
The Chelydridae is a family of turtles that has seven extinct and two extant genera. The extant genera are the snapping turtles, Chelydra and Macrochelys. Both are endemic to the Western Hemisphere. The extinct genera are Acherontemys, Chelydrops, Chelydropsis, Emarginachelys, Macrocephalochelys, Planiplastron, and Protochelydra.

Alcide Charles Victor Marie Dessalines d'Orbigny was a French naturalist who made major contributions in many areas, including zoology, palaeontology, geology, archaeology and anthropology.

Cetiosaurus meaning 'whale lizard', from the Greek keteios/κήτειος meaning 'sea monster' and sauros/σαυρος meaning 'lizard', is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Period, living about 168 million years ago in what is now Britain and probably France.
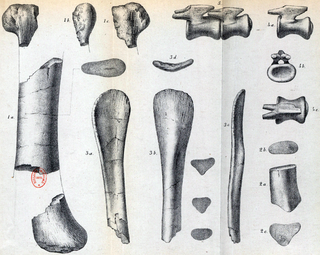
Hypselosaurus is a dubious genus of titanosaurian sauropod that lived in southern France during the Late Cretaceous, approximately 70 million years ago in the early Maastrichtian. Hypselosaurus was first described in 1846, but was not formally named until 1869, when Phillip Matheron named it under the binomial Hypselosaurus priscus. The holotype specimen includes a partial hindlimb and a pair of caudal vertebrae, and two eggshell fragments were found alongside these bones. Because of the proximity of these eggshells to the fossil remains, many later authors, including Matheron and Paul Gervais, have assigned several eggs from the same region of France all to Hypselosaurus, although the variation and differences between these eggs suggest that they do not all belong to the same taxon. Hypselosaurus has been found in the same formation as the dromaeosaurids Variraptor and Pyroraptor, the ornithopod Rhabdodon, and the ankylosaurian Rhodanosaurus, as well as indeterminate bones from other groups.

Teinurosaurus is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur. Teinurosaurus lived during the Late Jurassic in what is now France. The type species is Teinurosaurus sauvagei. It's been estimated to be 11.4 m (37.4 ft) in length and 3.6 tonnes in weight.
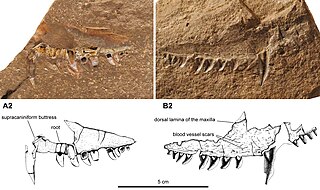
Neosaurus is an extinct genus of pelycosaur-grade synapsids from the Late Carboniferous-Early Permian of the Jura region of France. It is known only from a partial maxilla or upper jaw bone and an associated impression of the bone. The teardrop shape of the teeth in the jaw indicate that Neosaurus belongs to the family Sphenacodontidae, which includes the better-known Dimetrodon from the Southwestern United States. The maxilla was first attributed to an early diapsid reptile in 1857, and later a crocodylomorph in 1869, before finally being identified as a sphenacodont synapsid in 1899, a classification that still holds today.
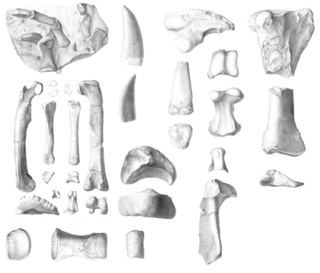
Erectopus is an extinct genus of basal allosauroid theropod from the Early Cretaceous La Penthiève Beds Formation of France and also possibly the Cernavodă Formation of southern Romania. The type species is E. superbus, which was initially known as a species of Megalosaurus.
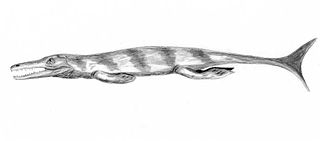
Enaliosuchus is a dubious genus of extinct marine crocodyliform within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Valanginian stage of the Early Cretaceous. It is known from fossil remains found in France and Germany and it was first described in 1883.

Proteroctopus is an extinct genus of cephalopod that lived in the Middle Jurassic, approximately 164 million years ago. It is only known from a single species P. ribeti. The single fossil specimen assigned to this species originates from the Lower Callovian of Voulte-sur-Rhône in France. It is currently on display at the Musée de Paléontologie de La Voulte-sur-Rhône. While originally interpreted as an early octopus, a 2016 restudy of the specimen considered it to be a basal member of the Vampyropoda, less closely related to octopus or vampire squid than either of the two groups are to each other. A phylogenetic analysis by Kruta et. al indicates that Proteroctopus may be more closely related to the Vampyromorpha based on its unique morphology: two fins, head fused to the body, eight arms, two rows of oblique sucker, a gladius and absence of an ink sac. A 2022 phylogenetic analysis also found it to be more closely related to vampire squid than to octopuses.

Louis Charles Émile Lortet was a French physician, botanist, zoologist and Egyptologist who was a native of Oullins.

Saint-Vallier is a commune in the Drôme department in southeastern France. It is an administrative, commercial and industrial town at the confluence of the rivers Galaure and Rhone.

Iberosuchus is a genus of extinct sebecosuchian mesoeucrocodylian found in Western Europe from the Eocene. Remains from Portugal was described in 1975 by Antunes as a sebecosuchian crocodilian. This genus has one species: I. macrodon. Iberosuchus was a carnivore. Unlike the crocodilians today, they were not aquatic but were instead terrestrial.

Sauravus is an extinct genus of nectridean tetrapodomorphs within the family Scincosauridae.
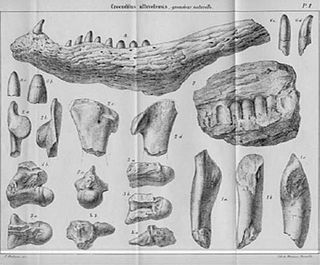
Massaliasuchus is an extinct monospecific genus of allodaposuchid eusuchian crocodyliform from the Late Cretaceous (Santonian–Campanian) Fuvelian Lignites of southeastern France. The type species is M. affuvelensis.

Gracilineustes is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform that lived in the oceans during the Middle to Late Jurassic. Gracilineustes was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. It was a small reptile, with G. leedsi measuring 2.25–3.11 m (7.4–10.2 ft) long and G. acutus measuring 3.77 m (12.4 ft) long.
Monopleura is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Monopleuridae. These fossils have been dated back to the Cretaceous Period.

Matheronodon is a genus of rhabdodontid ornithopod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous Period of the Grès à Reptiles Formation in France. The genus contains a single species, M. provincialis, which is known from a single maxilla and associated teeth. It was named by Pascal Godefroit and colleagues in 2017. The teeth of Matheronodon are large but few in number. The teeth are also in an unusual arrangement, emerging alternatingly from one of a pair of fused tooth sockets in its mouth. In life, the teeth would have functioned like a pair of scissors, allowing Matheronodon to feed on the tough leaves of monocot plants.
Solemys is an extinct genus of stem turtle known from the Late Cretaceous of southern France and eastern Spain.
Paraplacosauriops is an extinct genus of anguid lizards from the middle Eocene of France.

The Sainte-Victoire National Nature Reserve (RNN117) is a national nature reserve located in the Bouches-du-Rhône department. Covering 140 hectares, the nature reserve was established in 1994 to protect the fossilized dinosaur eggs preserved on the western foot of the Montagne Sainte-Victoire.

















