The Gurjara-Pratihara was a most powerful dynasty of Rajput clan that ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj.The people descent from this dynasty aslo describe themselves as Parihar or Padhiyar like Parihar Rajput of Mandor, Nagod State, Dewal Pratiharas of Bhinmal and Gwalior.
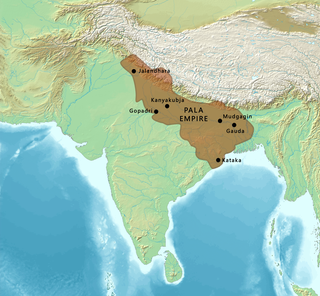
The Pāla Empire was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffix Pāla. The empire was founded with the election of Gopāla as the emperor of Gauda in late eighth century CE. The Pala stronghold was located in Bengal and eastern Bihar, which included the major cities of Gauḍa, Vikramapura, Pāṭaliputra, Monghyr, Somapura, Ramavati (Varendra), Tāmralipta and Jaggadala.

The Sena dynasty was a Hindu dynasty during the early medieval period on the Indian subcontinent, that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. The empire at its peak covered much of the north-eastern region of the Indian subcontinent. The rulers of the Sena Dynasty traced their origin to the south Indian region of Karnataka.

The Gahadavala dynasty also Gahadavalas of Kannauj was a Rajput dynasty that ruled parts of the present-day Indian states of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, during 11th and 12th centuries. Their capital was located at Banaras in the Gangetic plains, and for a brief period, they also controlled Kannauj.

Nalbari is a town in Nalbari district in the Indian state of Assam. Nalbari is also the headquarters of Nalbari District. Nalbari comes from two words "Nal & Bar"

The Kamboja-Pala dynasty ruled parts of Bengal in the 10th to 11th centuries CE, after invading the Palas during the reign of Gopala II. The last Kamboja ruler of the Kamboja-Pala Dynasty Dharmapala was defeated by the south Indian Emperor Rajendra Chola I of the Chola dynasty in the 11th century.
Devapala was the most powerful ruler of the Pala Empire of Bengal region in the Indian Subcontinent. He was the third king in the line, and had succeeded his father Dharamapala. Devapala expanded the frontiers of the empire by conquering the present-day Assam and Orissa. The Pala inscriptions also credit him with several other victories, but these claims are thought to be exaggerated.
Dharmapala was the second ruler of the Pala Empire of Bengal region in the Indian subcontinent. He was the son and successor of Gopala, the founder of the Pala Dynasty. Dharmapala was mentioned as the great king of Vangala in the Nesari plates of Rashtrakuta dynasty. He greatly expanded the boundaries of the empire, and made the Palas a dominant power in the northern and eastern India.

Deva Dynasty was a Bengali Hindu dynasty which originated in the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent; the dynasty ruled over eastern Bengal after the Sena dynasty. The capital of the dynasty was Bikrampur in present-day Munshiganj District of Bangladesh.

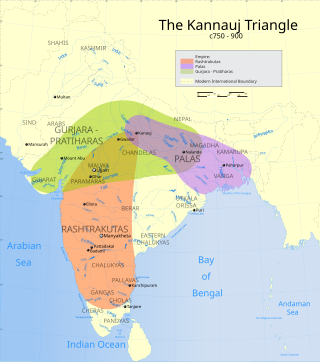
The Tripartite Struggle, also known as The Kannauj Triangle Wars, for control of northern India took place in the ninth century, among the Gurjara-Pratihara Empire, the Pala Empire and the Rashtrakuta Empire.
Baihata Chariali is a small town in Kamrup Rural district of Assam, India; situated at northern site of the river Brahmaputra. The place is called Chariali as it is a major road junction where National Highway 27 interconnect with National Highway 15.

Jaya Pala (1075-1100) was a ruler during the Pala Dynasty (900–1100) of Kamarupa Kingdom.

Dharma Pala (1035–1060) was ruler of Pala Dynasty (900–1100) of Kamarupa Kingdom.

Kamarupa – Late to end period was a period of Kamarupa kingdom from founding of Pala Dynasty by Brahma Pala to last ruler of dynasty Jaya Pala.
The Chalukyas of Lata were an Indian dynasty, which ruled the Lata region of present-day Gujarat during 10th and 11th centuries. They ruled as feudatories of the Western Chalukyas in their early years, and were ultimately defeated by the Chaulukyas of Gujarat (Solankis).
Durlabha-rāja I was an Indian ruler belonging to the Chahamana dynasty. He ruled parts of present-day Rajasthan in north-western India as a vassal of the Gurjara-Pratihara king Vatsaraja.

Govindachandra was an Indian king from the Gahadavala dynasty. He ruled the Antarvedi country in present-day Uttar Pradesh, including the major cities of Kanyakubja and Varanasi.
The Bhauma dynasty, also known as Kara dynasty, ruled in eastern India between 8th and 10th centuries. Their kingdom, called Toshala, included parts of present-day Odisha.

The Pahcimbhag copperplate inscription, Srichandra Paschimbhag copperplate inscription or simply Chandrapur inscription is a copperplate inscription issued in 935 by Srichandra, the second king of the Chandra Dynasty of south-east Bengal. The inscription was discovered in the village of Paschimbhag, Moulvibazar district. It is one of 12 known copperplate inscriptions by Chandra Dynasty kings. The inscription is mainly a deed of donation, in which Srichandra grants lands for many Brahmins and for nine monasteries in the Sylhet region, which formed Chandrapur University, named after Srichandra. It includes a detailed description of the Chandra kingdom and the Palas and Kamboja Pala rulers of Bengal and refers to the society of pre-medieval Bengal.

The Pīṭhīpatis of Bodh Gaya were the rulers of the area around Bodh Gaya from roughly the 11th to 13th centuries in the Magadha region of what is now Bihar in India. Pithi refers to the diamond throne where the Buddha was said to have gained enlightenment.