
Karma is an ancient Indian concept that refers to an action, work, or deed, and its effect or consequences. In Indian religions, the term more specifically refers to a principle of cause and effect, often descriptively called the principle of karma, wherein individuals' intent and actions (cause) influence their future (effect): Good intent and good deeds contribute to good karma and happier rebirths, while bad intent and bad deeds contribute to bad karma and worse rebirths. In some scriptures, however, there is no link between rebirth and karma. Karma is often misunderstood as fate, destiny, or predetermination.

Saṃsāra is a Pali and Sanskrit word that means "wandering" as well as "world," wherein the term connotes "cyclic change" or, less formally, "running around in circles." Saṃsāra is referred to with terms or phrases such as transmigration/reincarnation, karmic cycle, or Punarjanman, and "cycle of aimless drifting, wandering or mundane existence". When related to the theory of karma it is the cycle of death and rebirth.

Marshall David Sahlins was an American cultural anthropologist best known for his ethnographic work in the Pacific and for his contributions to anthropological theory. He was the Charles F. Grey Distinguished Service Professor Emeritus of Anthropology and of Social Sciences at the University of Chicago.
Rebirth in Buddhism refers to the teaching that the actions of a sentient being lead to a new existence after death, in an endless cycle called saṃsāra. This cycle is considered to be dukkha, unsatisfactory and painful. The cycle stops only if Nirvana (liberation) is achieved by insight and the extinguishing of craving. Rebirth is one of the foundational doctrines of Buddhism, along with karma and Nirvana. Rebirth was a key teaching of early Buddhism along with the doctrine of karma. In Early Buddhist Sources, the Buddha claims to have knowledge of his many past lives. Rebirth and other concepts of the afterlife have been interpreted in different ways by different Buddhist traditions.

Kannagi, sometimes spelled Kannaki, is a legendary Tamil woman who forms the central character of the Tamil epic Cilappatikaram. Kannagi is described as a chaste woman who stays with her husband despite his adultery, their attempt to rebuild their marriage after her unrepentant husband had lost everything, how he is framed then punished without the due checks and processes of justice. Kannagi proves and protests the injustice, then curses the king and city of Madurai leading to the death of the unjust Pandyan King of Madurai, who had wrongfully put her husband Kovalan to death. The society that had made her suffer, suffers in retribution as the city Madurai is burnt to the ground because of her curse. In Tamil folklore, Kannagi has been deified as the symbol – sometimes as goddess – of chastity, with sculptures or reliefs in Hindu temples iconographically reminding the visitor of her breaking her anklet or tearing her bleeding breast and throwing it at the city.

Ilango Adigal was a monk and a poet, sometimes identified as a Chera prince. He is traditionally credited as the author of Cilappatikaram, one of the Five Great Epics of Ancient Tamil literature. He is one of the greatest poets from Cheranadu. In a patikam (prologue) to the epic poem, he identifies himself as the brother of a famous Chera king Ceṅkuṭṭuvan (Senguttuvan). This Chera king, as stated by Elizabeth Rosen, ruled over his kingdom in late 2nd or early 3rd century CE. However, this is doubtful because a Sangam poem in Patiṟṟuppattu – the fifth ten – provides a biography of Ceṅkuṭṭuvan, his family and rule, but never mentions that he had a brother who became an ascetic or wrote one of the most cherished epics. This has led scholars to conclude that the legendary author Ilango Adikal myth was likely inserted later into the epic. In a 1968 note, Kamil Zvelebil suggested that, "this [Adigal claim] may be a bit of poetic fantasy, practised perhaps by a later member of the Chera Dynasty [5th or 6th century] recalling earlier events [2nd or 3rd century]".

Salagama is a Sinhalese caste found mostly in the southern coastal areas of Sri Lanka. The community was traditionally associated with the cultivation and management of cinnamon and were formerly also involved as weavers and soldiers.

Karava is a Sinhalese speaking ethnic group of Sri Lanka, whose ancestors migrated throughout history from the Coromandel coast, claiming lineage to the Kaurava royalty of the old Kingdom of Kuru in Northern India. The Tamil equivalent is Karaiyar. Both groups are also known as the Kurukula.
Pattini, is considered a guardian deity of Sri Lanka in Sri Lankan Buddhism and Sinhalese folklore. She is also worshipped by Sri Lankan Tamil Hindus by the name of Kannaki Amman.
Stanley Jeyaraja Tambiah was a social anthropologist and Esther and Sidney Rabb Professor (Emeritus) of Anthropology at Harvard University. He specialised in studies of Thailand, Sri Lanka, and Tamils, as well as the anthropology of religion and politics.

Ānantarya karma (Sanskrit) or Ānantarika kamma (Pāli) are the most serious offences in Buddhism that, at death, through the overwhelming karmic strength of any single one of them, bring immediate disaster. Both Buddhists and non-Buddhists must avoid them at all costs. Such offenses prevent perpetrators from attaining any of the stages of enlightenment and from ordaining into the Sangha. The offences are:
- Killing one's mother
- Killing one's father
- Killing an Arahant
- Wounding a Tathagata
- Creating schism in the Sangha

Richard Francis Gombrich is a British Indologist and scholar of Sanskrit, Pāli, and Buddhist studies. He was the Boden Professor of Sanskrit at the University of Oxford from 1976 to 2004. He is currently Founder-President of the Oxford Centre for Buddhist Studies. He is a past president of the Pali Text Society (1994–2002) and general editor emeritus of the Clay Sanskrit Library.
The Conquest of America: The Question of the Other is a book by Tzvetan Todorov first published in 1982, detailing Spanish colonials' contact with natives upon the discovery of the Americas.
There are a few differing Buddhist views on sin. American Zen author Brad Warner states that in Buddhism there is no concept of sin at all. The Buddha Dharma Education Association also expressly states "The idea of sin or original sin has no place in Buddhism." Zen student and author Barbara O'Brien has said that "Buddhism has no concept of sin." Walpola Rahula also disagreed with the notion of sin, saying "In fact there is no 'sin' in Buddhism, as sin is understood in some religions."
Valagamba, also known as the Great Black Lion, Wattagamani Abhaya and Valagambahu, was a king of the Anuradhapura Kingdom of Sri Lanka. Five months after becoming king, he was overthrown by a rebellion and an invasion from South India, but regained the throne by defeating the invaders fourteen years later. He is also known for the construction of the Abhayagiri Dagaba & Aluthepola Ganekanda Raja Maha Vihara.
Anne M. Blackburn is a historian of South and Southeast Asian Buddhism. She is Old Dominion Foundation Professor in the Humanities at Cornell University. Blackburn received her B.A. in Asian History and Religion in 1988 from Swarthmore College, her M.A. in Religious Studies in 1990 from University of Chicago Divinity School, and her Ph.D. in History of Religions in 1996 from the same institution. Blackburn's teachers include Steven Collins, Charles Hallisey, Frank E. Reynolds, and Donald Swearer.
Obeyesekere may refer to:

The Sahlins–Obeyesekere debate is an academic controversy in anthropology about the death of the British explorer James Cook, particularly whether the native Hawaiians believed him to be Lono, an akua "deity" associated with fertility, agriculture, rainfall, music and peace. The debate took shape in 1992, when Gananath Obeyesekere published The Apotheosis of Captain Cook, which criticized the work of Marshall Sahlins on the issue. In addition to the factual issues, the debate has become symbolic of deeper issues in anthropology, including whether Western scholars can understand non-Western cultures.
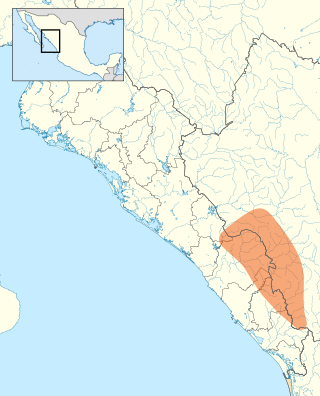
The Xixime were an indigenous people who inhabited a portion of the Sierra Madre Occidental mountains in the present day states of Durango and Sinaloa, Mexico. The Xixime are noted for their reported practice of cannibalism and resistance to Spanish colonization in the form of the Xixime Rebellion of 1610.











