
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
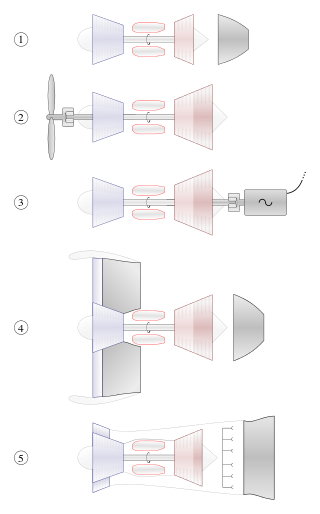
A gas turbine, gas turbine engine, or also known by its old name internal combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part and are, in the direction of flow:

The Fiat 128 is a transverse front-engine, front wheel drive small family car manufactured and marketed by Fiat from 1969 to 1985 as a two- or four-door sedan, three- or five-door station wagon as well as two- or three-door coupé. The 128 running gear and engine, reconfigured for a mid-engined layout, were used in the Fiat X1/9 sports car.

The Lancia Delta is a small family car produced by Italian automobile manufacturer Lancia in three generations. The first generation (1979-1994) debuted at the 1979 Frankfurt Motor Show, the second generation (1993-1999) debuted at the 1993 Geneva Motor Show, and the third generation (2008-2014) debuted at 2008 Geneva Motor Show.

The Fiat Uno is a supermini manufactured and marketed by Fiat. Launched in 1983, the Uno was produced over a single generation in three and five-door hatchback body styles until 1995 in Europe — and until 1 January 2014, in Brazil. Designed by Giorgetto Giugiaro of Italdesign, the Uno strongly recalled the high-roof, up-right packaging of Giugiaro's 1978 Lancia Megagamma concept, in a smaller configuration.

A suicide door is an automobile door hinged at its rear rather than the front. Such doors were originally used on horse-drawn carriages, but are rarely found on modern vehicles, primarily because they are less safe than a front-hinged door. Being rear-hinged, if the vehicle was moving and the door opened, aerodynamic drag would force the door open, and the driver/passenger would have to lean forward and out of the vehicle to close it. As seat belts were not in common use at that time, the risk of falling out of the car and into traffic was high, hence the name "suicide door".. Another reason could have been that while a door was open on a city street, a speeding car moving in the same direction as the parked car could rip a front-hinged door off the parked car but someone in side the adjacent seat, even if moving to leave the car, could not get scratched. However, with a suicide door, someone inside or partially outside the passenger compartment would get struck by the suicide door forcefully swinging back to a shut position due to the impact of the speeding car.

The Lancia Thema is an executive car produced by the Italian automaker Lancia between 1984 and 1994, and one of four cars to share the Type Four platform alongside the Alfa Romeo 164, Fiat Croma and Saab 9000. The Thema was first shown in Turin Motor Show in 1984.

The Fiat 1100 is a small family car produced from 1953 until 1969 by the Italian manufacturer Fiat. It was an all-new unibody replacement for the Fiat 1100 E, which descended from the pre-war, body-on-frame Fiat 508 C Balilla 1100. The 1100 was changed steadily and gradually until being replaced by the new Fiat 128 in 1969. There were also a series of light commercial versions of the 1100 built, with later models called the Fiat 1100T, which remained in production until 1971. The Fiat 1100 D also found a long life in India, where Premier Automobiles continued to build the car until the end of 2000.
The General Motors Firebird comprises a quartet of prototype cars that General Motors (GM) engineered for the 1953, 1956, and 1959 Motorama auto shows. The cars' designers, headed by Harley Earl, took Earl's inspiration from the innovations in fighter aircraft design at the time. General Motors never intended the cars for production, but rather to showcase the extremes in technology and design that the company was able to achieve.

The term turbo-diesel, also written as turbodiesel and turbo diesel, refers to any diesel engine equipped with a turbocharger. As with other engine types, turbocharging a diesel engine can significantly increase its efficiency and power output, especially when used in combination with an intercooler.

The Renault Étoile Filante was Renault's only attempt at both creating a gas turbine-powered car and setting a land speed record for such cars.

The Fiat 1400 and Fiat 1900 are passenger cars produced by Italian automotive manufacturer Fiat from 1950 to 1958 and from 1952 to 1959 respectively. The two models shared body and platform, but while the 1.4-litre 1400 was Fiat's intermediate offering, the upmarket 1900 had an enlarged 1.9-litre engine and more luxurious trim and equipment, to serve as flagship in the manufacturer's range.
The Turin Motor Show was an auto show held annually in Turin, Italy. The first official show took place between 21 and 24 April 1900, at the Castle of Valentino, becoming a permanent fixture in Turin from 1938 having shared it with Milan and Rome until that time. From 1972, the show was held biannually and in 1984, it moved into Fiat's shuttered Lingotto factory.

Fiat Automobiles S.p.A. is an Italian automobile manufacturer, formerly part of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, and since 2021 a subsidiary of Stellantis through its Italian division Stellantis Europe. Fiat Automobiles was formed in January 2007 when Fiat S.p.A. reorganized its automobile business, and traces its history back to 1899, when the first Fiat automobile, the Fiat 4 HP, was produced.

The Rover-BRM was a prototype gas turbine-powered racing car, jointly developed in the early 1960s by the British companies Rover and British Racing Motors (BRM). The car is part of the collection at the British Motor Museum.
Toyota Concept Vehicles produced between 1980 and 1989 include:

The Alfa Romeo Giulia is a compact executive car produced by the Italian manufacturer Alfa Romeo. Known internally as the Type 952, it was unveiled in June 2015, with market launch scheduled for February 2016, and it is the first saloon offered by Alfa Romeo after the production of the 159 ended in 2011. The Giulia is also the first mass-market Alfa Romeo vehicle in over two decades to use a longitudinal rear-wheel drive platform, since the 75 which was discontinued in 1992. The Giulia was second in 2017 European Car of the Year voting and was named Motor Trend Car of the Year for 2018. In 2018, Giulia was awarded the Compasso d'Oro industrial design award.

The Fiat 500L is a mini MPV manufactured by Fiat under the Fiat Serbia joint venture and marketed globally since its debut at the 2012 Geneva Motor Show.

An aero-engined car is an automobile powered by an engine designed for aircraft use. Most such cars have been built for racing, and many have attempted to set world land speed records. While the practice of fitting cars with aircraft engines predates World War I by a few years, it was most popular in the interwar period between the world wars when military-surplus aircraft engines were readily available and used to power numerous high-performance racing cars. Initially powered by piston aircraft engines, a number of post-World War II aero-engined cars have been powered by aviation turbine and jet engines instead. Piston-engined, turbine-engined, and jet-engined cars have all set world land speed records. There have also been some non-racing automotive applications for aircraft engines, including production vehicles such as the Tucker 48 and prototypes such as the Chrysler Turbine Car, Fiat Turbina, and General Motors Firebirds. In the late 20th century and into the 21st century, there has also been a revival of interest in piston-powered aero-engined racing cars.

The GMWhirlfire gas turbine engines were developed in the 1950s by the research division of General Motors Corporation and fitted to concept vehicles, including the Firebird concept cars, Turbo-Cruiser buses, and Turbo-Titan trucks through the 1960s. They are free-turbine turboshaft machines with two spools: one compressor/gasifier turboshaft and one power/output turboshaft sharing a common axis without a mechanical coupling between them. Fuel consumption of the first-generation GT-300 was high compared to piston engines, so thermal wheel regenerators were added to the second-generation GT-304, cutting consumption by approximately 1⁄2.




















