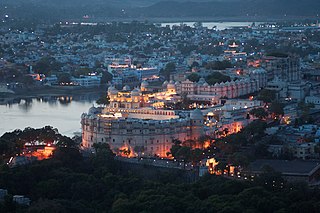Rajasthan is a state in northern India. It covers 342,239 square kilometres (132,139 sq mi) or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern side, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej-Indus River valley. It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab to the north; Haryana and Uttar Pradesh to the northeast; Madhya Pradesh to the southeast; and Gujarat to the southwest. Its geographical location is 23.3 to 30.12 North latitude and 69.30 to 78.17 East longitude, with the Tropic of Cancer passing through its southernmost tip.

The Udaipur Solar Observatory (USO) is in Udaipur, Rajasthan in India on an island in the Fateh Sagar Lake. The sky conditions at Udaipur are quite favourable for solar observations. Since the observatory is situated amidst a large mass of water, air turbulence which occurs due to ground heating by sun's rays is decreased. This improves the image quality and accuracy.

Osman Sagar is a reservoir in the Indian city of Hyderabad. The lake is around 46 km², and the reservoir is around 29 km², with total level of 1,790 feet and a capacity of 3.9 tmc ft.

The Chambal River is a tributary of the Yamuna River in Central and Northern India, and thus forms part of the greater Gangetic drainage system. The river flows north-northeast through Madhya Pradesh, running for a time through Rajasthan then forming the boundary between Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh before turning southeast to join the Yamuna in Uttar Pradesh state.
Banswara is a city in the Banswara district in southern Rajasthan, India. The name, Banswara, came from "Bans wala" (bamboo) forests, as Bamboo grew in abundance around this place within the area.

The Ahar River is a tributary of the Berach River.
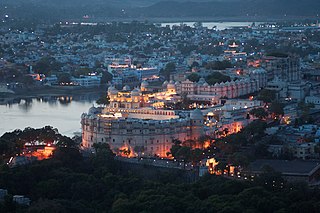
Udaipur, historically named as Udayapura, is a city in the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the historic capital of the kingdom of Mewar in the former Rajputana Agency. It was founded in 1559 by Udai Singh II of the Sisodia clan of Rajput, when he shifted his capital from the city of Chittorgarh to Udaipur after Chittorgarh was besieged by Akbar. It remained as the capital city till 1818 when it became a British princely state, and thereafter the Mewar province became a part of Rajasthan when India gained independence in 1947.

Jal Mahal is a palace in the middle of the Man Sagar Lake in Jaipur city, the capital of the state of Rajasthan, India. The palace was originally constructed in 1699; the building and the lake around it were later renovated and enlarged in the 18th century by Maharaja Jai Singh II of Amber.

The Rana Pratap Sagar Dam is a gravity masonry dam of 53.8 metres (177 ft) height built on the Chambal River at Rawatbhata in Rajasthan in India. It is part of integrated scheme of a cascade development of the river involving four projects starting with the Gandhi Sagar Dam in the upstream reach in Madhya Pradesh and the Jawahar Sagar Dam on the downstream with a terminal structure of the Kota Barrage in Rajasthan for irrigation.

The green avadavat or green munia is a species of Estrildid finch with green and yellow on the body, a bright red bill and black "zebra stripes" on the flanks. They are endemic to the Indian subcontinent and were formerly popular as cagebirds. The name "avadavat" is a corruption of the name the city of Ahmedabad in Gujarat, India, which was a centre of bird trade. They have a restricted distribution and populations are threatened by the bird trade.

Lake Pichola, situated in Udaipur city in the Indian state of Rajasthan, is an artificial fresh water lake, created in the year 1362, named after the nearby Picholi village. It is one of the several contiguous lakes, and developed over the last few centuries in and around the famous Udaipur city. The lakes around Udaipur were primarily created by building dams to meet the drinking water and irrigation needs of the city and its neighbourhood. Two islands, Jag Niwas and Jag Mandir are located within Pichola Lake, and have been developed with several palaces to provide views of the lake.

Fateh Sagar Lake is situated in the city of Udaipur in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is an artificial lake named after Maharana Fateh Singh of Udaipur and Mewar, constructed north-west of Udaipur, to the north of Lake Pichola in the 1680s.

Udaipur city in Rajasthan state has five major lakes, as listed below, which are under restoration with funds provided by the National Lake Conservation Plan (NLCP) of the Government of India.

Neemach Mata Temple is located on a hill on the banks of the Fateh Sagar Lake in the city of Udaipur, Rajasthan,India. This temple is located on a green hill in the Dewali area of Udaipur. It has both stairs and uphill slope walk way to climb, which is around 900 metres long. It enshrines the stone idol of Neemach Mata Devi. There is also an idol of Lord Ganesh and three west-facing lions of stone.
Udaisagar Lake, one of the five prominent lakes of Udaipur, is situated around 13 km in the east of Udaipur. This lake was built by Maharana Udai Singh in 1565. Udai Sagar Lake is around 4 km in length, 2.5 km in width and 9 meters deep at the maximum. It is fed by the Ahar River.

Rajiv Gandhi Garden is one of the big gardens in Udaipur, Rajasthan, India. It is situated near the back of Fateh Sagar Lake, and contains a statue of Late Rajiv Gandhi, besides several other attractions like spacious children's park and a food court.

Phulwari ki Nal Wildlife Sanctuary is in Udaipur District of Rajasthan, in the southern Aravalli Hills bordering the state of Gujarat, India. It was declared a Wildlife Sanctuary on 6 October 1983 by the Government of Rajasthan.
Swaroop Sagar Lake is situated in the city of Udaipur in the Rajasthan state of India. It is an artificially created lake, named after Maharana Swarup Singh of Udaipur. It is also known as Kumharia Talab, which is a combined water body comprising other nearby lakes Fateh Sagar Lake and Lake Pichola.
Rang Sagar Lake is situated in the city of Udaipur in the Rajasthan state of India. It is an artificially created lake, built in 1668. It is also known as Amarkunt, that connects Swaroop Sagar Lake and Pichola Lake. It is situated Ambamata connecting to Swaroop Sagar lake.