 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
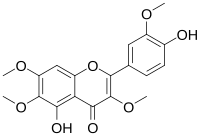
| IUPAC name 4′,5-Dihydroxy-3,3′,6,7-tetramethoxyflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 5-Hydroxy-4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3,6,7-trimethoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names Chrysosplenetin B 3,6,7,3'-Tetra-methylquercetagetin Quercetagetin 3,6,7,3'-tetramethyl ether | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H18O8 | |
| Molar mass | 374.345 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.448 g/mL |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Chrysosplenetin is an O-methylated flavonol. It can be found in the root of Berneuxia thibetica and in Chamomilla recutita . [1]