In Hindu culture, the term gotra is considered to be equivalent to lineage. It broadly refers to people who are descendants in an unbroken male line from a common male ancestor or patriline. Generally, the gotra forms an exogamous unit, with marriage within the same gotra being regarded as incest and prohibited by custom. The name of the gotra can be used as a surname, but it is different from a surname and is strictly maintained because of its importance in marriages among Hindus, especially among castes. Pāṇini defines gotra as apatyam pautraprabhrti gotram, which means "the word gotra denotes the descendance, apatya, of a couple consisting of a pautra, a son and a bharti, a mother, i.e. a daughter-in-law."

Kamarupa, an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was the first historical kingdom of Assam.

The Saptarshi are the seven seers of ancient India who are extolled in the Vedas, and other Hindu literature such as the "Skanda Purana". The Vedic Samhitas never enumerate these rishis by name, although later Vedic texts such as the Brahmanas and Upanisads do so.

The history of Assam is the history of a confluence of people from the east, west, south and the north; the confluence of the Austroasiatic, Tibeto-Burman (Sino-Tibetan), Tai and Indo-Aryan cultures. Although invaded over the centuries, it was never a vassal or a colony to an external power until the third Burmese invasion in 1821, and, subsequently, the British ingress into Assam in 1824 during the First Anglo-Burmese War.

The Varman dynasty (350–650) was the first historical dynasty of the Kamarupa kingdom. It was established by Pushyavarman, a contemporary of Samudragupta. The earlier Varmans were subordinates of the Gupta Empire, but as the power of the Guptas waned, Mahendravarman (470–494) performed two horse sacrifices and the status of Kamarupa as an independent state remained unimpaired. As per the Apsad Inscription of Adityasen, Susthivarman was defeated by Mahasengupta on the bank of Lauhitya. The first of the three Kamarupa dynasties, the Varmans were followed by the Mlechchha and then the Pala dynasties.

North Guwahati is a Northern part of Guwahati city. And serves headquarters of Kamrup rural district in the Indian state of Assam. This place abounds in historical places and picnic spots. The place is famous for Doul Govinda Temple. North Guwahati Ancient name is Durjaya.

Habung is a historical region in present-day Lakhimpur district of Assam, India, although Tai-ahom claim it to be a part of present-day Dhemaji district. As per epigrahic records, Habung (Ha-vrnga-Vishaya) was a vishaya or province where Brahmins were settled by Ratna Pala of the Pala dynasty of Kamarupa in the 10th century.
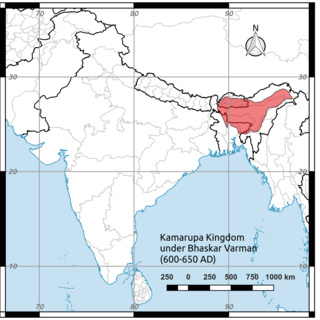
Bhaskaravarman was king of medieval Kamarupa and the last of the Varman dynasty. After being captured by the Gauda king during the reign of his father, he was able to re-establish the rule of the Varmans. He made political alliances with Harshavardhana of Thaneswar, against the alliance of the Gauda and East Malwa. He was visited by Xuanzang and Wang Xuance, the envoys of the Tang dynasty who have left accounts of the king and the kingdom.
In Hindu culture, a Pravara refers to a system of identity, particularly a family line. The Pravar system is based on the descendants of a rishi (sage) after whom a "gotra" (clan) is named, and these descendants are considered eponyms by the members of the "gotra." It represents a secondary level of segmentation within the gotra system. The Pravara is a significant aspect of the exogamous system in ancient Brahmanical families.

Kalita is an ethnic group or a caste of Assamese Hindus belonging to the state of Assam in North East India. Kalita is a forward caste and belongs to General or Unreserved category. Kalita represents a category in the tribe-caste continuum of Assamese society that is placed between the Keot on one side and Ganak and Brahmin on the other. According to historians like S.L.Barua, Kalitas started migrating from North and East India to Assam during the 11th century rule of Dharmapal.
The Chamak copper plates are an epigraphic record of the Vākāṭaka dynasty, documenting a land donation to brāhmaṇas in the reign of king Pravarasena II in the fifth century CE. They were found at Chamak, in District Amravati, Maharashtra, India.

The earliest Indo-Aryan migration to Assam is estimated to have occurred between the 2nd century BCE and 1st century CE—not earlier than 500 BCE. The earliest epigraphic record suggests that the Indo-Aryan migration began latest by the middle of the 4th century CE. They came from the Gangetic Plains into a region already inhabited by people who spoke Austroasiatic and Tibeto-Burman languages.

Dharma Pala (1035–1060) was ruler of Pala Dynasty (900–1100) of Kamarupa Kingdom.

Kamarupa was a kingdom in Northeast India that was ruled by three dynasties from their capitals in Pragjyotishpura, Haruppeshwara, and Durjaya. The kingdom was known for its power and influence in the region.

Kamrupi dialects are a group of regional dialects of Assamese, spoken in the Kamrup region. It formerly enjoyed prestige status. It is one of two western dialect groups of the Assamese language, the other being Goalpariya. Kamrupi is heterogeneous with three subdialects— Barpetia dialect, Nalbariya dialect and Palasbaria dialect.

The Nidhanpur copperplate inscription of the 7th-century Kamarupa king Bhaskaravarman gives a detailed account of land grants given to Brahmins. It records land grants to more than two hundred vaidika brahmanas belonging to 56 gotras. The copper plates were found mostly in Panchakhanda pargana where, according to historians, the actual granted lands were located. This Sanskrit inscription contains the names of donees which are more than two hundred in numbers.

Kamarupi script was the script used in ancient Kamarupa from as early as 5th century to 13th century, from which the modern Assamese script eventually evolved. In the development of the Assamese script, this phase was followed by the medieval and then by the modern Assamese scripts.

Davaka was a kingdom of ancient Indian subcontinent, located in current central region of Assam state. The references to it comes from the 4th century Allahabad pillar inscription of Samudragupta, where it is mentioned as one of five frontier kingdoms of the Gupta Empire.

A Hindu Gotra is an exogamous unit used to denote the paternal lineage of individuals belonging to the Brahmin in the Hindu Varna system. In Hindu culture, the Brahmin considered to be one of the four major social classes of the Varna system. In Sanskrit, one of the meanings of the word Gotra is “a descendant through an unbroken patriline”. According to Hindu scripture, members of the Hindu community are believed to have descended from the first seven Sanatan saints of the Vedic period. A Gotra represents the lineage of an individual saint and a Brahmin’s Gotra denotes which of these saints is their ancestor.

Assamese Brahmins are the Brahmins present in the Assamese society. There they promoted learning, Vedic religion, astrology, ayurveda and as well as imparting general vedic knowledge to the public. The Brahmins migrated to Assam from Videha (Mithila), Kannauj, Bengal and many other places.














