
Starlings are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Sturnidae. The Sturnidae are named for the genus Sturnus, which in turn comes from the Latin word for starling, sturnus. Many Asian species, particularly the larger ones, are called mynas, and many African species are known as glossy starlings because of their iridescent plumage. Starlings are native to Europe, Asia, and Africa, as well as northern Australia and the islands of the tropical Pacific. Several European and Asian species have been introduced to these areas, as well as North America, Hawaii, and New Zealand, where they generally compete for habitats with native birds and are considered to be invasive species. The starling species familiar to most people in Europe and North America is the common starling, and throughout much of Asia and the Pacific, the common myna is indeed common.

The mynas are a group of birds in the starling family (Sturnidae). This is a group of passerine birds which are native to southern Asia, especially India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka. Several species have been introduced to areas like North America, Australia, South Africa, Fiji and New Zealand, especially the common myna, which is often regarded as an invasive species.

The brahminy starling or brahminy myna is a member of the starling family of birds. It is usually seen in pairs or small flocks in open habitats on the plains of the Indian subcontinent.

The chestnut-tailed starling, also called grey-headed starling and grey-headed myna is a member of the starling family. It is a resident or partially migratory species found in wooded habitats in India and Southeast Asia. The species name is after the distribution of a former subspecies in the Malabar region. While the chestnut-tailed starling is a winter visitor to peninsular India, the closely related resident breeding population with a white head is now treated as a full species, the Malabar starling.

The warbling white-eye, also known as the Japanese white-eye and mountain white-eye, is a small passerine bird in the white-eye family. The specific epithet is occasionally written japonica, but this is incorrect due to the gender of the genus. Its native range includes much of East Asia, including the Russian Far East, Japan, Indonesia, Korea, and the Philippines. It has been intentionally introduced to other parts of the world as a pet and as pest control, with mixed results. As one of the native species of the Japanese islands, it has been depicted in Japanese art on numerous occasions, and historically was kept as a cage bird.
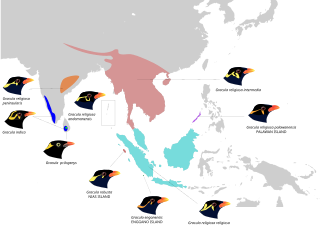
Gracula is a genus of mynas, tropical members of the starling family of birds found in southern Asia and introduced to Florida in the United States.

Lamprotornis is a large genus of glossy-starlings all of which occur in Africa south of the Sahara. They have glossy blue or green upper parts, which is due to hollow melanin granules arranged in a single layer near the feather barbule's surface. This unique arrangement led to some glossy starlings formerly placed in the genus Spreo being transferred to Lamprotornis, since they shared this feature.

The pied starling or African pied starling is a bird endemic to South Africa, Lesotho and Eswatini. It is common in most of its range, but largely absent from the arid northwest and the eastern lowlands of South Africa. It is found in open habitats such as grassland, karoo scrub, thornbush and agricultural land, and often associates with farm animals.

The wattled starling is a nomadic resident bird in eastern and southern Africa. It is a species of grassland, open woodland, and cultivation.

The Sulawesi myna is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. It is endemic to Sulawesi, Indonesia. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.

The Apo myna is a species of starling in the starling family Sturnidae. The species is also known as the Mount Apo starling or the Mount Apo king starling. It is the only member of the genus Goodfellowia. It is endemic to the Philippines found only in the tropical montane forests of Mindanao. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Abbott's starling is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. It is found in Kenya and Tanzania. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist montane forests. It is threatened by habitat loss, and its population is estimated at 2500–9999. This species, at 16 to 18 cm long, is the smallest species of starling. It is in the monotypic genus Arizelopsar.

The yellow-faced myna is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. It is found in New Guinea and nearby smaller islands, where its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests. The long-tailed myna was formerly included as a subspecies. One of the largest species of starling, this species attains 23 to 26 cm in length and weighs around 217 g (7.7 oz). They have dark plumage with a metallic lustre and bright orange facial markings and beak. These birds are social and omnivorous. Their diet consists of fruit and insects for which they forage high in the canopy. They are common birds with a wide range, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed their conservation status as being of "least concern". It was named after Charles Dumont.

The grosbeak starling, also known as the grosbeak myna, finch-billed myna, or scissor-billed starling, is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. It is monotypic in the genus Scissirostrum. It is endemic to Sulawesi, Indonesia.

The black-winged myna is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. The species is also known as the black-winged starling or the white-breasted starling. It is endemic to Indonesia. There are three recognised subspecies: the nominate race, which occurs across much of the island of Java; tricolor, which is restricted to south east Java; and tertius, which is found on Bali and possibly Lombok. The validity of the records on Lombok has been called into question, as there are only a few records and those may represent escapees from the caged-bird trade or natural vagrants. The species has often been assigned to the starling genus Sturnus, but is now placed in Acridotheres because it is behaviourally and vocally closer to the birds in that genus.

The black-collared starling is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. Its plumage is black and white, with a black collar. It is found in southern China and most of mainland Southeast Asia, and has been introduced to Taiwan, Malaysia and Singapore. Its habitats include grassland, dry forest and human settlements. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has assessed it as being of least concern.

The black cuckoo-dove, also known as the slaty cuckoo-dove, is a species of bird in the family Columbidae. It is endemic to the Lesser Sunda Islands, being found on Timor, Wetar, Rote, and Atauro. It inhabits primary and secondary monsoon forest, eucalyptus forest, and woodlands. It is 38.5 cm (15.2 in) long on average and is mainly dark bluish-gray, lighter on the head and underparts and darker on the wings and tail. It has yellow orbital skin.

The Sulawesi thrush is a species of passerine bird in the thrush family, Turdidae. It is endemic to the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia, where it inhabits evergreen montane forests at altitudes of 1,100–2,400 m (3,600–7,900 ft). Although it has a limited range and is not a common bird, the IUCN has assessed it as being a "least-concern species".

The Nias hill myna or Nias myna is a member of the starling family. It is an endemic resident of Nias and other nearby islands off western Sumatra. Clements lumps this species with the common hill myna.

The long-tailed myna is a member of the starling family. It is native to the Bismarck and Solomon archipelagos. It resembles the yellow-faced myna, and the two were formerly considered conspecific.





















