
Guava is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava Psidium guajava is a small tree in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae), native to Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and northern South America. The name guava is also given to some other species in the genus Psidium such as strawberry guava and to the pineapple guava, Feijoa sellowiana. In 2019, 55 million tonnes of guavas were produced worldwide, led by India with 45% of the total. Botanically, guavas are berries.

Psidium is a genus of trees and shrubs in the family Myrtaceae. It is native to warmer parts of the Western Hemisphere.
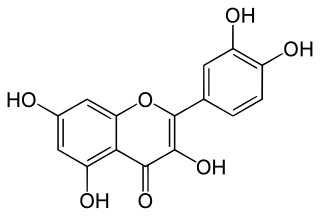
Quercetin is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains; capers, red onions, and kale are common foods containing appreciable amounts of it. It has a bitter flavor and is used as an ingredient in dietary supplements, beverages, and foods.

Rutin is the glycoside combining the flavonol quercetin and the disaccharide rutinose. It is a flavonoid glycoside found in a wide variety of plants, including citrus.
Erwinia psidii is a Gram-negative bacterium and a phytopathogen of the common guava (Psidium guajava), causing rot in branches, flowers and fruits. Recently, it was demonstrated that this species produces two acyl homoserine lactones (S-(-)-N-hexanoyl- and N-heptanoyl-homoserine lactone), widely recognized bacterial quorum sensing signaling substances, and employed in bacterial cell-to-cell communication systems.

Psidium cattleyanum , commonly known as Cattley guava, strawberry guava or cherry guava, is a small tree in the Myrtaceae (myrtle) family. The species is named in honour of English horticulturist William Cattley. Its genus name Psidium comes from the Latin psidion, or "armlet." The red-fruited variety, P. cattleyanum var. cattleyanum, is commonly known as purple guava, red cattley guava, red strawberry guava and red cherry guava. The yellow-fruited variety, P. cattleyanum var. littorale is variously known as yellow cattley guava, yellow strawberry guava, yellow cherry guava, lemon guava and in Hawaii as waiawī. Although P. cattleyanum has select economic uses, it is considered the most invasive plant in Hawaii.

Rheum nobile, the Sikkim rhubarb or noble rhubarb or पदमचाल, is a giant herbaceous plant native to the Himalaya, from northeastern Afghanistan, east through northern Pakistan and India, Nepal, Sikkim, Bhutan, and Tibet to Myanmar, occurring in the alpine zone at 4000–4800 m altitude.

Psidium guajava, the common guava, yellow guava, lemon guava, or apple guava is an evergreen shrub or small tree native to the Caribbean, Central America and South America. It is easily pollinated by insects; when cultivated, it is pollinated mainly by the common honey bee, Apis mellifera.
Psidium dumetorum, the Jamaican guava or Jamaican psidium, is an extinct species of guava in the family Myrtaceae that was endemic to Clarendon Parish, Jamaica. It is now extinct due to habitat loss.
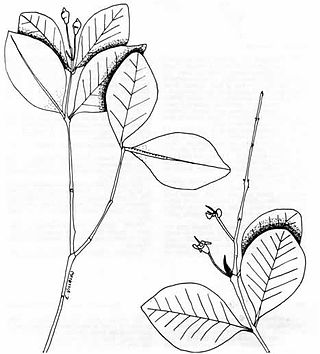
Psidium sintenisii is a species of flowering plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. It is endemic to Puerto Rico, where it is known from three or four small subpopulations, mainly within El Yunque National Forest. It grows in wet mountain forest habitat. Its common names are Sintenis' guava and hoja menuda.

Isorhamnetin is an O-methylated flavon-ol from the class of flavonoids. A common food source of this 3'-methoxylated derivative of quercetin and its glucoside conjugates are pungent yellow or red onions, in which it is a minor pigment, quercetin-3,4'-diglucoside and quercetin-4'-glucoside and the aglycone quercetin being the major pigments. Pears, olive oil, wine and tomato sauce are rich in isorhamnetin. Almond skin is a rich source of isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside and isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside, in some cultivars they comprise 75% of the polyphenol content, the total of which can exceed 10 mg/100 gram almond. Others sources include the spice, herbal medicinal and psychoactive Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida), which is described as accumulating isorhamnetin and its 7-O-glucoside derivate. Nopal is also a good source of isorhamnetin, which can be extracted by supercritical fluid extraction assisted by enzymes.

Morin is a yellow chemical compound that can be isolated from Maclura pomifera (Osage orange), Maclura tinctoria (old fustic), and from leaves of Psidium guajava (common guava). In a preclinical in vitro study, morin was found to be a weak inhibitor of fatty acid synthase with an IC50 of 2.33 μM. Morin was also found to inhibit amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide (or amylin) and disaggregate amyloid fibers.
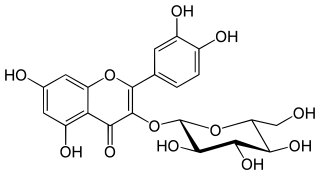
Isoquercetin, isoquercitrin or isotrifoliin is a flavonoid, a type of chemical compound. It is the 3-O-glucoside of quercetin. Isoquercitrin can be isolated from various plant species including Mangifera indica (mango) and Rheum nobile. It is also present in the leaves of Annona squamosa, Camellia sinensis (tea). and Vestia foetida

Leucocyanidin is a colorless chemical compound that is a member of the class of natural products known as leucoanthocyanidins.

Coscinoptycha improbana, the Australian guava moth, is a moth of the family Carposinidae and only member of the genus Coscinoptycha. It is native to Australia, where it is found from Eungella in Queensland down through New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania. It also occurs on Norfolk Island and has been recorded from New Zealand since 1997. The presence of this species has also been detected in New Caledonia in 2012.

Miquelianin is a flavonol glucuronide, a type of phenolic compound present in wine, in species of St John's wort, like Hypericum hirsutum, in Nelumbo nucifera or in green beans.

Psidium rufum is commonly known as the purple guava. It is endemic to Brazil and bears an edible fruit. Psidium rufum var. widgrenianum is listed on the IUCN Red List vulnerable species (Plantae).

Psidium guineense is a species of guava.
Psidium amplexicaule, which is commonly known as mountain guava, is a species in the family Myrtaceae that is native to the Caribbean. It is rare in a moist limestone forest at 100–600 feet altitude on north coast of Puerto Rico. This plant can also be found on islands such as St. Thomas and St. John in the United States Virgin Islands and in Tortola and Virgin Gorda of the British Virgin Islands.

Psidium galapageium, the Galápagos guava or guayabillo, is a small tree or shrub found in tropical areas, formerly endemic to the Galápagos Islands.

















