Highway 1 is a provincial highway in British Columbia, Canada, that carries the main route of the Trans-Canada Highway (TCH). The highway is 1,047 kilometres (651 mi) long and connects Vancouver Island, the Greater Vancouver region in the Lower Mainland, and the Interior. It is the westernmost portion of the main TCH to be numbered "Highway 1", which continues through Western Canada and extends to the Manitoba–Ontario boundary. The section of Highway 1 in the Lower Mainland is the second-busiest freeway in Canada, after Ontario Highway 401 in Toronto.
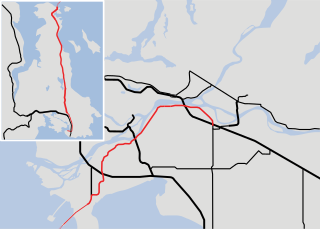
Highway 17 is a provincial highway in British Columbia, Canada. It comprises two separate sections connected by a ferry link. The Vancouver Island section is known as the Patricia Bay Highway and connects Victoria to the Swartz Bay ferry terminal in North Saanich. The Lower Mainland section is known as the South Fraser Perimeter Road and connects the Tsawwassen ferry terminal to Delta and Surrey, terminating at an interchange with Highway 1 in the Fraser Valley.
Highway 99 is a provincial highway in British Columbia that runs 377 kilometres (234 mi) from the U.S. border to near Cache Creek, serving Greater Vancouver and the Squamish–Lillooet corridor. It is a major north–south artery within Vancouver and connects the city to several suburbs as well as the U.S. border, where it continues south as Interstate 5. The central section of the route, also known as the Sea to Sky Highway, serves the communities of Squamish, Whistler, and Pemberton. Highway 99 continues through Lillooet and ends at a junction with Highway 97 near Cache Creek.

Highway 7, known for most of its length as the Lougheed Highway and Broadway, is an alternative route to Highway 1 through the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. Whereas the controlled-access Highway 1 follows the southern bank of the Fraser River, Highway 7 follows the northern bank.
Highway 99A is a series of former highways in the southwestern part of British Columbia, Canada. It was the designation of the former 1942 alignment of Highway 99 as well a various alternate routes which existed in the 1950s and 1960s. The last official use of '99A' was decommissioned in 2006, although some present-day, commercially published road maps still show it and some remnant signage still remains.
There are many roads in the southwestern part of British Columbia and Vancouver Island that were designated as Highway 1A. These roads were sections of the original 1941 route of Highway 1 before its various re-alignments, and are used today as service routes and frontage roads. The "B.C. Highway 1A" designations were removed from these sections by the province between 2005 and 2010, although signage remains along some of the route and the designation on some maps.

Cambie Street is a street in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It is named for Henry John Cambie, chief surveyor of the Canadian Pacific Railway's western division.

Route 123 is a state highway running 7.8 miles (12.6 km) in the U.S. state of Rhode Island. Its western terminus is at Route 116 in Lincoln, and its eastern terminus is at the Massachusetts border where it continues as Massachusetts Route 123.

Burrard Street is a major thoroughfare in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It is the central street of Downtown Vancouver and the Financial District. The street is named for Burrard Inlet, located at its northern terminus, which in turn is named for Sir Harry Burrard-Neale.

The Arthur Laing Bridge is a crossing over the north arm of the Fraser River, and several minor roads, in Metro Vancouver.

The Moray Bridge, also known as the Moray Channel Bridge, and formerly the Middle Arm Bridge, is a crossing over the middle arm of the Fraser River in Metro Vancouver. Richard Moody, who would name geographical features, such as this channel, after acquaintances, honoured Jonathan Moray (1824–84), a sergeant in the Corps of Royal Engineers, and later the New Westminster police chief.

The Sea Island Connector, is a crossing over the middle arm of the Fraser River in Metro Vancouver.

Marpole, originally a Musqueam village named c̓əsnaʔəm, is a mostly residential neighbourhood of 23,832 in 2011, located on the southern edge of the city of Vancouver, British Columbia, immediately northeast of Vancouver International Airport, and is approximately bordered by Angus Drive to the west, 57th Avenue to the north, Ontario Street to the east and the Fraser River to the south. It has undergone many changes in the 20th century, with the influx of traffic and development associated with the construction of the Oak Street Bridge and the Arthur Laing Bridge.

The Dinsmore Bridge is a crossing over the middle arm of the Fraser River, and a former section of River Rd., in Metro Vancouver.

Sea Island is an island in the Fraser River estuary in the city of Richmond, British Columbia. It is located south of the city of Vancouver and north and west of Lulu Island. Sea Island is the home to Vancouver International Airport (YVR), a nature conservation area, and a permanent resident population of 814, most of which live in the neighbourhood of Burkeville. A small part of the island is under the administration of the Musqueam Indian Band.

Sea Island Centre is an at-grade station on the Canada Line of Metro Vancouver's SkyTrain rapid transit system. The station is located on Sea Island in Richmond, British Columbia.

Knight Street is a major north-south roadway in Vancouver and Richmond, British Columbia, Canada. It is a four-to-six lane freeway from Westminster Highway in Richmond to Marine Drive in Vancouver, thus serving as an alternate way to exit Vancouver southbound, rather than the Granville Street/Oak Street corridor. Upon entering Vancouver, Knight Street provides major access routes to East Vancouver; at 14th Avenue, the road turns into Clark Drive, and runs northbound until it reaches the Port of Vancouver at Burrard Inlet. It is the busiest truck route in Vancouver, and a key link between Vancouver and its neighbours to the south.

Main Street is a major north–south thoroughfare bisecting Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It runs from Waterfront Road by Burrard Inlet in the north, to Kent Avenue alongside the north arm of the Fraser River in the south.
King's Highway 130, commonly known as Highway 130, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. It begins at a junction with Highway 61 and travels 15.4 km (9.6 mi) north-west to the Trans-Canada Highway, Highway 11 and Highway 17, west of Thunder Bay. Highway 130 is a short connecting highway, and passes entirely through the outskirts of Thunder Bay, connecting several minor communities and providing a shortcut for traffic travelling from the south to the west or vice versa. The speed limit along the highway is 80 km/h (50 mph); it is patrolled by the Ontario Provincial Police.
Marine Drive is the name for three major roadways in Greater Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. The roads are known for running parallel to major bodies of water, with some sections being a major arterial road, while other serve local traffic. Marine Way is the name applied to a section of Marine Drive that was bypassed in the early 1980s.















