
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as tales, myths, legends, proverbs, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also includes material culture, such as traditional building styles common to the group. Folklore also encompasses customary lore, taking actions for folk beliefs, and the forms and rituals of celebrations such as Christmas, weddings, folk dances, and initiation rites.
The folklore of India encompasses the folklore of the nation of India and the Indian subcontinent. India is an ethnically and religiously diverse country. Given this diversity, it is difficult to generalize the vast folklore of India as a unit.

Folklore studies is the branch of anthropology devoted to the study of folklore. This term, along with its synonyms, gained currency in the 1950s to distinguish the academic study of traditional culture from the folklore artifacts themselves. It became established as a field across both Europe and North America, coordinating with Volkskunde (German), folkeminner (Norwegian), and folkminnen (Swedish), among others.

Folk art covers all forms of visual art made in the context of folk culture. Definitions vary, but generally the objects have practical utility of some kind, rather than being exclusively decorative. The makers of folk art are typically trained within a popular tradition, rather than in the fine art tradition of the culture. There is often overlap, or contested ground with 'naive art'. "Folk art" is not used in regard to traditional societies where ethnographic art continue to be made.
Public folklore is the term for the work done by folklorists in public settings in the United States and Canada outside of universities and colleges, such as arts councils, museums, folklife festivals, radio stations, etc., as opposed to academic folklore, which is done within universities and colleges. The term is short for "public sector folklore" and was first used by members of the American Folklore Society in the early 1970s.
An intangible cultural heritage (ICH) is a practice, representation, expression, knowledge, or skill considered by UNESCO to be part of a place's cultural heritage. Buildings, historic places, monuments, and artifacts are cultural property. Intangible heritage consists of nonphysical intellectual wealth, such as folklore, customs, beliefs, traditions, knowledge, and language. Intangible cultural heritage is considered by member states of UNESCO in relation to the tangible World Heritage focusing on intangible aspects of culture. In 2001, UNESCO made a survey among states and NGOs to try to agree on a definition, and the Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage was drafted in 2003 for its protection and promotion.
The Center for Folklife & Cultural Heritage (CFCH) is one of three cultural centers within the Smithsonian Institution in the United States. Its motto is "culture of, by, and for the people", and it aims to encourage understanding and cultural sustainability through research, education, and community engagement. The CFCH contains (numerically) the largest collection in the Smithsonian, but is not fully open to the public. Its budget comes primarily from grants, trust monies, federal government appropriations, and gifts, with a small percentage coming from the main Smithsonian budget.
Cultural retention is the act of retaining the culture of a specific ethnic group of people, especially when there is reason to believe that the culture, through inaction, may be lost. Many African-American, European and Asian organizations have cultural retention programs in place.

The National Intangible Cultural Heritage of Indonesia is a "living culture" that contains philosophical elements from the traditions of society and is still handed down from generation to generation. Edi Sedyawati added an important element in the notion of intangible cultural heritage is the nature of culture that cannot be held (abstract), such as concepts and technology, its nature can pass and disappear in time with the times such as language, music, dance, ceremony, and various other structured behaviors. Thus, cultural heritage is shared by a community or community and experiences development from generation to generation, in the flow of a tradition. The Ministry of Education and Culture of Indonesia records and establishes a list of intangible cultural heritage. As of June 2020, a total of 9,770 cultural heritages have been recorded and 1,086 of them have been designated.
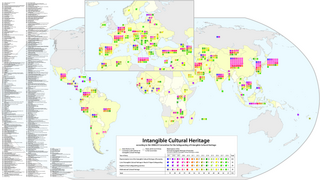
UNESCO established its Lists of Intangible Cultural Heritage with the aim of ensuring better protection of important intangible cultural heritages worldwide and the awareness of their significance. This list is published by the Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage, the members of which are elected by State Parties meeting in a General Assembly. Through a compendium of the different oral and intangible treasures of humankind worldwide, the programme aims to draw attention to the importance of safeguarding intangible heritage, which UNESCO has identified as an essential component and as a repository of cultural diversity and of creative expression.
The Center for Traditional Music and Dance (CTMD) is a leading folk/traditional arts organization based in New York City. Originally established as the Balkan Arts Center in 1968, CTMD assists the city's ethnic and immigrant communities in maintaining their traditions and cultural heritage. CTMD has developed a range of programs that emphasize research, documentation, collaboration, presentation, and education to help advance its mission of cultural equity. Over the past five decades, CTMD's programs have led to the creation of nationally renowned ensembles, folk arts festivals, and community-based cultural organizations. CTMD provides the public with a full calendar of events designed to showcase and promote the diversity of New York City's performing arts traditions.

A Cultural Property is administered by the Japanese government's Agency for Cultural Affairs, and includes tangible properties ; intangible properties ; folk properties both tangible and intangible; monuments historic, scenic and natural; cultural landscapes; and groups of traditional buildings. Buried properties and conservation techniques are also protected. Together these cultural properties are to be preserved and utilized as the heritage of the Japanese people.

The International Council of Organizations of Folklore Festivals and Folk Arts is an international nongovernmental organization (NGO) in Official partnership with UNESCO and is accredited to provide advisory service to the Committee of the UNESCO Convention for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage. CIOFF has 63 full members, 21 associate members and 18 corresponding members worldwide and 3 partner members. Its headquarters are in Confolens in France. Full members are National Sections with the aim to preserve traditional art, to organize Folklore Festivals or similar activities as well as unite voluntary organizations, working in the field of dance, music, costumes, customs and ethnography. The National Sections belong to sectors in the organization according to their geographic location.

Czech folklore is the folk tradition which has developed among the Czech people over a number of centuries. Czech folklore was influenced by a mix of Christian and pagan customs. Nowadays it is preserved and kept alive by various folklore ensembles uniting members of all ages, from children to seniors, showing their talent during competitions, folklore festivals or other performances.
Family folklore is the branch of folkloristics concerned with the study and use of folklore and traditional culture transmitted within an individual family group. This includes craft goods produced by family members or memorabilia that have been saved as reminders of family events. It includes family photos, photo albums, along with bundles of other pages held for posterity such as certificates, letters, journals, notes, and shopping lists. Family sayings and stories which recount true events are retold as a means of maintaining a common family identity. Family customs are performed, modified, sometimes forgotten, created or resurrected with great frequency. Each time the result is to define and solidify the perception of the family as unique.
Museum folklore is a domain of scholarship and professional practice within the field of folklore studies (folkloristics).

Kay Turner is an artist and scholar working across disciplines including performance, writing, music, exhibition curation, and public and academic folklore. She is noted for her feminist writings and performances on subjects such as women’s home altars, fairy tale witches, and historical goddess figures. She co-founded “Girls in the Nose,” a lesbian feminist rock punk band that anticipated riot grrl.

Folk and traditional arts are rooted in and reflective of the cultural life of a community. They encompass the body of expressive culture associated with the fields of folklore and cultural heritage. Tangible folk art includes historic objects which are crafted and used within a traditional community. Intangible folk arts include forms such as music, dance and narrative structures. Tangible and intangible folk arts were developed to address a need, and are shaped by generational values derived from family and community, through demonstration, conversation and practice.
David "Doc" Rowe is a folklorist, author and film-maker who lives and works in the United Kingdom. A graduate of Hornsey College of Arts, he is a prominent lecturer on and advocate for folk traditions and folk music.

Arna Jharna Museum is a folk museum located in a village called Moklawas near Jodhpur in Rajasthan. The museum opened in 2000 under the aegis of Rupayan Sansthan. It is a Museum of Folk Culture envisioned by eminent folklorist and ethno-musicologist, Padma Bhushan Komal Kothari. Arna Jharna literally means Forest and Spring. Its location showcases the terrain of Marwar region through rocky outcrops, desert cacti, and ravines.










