
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

Sodium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood, sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the Chlor-alkali process.

Kala namak or black salt is a kiln-fired rock salt with a sulphurous, pungent smell used in the Indian subcontinent. It is also known as "Himalayan black salt", Sulemani namak, bit noon, bire noon, bit loona, bit lobon, kala loon, sanchal, guma loon, or pada loon, and is manufactured from the salts mined in the regions surrounding the Himalayas.
Sulfur dyes are the most commonly used dyes manufactured for cotton in terms of volume. They are inexpensive, generally have good wash-fastness, and are easy to apply. Sulfur dyes are predominantly black, brown, and dark blue. Red sulfur dyes are unknown, although a pink or lighter scarlet color is available.
The Leblanc process was an early industrial process for making soda ash used throughout the 19th century, named after its inventor, Nicolas Leblanc. It involved two stages: making sodium sulfate from sodium chloride, followed by reacting the sodium sulfate with coal and calcium carbonate to make sodium carbonate. The process gradually became obsolete after the development of the Solvay process.

Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 million tonnes, the decahydrate is a major commodity chemical product. It is mainly used as a filler in the manufacture of powdered home laundry detergents and in the Kraft process of paper pulping for making highly alkaline sulfides.

The kraft process (also known as kraft pulping or sulfate process) is a process for conversion of wood into wood pulp, which consists of almost pure cellulose fibres, the main component of paper. The kraft process involves treatment of wood chips with a hot mixture of water, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and sodium sulfide (Na2S), known as white liquor, that breaks the bonds that link lignin, hemicellulose, and cellulose. The technology entails several steps, both mechanical and chemical. It is the dominant method for producing paper. In some situations, the process has been controversial because kraft plants can release odorous products and in some situations produce substantial liquid wastes.
Classical qualitative inorganic analysis is a method of analytical chemistry which seeks to find the elemental composition of inorganic compounds. It is mainly focused on detecting ions in an aqueous solution, therefore materials in other forms may need to be brought to this state before using standard methods. The solution is then treated with various reagents to test for reactions characteristic of certain ions, which may cause color change, precipitation and other visible changes.

In photography, toning is a method of altering the color of black-and-white photographs. In analog photography, it is a chemical process carried out on metal salt-based prints, such as silver prints, iron-based prints, or platinum or palladium prints. This darkroom process cannot be performed with a color photograph. The effects of this process can be emulated with software in digital photography. Sepia is considered a form of black-and-white or monochrome photography.
Sodium oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2O. It is used in ceramics and glasses. It is a white solid but the compound is rarely encountered. Instead "sodium oxide" is used to describe components of various materials such as glasses and fertilizers which contain oxides that include sodium and other elements.
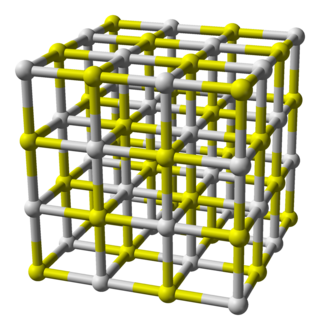
Calcium sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula CaS. This white material crystallizes in cubes like rock salt. CaS has been studied as a component in a process that would recycle gypsum, a product of flue-gas desulfurization. Like many salts containing sulfide ions, CaS typically has an odour of H2S, which results from small amount of this gas formed by hydrolysis of the salt.

Magnesium sulfide is an inorganic compound with the formula MgS. It is a white crystalline material but often is encountered in an impure form that is brown and non-crystalline powder. It is generated industrially in the production of metallic iron.

In industrial chemistry, black liquor is the by-product from the kraft process when digesting pulpwood into paper pulp removing lignin, hemicelluloses and other extractives from the wood to free the cellulose fibers.

Sodium sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2S, or more commonly its hydrate Na2S·9H2O. Both the anhydrous and the hydrated salts in pure crystalline form are colorless solids, although technical grades of sodium sulfide are generally yellow to brick red owing to the presence of polysulfides and commonly supplied as a crystalline mass, in flake form, or as a fused solid. They are water-soluble, giving strongly alkaline solutions. When exposed to moist air, Na2S and its hydrates emit hydrogen sulfide, an extremely toxic, flammable and corrosive gas which smells like rotten eggs.
Spent caustic is a waste industrial caustic solution that has become exhausted and is no longer useful (or spent). Spent caustics are made of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, water, and contaminants. The contaminants have consumed the majority of the sodium (or potassium) hydroxide and thus the caustic liquor is spent, for example, in one common application H2S (gas) is scrubbed by the NaOH (aqueous) to form NaHS (aq) and H2O (l), thus consuming the caustic.

Strontium carbonate (SrCO3) is the carbonate salt of strontium that has the appearance of a white or grey powder. It occurs in nature as the mineral strontianite.
Soda pulping is a chemical process for making wood pulp with sodium hydroxide as the cooking chemical. In the Soda-AQ process, anthraquinone (AQ) may be used as a pulping additive to decrease the carbohydrate degradation. The soda process gives pulp with lower tear strength than other chemical pulping processes, but has still limited use for easily pulped materials like straw and some hardwoods.
White liquor is a strongly alkaline solution mainly of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide. It is used in the first stage of the Kraft process in which lignin and hemicellulose are separated from cellulose fiber for the production of pulp. The white liquor breaks the bonds between lignin and cellulose. It is called white liquor due to its white opaque colour.










