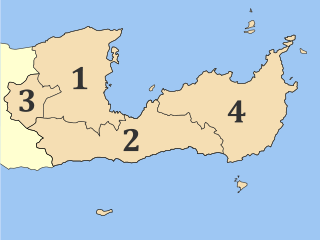
Lasithi is the easternmost regional unit on the island of Crete, to the east of Heraklion. Its capital is Agios Nikolaos, the other major towns being Ierapetra and Sitia. The mountains include the Dikti in the west and the Thrypti in the east. The Sea of Crete lies to the north and the Libyan Sea to the south.

Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the triarylmethane dyes. They are derivatives of xanthene. Important members of the rhodamine family are rhodamine 6G, Rhodamin WT, Texas Red, rhodamine 123, and rhodamine B. They are mainly used to dye paper and inks, but they lack the lightfastness for fabric dyeing.

Gortyna, is a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Megalopoli, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 116.205 km2. Its seat was in the village Karytaina. The name of the municipality was taken from the ancient city of Gortys.

Gortyn, Gortys or Gortyna is a municipality, and an archaeological site, on the Mediterranean island of Crete 45 km (28 mi) away from the island's capital, Heraklion. The seat of the municipality is the village Agioi Deka. Gortyn was the Roman capital of Creta et Cyrenaica. The area was first inhabited around 7000 BC.

Gortyna was a town of ancient Crete which appears in the Homeric poems under the form of Γορτύν; but afterwards became usually Gortyna (Γόρτυνα). According to Stephanus of Byzantium it was originally called Larissa (Λάρισσα) and Cremnia or Kremnia (Κρήμνια).

Xanthone is an organic compound with the molecular formula C13H8O2. It is a white solid.
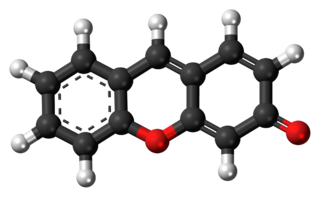
Fluorone is a heterocyclic chemical compound. It forms the core structure for various chemicals, most notably fluorone dyes, including fluorescein, erythrosine and rhodamine. It is an isomer of xanthone, sometimes referred to as an isoxanthone.

Karytaina or Karitaina is a village and a community in Arcadia, Greece. Karytaina is situated on a hill on the right bank of the river Alpheios, near its confluence with the Lousios. The village dates back to the Middle Ages, but its history is unknown before the Crusader conquest ca. 1205. Karytaina became the seat of a barony under the Frankish Principality of Achaea, and the Castle of Karytaina was built in the mid-13th century on a steep rocky outcrop by Baron Geoffrey of Briel. The area returned to Byzantine control in 1320, and came under Ottoman control in 1460. After a brief period of Venetian rule (1687–1715), Karytaina returned to Ottoman control, and prospered as an administrative and commercial centre. Karytaina and its inhabitants were among the first to rise up during the Greek War of Independence of 1821–29. Today Karytaina is a protected traditional settlement and has, alongside the remains of its Frankish castle, several other medieval and Ottoman monuments.

Thioxanthene is a chemical compound in which the oxygen atom in xanthene is replaced with a sulfur atom. It is also related to phenothiazine. Several of its derivatives are used as typical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychoses.

The Lousios, also known in antiquity as Gortynius or Gortynios, is a river and a gorge in western Arcadia that stretches from Karytaina north to Dimitsana in Greece. The river begins near Lykochori and flows through the Lousios Gorge. The river is treacherous and flows rapidly. It empties into the Alfeios 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) northwest of Karytaina and south of Atsicholos.
Triarylmethane dyes are synthetic organic compounds containing triphenylmethane backbones. As dyes, these compounds are intensely colored. They are produced industrially as dyes.
Margherita Guarducci, also spelled Guarduci, was an Italian archaeologist, classical scholar, and epigrapher. She was a major figure in several crucial moments of the 20th-century academic community. A student of Federico Halbherr, she edited his works after his death. She was the first woman to lead archaeological excavations at the Vatican, succeeding Ludwig Kaas, and completed the excavations on Saint Peter's tomb, identifying finds as relics of Saint Peter. She has also engaged in discussions on the authenticity of the Praeneste fibula, arguing that its inscription is a forgery.

Gortyna is a moth genus in the family Noctuidae.
Saint Philip of Gortyna was Bishop of Gortyna on Crete. Little is known about him except for his authorship of a now lost treatise against the Gnostics. An early Christian Apologist, he wrote in the time of Marcus Aurelius against Marcion. He was mentioned with great praise by Dionysius of Corinth in one of his letters to the Christian Community in Gortyna. He is generally commemorated with a feast day on 11 April, however in the Church of Crete his feast day is on 8 October.

The frosted orange moth is a moth of the family Noctuidae which is found in Europe, Armenia, Syria and east through the Palearctic to western Siberia. It has also been recorded in Algeria. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. The frosted orange is a night-flying species with orange and brown speckled wings allow for perfect camouflage against autumn leaves in the daytime. It is attracted to light and does not come to flowers, and its larva inhabit the stems and roots of the species' food plants.

Ro67-4853 is a drug used in scientific research, which acts as a selective positive allosteric modulator for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR1. It was derived by modification of the simpler compound Ro01-6128, and has itself subsequently been used as a lead compound to develop a range of potent and selective mGluR1 positive modulators.

Gortyna flavina is a moth in the family Noctuidae. It is found in Taiwan.
Papaipema appassionata, the pitcher plant borer, is a species of moth described by Leon F. Harvey in 1876. It is native to North America, where it has been recorded from Florida, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, New Brunswick, Quebec, Rhode Island, South Carolina and Wisconsin. It is listed as threatened in the US state of Connecticut.
Papaipema circumlucens, the hops-stalk borer moth, is a species of moth native to North America, where it has been recorded from Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Missouri, New Hampshire, Ohio, Saskatchewan and Wisconsin. The species was described by Smith in 1899. It is listed as a species of special concern and is believed to be extirpated from the US state of Connecticut.













