
Bloody Friday is the name given to the bombings by the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) in Belfast, Northern Ireland on 21 July 1972, during the Troubles. At least twenty bombs exploded in the space of eighty minutes, most within a half-hour period. Most of them were car bombs and most targeted infrastructure, especially the transport network. Nine people were killed: five civilians, two British soldiers, a Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC) reservist, and an Ulster Defence Association (UDA) member, while 130 were injured. The IRA said it sent telephoned warnings at least thirty minutes before each explosion and said that the security forces wilfully ignored some of the warnings for their own ends. The security forces said that was not the case and said they were overstretched by the sheer number of bombs and bomb warnings, some of which were hoaxes.

York Road railway station served the north of Belfast in Northern Ireland. It was formerly one of the three terminus railway stations in Belfast. The others were Great Victoria Street, and Queen's Quay.
Belfast City Centre is the central business district of Belfast, Northern Ireland.

Belfast City Hall is the civic building of Belfast City Council located in Donegall Square, Belfast, Northern Ireland. It faces North and effectively divides the commercial and business areas of the city centre. It is a Grade A listed building.

The Crown Liquor Saloon, also known as the Crown Bar, is a pub in Great Victoria Street in Belfast, Northern Ireland. Refurbished in 1885, and at least twice since, it is an outstanding example of a Victorian gin palace, and one of Northern Ireland's best-known pubs. It is owned by the National Trust and is leased to Mitchells & Butlers who run it as a Nicholson's pub.

Donegall Square is a square in the centre of Belfast, County Antrim, Northern Ireland. In the centre is Belfast City Hall, the headquarters of Belfast City Council. Each side of the square is named according to its geographical location, i.e. Donegall Square North, South, East and West. It is named after the Donegall family. Other streets to bear their name in Belfast are Donegall Road, Donegall Pass and Donegall Street. Donegall Place, the city's main shopping street, runs from the north side of the square.

Yorkgate railway station served the north of the city of Belfast, Northern Ireland. The station opened in 1992, replacing the previous York Road railway station nearby. The station was in turn replaced by the nearby York Street station in 2024, with the new station re-using the existing platforms of Yorkgate.

The Europa Hotel is a four-star hotel in Great Victoria Street, Belfast, Northern Ireland.

The Cathedral Quarter in Belfast, Northern Ireland, is a developing area of the city, roughly situated between Royal Avenue near where the Belfast Central Library building is, and the Dunbar Link in the city centre. From one of its corners, the junction of Royal Avenue, Donegall Street and York Street, the Cathedral Quarter lies south and east. Part of the area, centred on Talbot Street behind the cathedral, was formerly called the Half Bap. The "Little Italy" area was on the opposite side of Great Patrick Street centred on Little Patrick Street and Nelson Street.

Titanic Quarter in Belfast, Northern Ireland, is a large-scale waterfront regeneration, comprising historic maritime landmarks, film studios, education facilities, apartments, a riverside entertainment district, and the world's largest Titanic-themed attraction centred on land in Belfast Harbour, known until 1995 as Queen's Island. The 185-acre (75 ha) site, previously occupied by part of the Harland and Wolff shipyard, is named after the company's, and the city's, most famous product, RMS Titanic. Titanic Quarter is part of the Dublin-based group, Harcourt Developments, which has held the development rights since 2003.

The buildings and structures of Belfast, Northern Ireland comprise many styles of architecture ranging from Edwardian through to state-of-the-art modern buildings like the Waterfront Hall. The city's beautiful Edwardian buildings are notable for their display of a large number of sculptures. Many of Belfast's Victorian landmarks, including the main Lanyon Building at Queens University in 1849, were designed by Sir Charles Lanyon.

The Linen Quarter is an area of Belfast, Northern Ireland. The name is derived from the great many linen warehouses that are still present in the area. The Linen Quarter is host to some of the major cultural venues of Belfast, including the Ulster Hall and Grand Opera House, alongside a large number of hotels, bars, restaurants and cafes. The district also includes the main transport hub of Belfast.

Great Victoria Street was a railway station that served the city centre of Belfast, Northern Ireland. It was one of two main stations in the city, along with Lanyon Place, and was nearest to the city centre. The station was situated beside Great Victoria Street and shared a site with the Europa Buscentre, Belfast's former main bus station. The railway and bus stations were replaced by the adjacent Belfast Grand Central station with the official opening on 13 October 2024. Great Victoria Street railway station closed permanently on 10 May 2024, with a bus transfer service operating until rail services commenced from Belfast Grand Central, with a service to Dublin at 8:05 a.m. on 13 October 2024. Europa Buscentre closed permanently on 7 September 2024, with bus services immediately transferring to the new station, commencing with a service to Dublin at 5 a.m. on 8 September 2024.
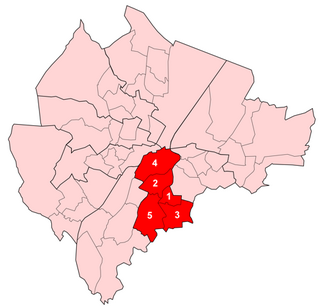
Laganbank was one of the nine district electoral areas in Belfast, Northern Ireland which existed from 1985 to 2014. Located in the south of the city, the district elected five members to Belfast City Council and contained the wards of Ballynafeigh, Botanic, Shaftesbury, Stranmillis, and Rosetta. Laganbank, along with neighbouring Balmoral, formed the greater part of the Belfast South constituencies for the Northern Ireland Assembly and UK Parliament.

Royal Avenue is a street in the heart of Belfast city centre, Northern Ireland. It runs for about 500 metres from the junction with Castle Place and Donegall Place to the junction with Donegall Street. It lies between the Cathedral Quarter and the Smithfield and Union Quarter of the city. It has been the city's principal shopping thoroughfare since its establishment in 1881. Today Royal Avenue is one of Belfast's main commercial centres and is home to the £40 million shopping complex Westfield CastleCourt.

Shaftesbury Square is in Belfast, Northern Ireland at the southern end of Great Victoria Street and Dublin road, with the adjoining streets of Lisburn Road and the Donegall Road converging at this junction. It is in the area commonly known as the Golden Mile.

Queen's Quay railway station served the east of Belfast in Northern Ireland. It was formerly one of the three terminus railway stations in Belfast. The others were Great Victoria Street, and York Road.
Queen's Bridge railway station was the terminus of the Belfast Central Railway which ran from the Ulster Junction on the Ulster Railway to Ballymacarrett Junction on the Belfast and County Down Railway, through central Belfast, Ireland.

















