide resistance in insect and mite pests. IRAC strives to facilitate communication and education on insecticide and traits resistance as well as to promote the development and facilitate the implementation of insecticide resistance management strategies.
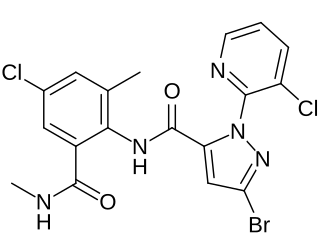
Chlorantraniliprole is an insecticide of the diamide class used for insects found on fruit and vegetable crops as well as ornamental plants.

Tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus (TSWV) is a spherical negative-sense RNA virus. Transmitted by thrips, it causes serious losses in economically important crops and it is one of the most economically devastating plant viruses in the world.

Nereistoxin is a natural product identified in 1962 as the toxic organic compound N,N-dimethyl-1,2-dithiolan-4-amine. It had first been isolated in 1934 from the marine annelid Lumbriconereis heteropoda and acts by blocking the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Researchers at Takeda in Japan investigated it as a possible insecticide. They subsequently developed a number of derivatives that were commercialised, including those with the ISO common names bensultap, cartap, thiocyclam and thiosultap.

Flupyradifurone is a systemic butenolide insecticide developed by Bayer CropScience under the name Sivanto. Flupyradifurone protects crops from sap-feeding pests such as aphids and is safer for non-target organisms compared to other insecticides. Sivanto was launched in 2014 since it obtained its first commercial registration in central America. Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) classified Flupyradifurone as 4D subset (butenolide) and it is the first pesticide in the butenolide category. It was approved by European Union in 2015.

Halotydeus destructor is a species of earth mites in the family of Penthaleidae, first described by Tucker in 1925 as Penthaleus destructor.

Diafenthioron is a pesticide, specifically an insecticide. It is a chemical compound which belongs to the thiourea group. Diafenthiuron is sold under the brand names Derby, Diron, Pegasus, Polar and Polo.




















