Yoga is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines that originated in ancient India, aimed at controlling body and mind to attain various salvation goals, as practiced in the Hindu, Jain, and Buddhist traditions.
Maya, literally "illusion" or "magic", has multiple meanings in Indian philosophies depending on the context. In later Vedic texts, māyā connotes a "magic show, an illusion where things appear to be present but are not what they seem"; the principle which shows "attributeless Absolute" as having "attributes". Māyā also connotes that which "is constantly changing and thus is spiritually unreal", and therefore "conceals the true character of spiritual reality".
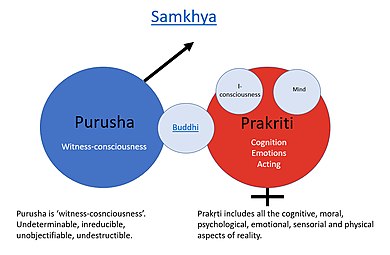
Purusha is a complex concept whose meaning evolved in Vedic and Upanishadic times. Depending on source and historical timeline, it means the cosmic being or self, awareness, and universal principle.
Hindu philosophy or Vedic philosophy is the set of philosophical systems that developed in tandem with the first Hindu religious traditions during the iron and classical ages of India. In Indian philosophy, of which Hindu philosophy is a prominent subset, the word used for philosophy is Darshana, from the Sanskrit root 'दृश' meaning 'to see, to experience'.

The Yoga Sutras of Patañjali is a compilation "from a variety of sources" of Sanskrit sutras (aphorisms) on the practice of yoga – 195 sutras and 196 sutras. The Yoga Sutras were compiled in India in the early centuries CE by the sage Patanjali, who collected and organized knowledge about yoga from Samkhya, Buddhism, and older Yoga traditions, and possibly another compiler who may have added the fourth chapter. He may also be the author of the Yogabhashya, a commentary on the Yoga Sutras, traditionally attributed to the legendary Vedic sage Vyasa, but possibly forming a joint work of Patanjali called the Pātañjalayogaśāstra.
In Sanskrit texts, Rāja yoga was both the goal of yoga and a method to attain it. The term also became a modern name for the practice of yoga in the 19th-century when Swami Vivekananda gave his interpretation of the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali in his book Raja Yoga. Since then, Rāja yoga has variously been called aṣṭāṅga yoga, royal yoga, royal union, sahaja marg, and classical yoga.
Prakriti is "the original or natural form or condition of anything, original or primary substance". It is a key concept in Hinduism, formulated by its Sāṅkhya school, where it does not refer to matter or nature, but "includes all the cognitive, moral, psychological, emotional, sensorial and physical aspects of reality", stressing "Prakṛti's cognitive, mental, psychological and sensorial activities". Prakriti has three different innate qualities (guṇas), whose equilibrium is the basis of all observed empirical reality as the five panchamahabhootas namely Akasha, Vayu, Agni, Jala, Pruthvi. Prakriti, in this school, contrasts with Puruṣa, which is pure awareness and metaphysical consciousness. The term is also found in the texts of other Indian religions such as Jainism and Buddhism.

Ishvara is a concept in Hinduism, with a wide range of meanings that depend on the era and the school of Hinduism. In ancient texts of Hindu philosophy, depending on the context, Ishvara can mean supreme Self, ruler, lord, king, queen or husband. In medieval era Hindu texts, depending on the school of Hinduism, Ishvara means God, Supreme Being, personal God, or special Self. In Shaivism, Ishvara is an epithet of Shiva. In Vaishnavism it is synonymous with Vishnu, like in his epithet of Venkateswara. In traditional Bhakti movements, Ishvara is one or more deities of an individual's preference (Iṣṭa-devatā) from Hinduism's polytheistic canon of deities. In modern-day sectarian movements such as Arya Samaj and Brahmoism, Ishvara takes the form of a monotheistic God. In the Yoga school of Hinduism, it is any "personal deity" or "spiritual inspiration". In Advaita Vedanta, Ishvara is the manifested form of Brahman.
Hindu cosmology is the description of the universe and its states of matter, cycles within time, physical structure, and effects on living entities according to Hindu texts. Hindu cosmology is also intertwined with the idea of a creator who allows the world to exist and take shape.

The Shvetashvatara Upanishad is an ancient Sanskrit text embedded in the Yajurveda. It is listed as number 14 in the Muktika canon of 108 Upanishads. The Upanishad contains 113 mantras or verses in six chapters.
The Samkhyakarika is the earliest surviving text of the Samkhya school of Indian philosophy. The text's original composition date is unknown, but its terminus ad quem date has been established through its Chinese translation that became available by 569 CE. It is attributed to Ishvara Krishna.
The Samkhya Pravachana Sutra is a collection of major Sanskrit texts of the Samkhya school of Hindu philosophy. It includes the ancient Samkhya Sutra of Kapila, Samkhya karika of Ishvarakrishna, Samkhya Sutra Vritti of Aniruddha, the Bhasya (commentary) of Vijnana Bhikshu, the Vrittisara of Vedantin Mahadeva, Tattva Samasa and commentary of Narendra, and works of Gaudapada, Vachaspati Mishra, and Panchashikha.

The Nadabindu Upanishad is an ancient Sanskrit text and one of the minor Upanishads of Hinduism. It is one of twenty Yoga Upanishads in the four Vedas. It also known as Amrita Nada Bindu Upanishad.(Sanskrit: अमृतनादबिन्दु उपनिषद)
In Samkhya, pradhāna is the "primal matter," "the first principle from which all material things have evolved. It is an alternate term for prakriti in a state of equilibrium of the three gunas – sattva, rajas and tamas, the three modes of prakrti. When purusha comes in contact with prakriti, the balance is distorted, and the 23 principles evolves from prakriti.
The Samkhya school of philosophy, which follows Prakṛti Parinama-vada, describes the origination and evolution of universe through its theory of Satkāryavāda which is the theory of causation. According to this theory, the manifested effect is pre-existent in the cause; and the original material cause of everything that is perceived is Prakriti. When Prakriti is not in proximity with immutable Purusha, the conscious ability (chiti-shakti), the three modes of prakriti are in equipoise and prakriti is an unmanifest potential. When the conscious ability and the objective ability interact the three modes of the objective nature become disturbed and enter a state of flux giving rise to diverse manifest appearance.

The Avyakta Upanishad is a Sanskrit text and a minor Upanishad of Hinduism. It is one of 16 Upanishads attached to the Samaveda, and classified under the 17 Vaishnava Upanishad.
Yoga philosophy is one of the six major important schools of Hindu philosophy, though it is only at the end of the first millennium CE that Yoga is mentioned as a separate school of thought in Indian texts, distinct from Samkhya. Ancient, medieval and most modern literature often refers to Yoga-philosophy simply as Yoga. A systematic collection of ideas of Yoga is found in the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali, a key text of Yoga which has influenced all other schools of Indian philosophy.

The Sariraka Upanishad is one of the minor Upanishads and is listed at 62 in the modern era anthology of 108 Upanishads. Composed in Sanskrit, it is one of the 32 Upanishads that belongs to the Krishna Yajurveda, and is classified as one of the Samanya (general), and is one of several dedicated mystical physiology Upanishads.

The Devi Upanishad, is one of the minor Upanishads of Hinduism and a text composed in Sanskrit. It is one of the 19 Upanishads attached to the Atharvaveda, and is classified as one of the eight Shakta Upanishads. It is, as an Upanishad, a part of the corpus of Vedanta literature collection that present the philosophical concepts of Hinduism.

The Mantrika Upanishad is a minor Upanishad of Hinduism. The Sanskrit text is one of the 22 Samanya Upanishads, is part of the Vedanta and Yoga schools of Hindu philosophy literature, and is one of 19 Upanishads attached to the Shukla Yajurveda. In the Muktika canon, narrated by Rama to Hanuman, it is listed at number 32 in the anthology of 108 Upanishads.