
The dodo is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The two formed the subfamily Raphinae, a clade of extinct flightless birds that were a part of the family including pigeons and doves. The closest living relative of the dodo is the Nicobar pigeon. A white dodo was once thought to have existed on the nearby island of Réunion, but it is now believed that this assumption was merely confusion based on the also-extinct Réunion ibis and paintings of white dodos.
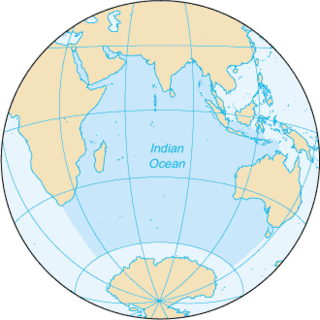
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering 70,560,000 km2 (27,240,000 sq mi) or 19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, the Laccadive Sea, the Somali Sea, Bay of Bengal, and the Andaman Sea.

Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island, as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga and St. Brandon. The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion, are part of the Mascarene Islands. The capital and largest city, Port Louis, is located in Mauritius, where most of the population is concentrated. The country spans 2,040 square kilometres (790 sq mi) and has an exclusive economic zone covering 2.3 million square kilometres.

The Nymphalidae are the largest family of butterflies, with more than 6,000 species distributed throughout most of the world. Belonging to the superfamily Papilionoidea, they are usually medium-sized to large butterflies. Most species have a reduced pair of forelegs and many hold their colourful wings flat when resting. They are also called brush-footed butterflies or four-footed butterflies, because they are known to stand on only four legs while the other two are curled up; in some species, these forelegs have a brush-like set of hairs, which gives this family its other common name. Many species are brightly coloured and include popular species such as the emperors, monarch butterfly, admirals, tortoiseshells, and fritillaries. However, the under wings are, in contrast, often dull and in some species look remarkably like dead leaves, or are much paler, producing a cryptic effect that helps the butterflies blend into their surroundings.
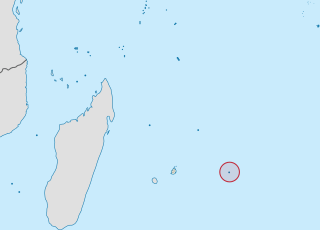
Rodrigues is a 108 km2 (42 sq mi) autonomous outer island of the Republic of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean, about 560 km (350 mi) east of Mauritius. It is part of the Mascarene Islands, which include Mauritius and Réunion. Rodrigues is of volcanic origin and is surrounded by coral reef, and some tiny uninhabited islands lie just off its coast. The island used to be the tenth District of Mauritius; it gained autonomous status on 10 December 2002, and it is governed by the Rodrigues Regional Assembly. The capital of the island is Port Mathurin.

The Chagos Archipelago or Chagos Islands is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos-Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelson's Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle, Egmont and Danger Island(s); southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far, the largest island. All are low-lying, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons.

Gulf St Vincent, sometimes referred to as St Vincent Gulf, St Vincent's Gulf or Gulf of St Vincent, is the eastern of two large inlets of water on the southern coast of Australia, in the state of South Australia, the other being the larger Spencer Gulf, from which it is separated by Yorke Peninsula. On its eastern side the gulf is bordered by the Adelaide Plains and the Fleurieu Peninsula. To the south it is defined by a line from Troubridge Point on Yorke Peninsula to Cape Jervis on Fleurieu Peninsula. Its entrances from the southwest are from Investigator Strait, and to the southeast from Backstairs Passage, which separate Kangaroo Island from the mainland. Adelaide, the South Australian capital, lies midway along the gulf's east shore. Other towns located on the gulf, from west to east include Edithburgh, Port Vincent, Ardrossan and Port Wakefield and Normanville.

Chayote, also known as mirliton and choko, is an edible plant belonging to the gourd family, Cucurbitaceae. This fruit was first cultivated in the Mesoamericas between southern Mexico and Honduras, with the most genetic diversity available in both Mexico and Guatemala. It is one of several foods introduced to the Old World during the Columbian Exchange. At that time, the plant spread to other parts of the Americas, ultimately causing it to be integrated into the cuisine of many Latin American nations.

Vinca is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, native to Europe, northwest Africa and southwest Asia. The English name periwinkle is shared with the related genus Catharanthus.

The echo parakeet is a species of parrot endemic to the Mascarene Islands of Mauritius and formerly Réunion. It is the only living native parrot of the Mascarene Islands; all others have become extinct due to human activity. Two subspecies have been recognised, the extinct Réunion parakeet and the living echo parakeet, sometimes known as the Mauritius parakeet. The relationship between the two populations was historically unclear, but a 2015 DNA study determined them to be subspecies of the same species by comparing the DNA of echo parakeets with a single skin thought to be from a Réunion parakeet, but it has also been suggested they did not constitute different subspecies. As it was named first, the binomial name of the Réunion parakeet is used for the species; the Réunion subspecies thereby became P. eques eques, while the Mauritius subspecies became P. eques echo. Their closest relative was the extinct Newton's parakeet of Rodrigues, and the three are grouped among the subspecies of the rose-ringed parakeet of Asia and Africa.

Plant anatomy or phytotomy is the general term for the study of the internal structure of plants. Originally it included plant morphology, the description of the physical form and external structure of plants, but since the mid-20th century plant anatomy has been considered a separate field referring only to internal plant structure. Plant anatomy is now frequently investigated at the cellular level, and often involves the sectioning of tissues and microscopy.

Kora-class corvettes are guided missile corvettes, in active service with the Indian Navy and the National Coast Guard of Mauritius. Four vessels were built at Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) and outfitted at Mazagon Dock Limited (MDL).
Faujasiopsis reticulata, the oreille de souris, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only in Mauritius. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests.

Faujasia is a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family, native to certain islands in the Indian Ocean.

Jeffrey Schlupp is a Ghanaian professional footballer who plays as a forward or winger or occasional left back for Premier League club Crystal Palace and the Ghana national team. Schlupp started his career as a striker.
Parafaujasia is a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family, native to certain islands in the Indian Ocean.

Dr. Bibi Ameenah Firdaus Gurib-FakimGCSK is a Mauritian politician and biodiversity scientist who served as the sixth president of Mauritius from 2015 to 2018. In December 2014, she was selected to be the presidential candidate of the Alliance Lepep. After Kailash Purryag resigned on 29 May 2015, both Prime Minister Sir Anerood Jugnauth and Leader of the Opposition Paul Berenger positively welcomed her nomination, which was unanimously approved in a vote in the National Assembly.
Cannabis in Mauritius is illegal; locally it is known as gandia.














