The dinoflagellates, also called dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey.

Karlodinium is a genus of athecate dinoflagellates that lives worldwide. They are often toxin producing, and compared to the other members of the Kareniaceae, are fairly small at <8-15 μm diameter. They are also able to form intense algal blooms. This species relies of photosynthesis and phagotrphy to grow.

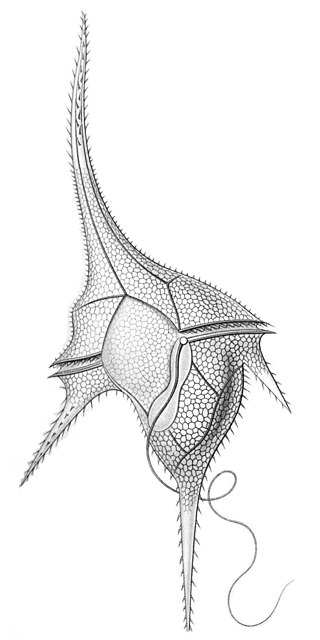
Ornithocercus is a genus of planktonic dinoflagellate that is known for its complex morphology that features considerable lists growing from its thecal plates, giving an attractive appearance. Discovered in 1883, this genus has a small number of species currently categorized but is widespread in tropical and sub-tropical oceans. The genus is marked by exosymbiotic bacteria gardens under its lists, the inter-organismal dynamics of which are a current field of research. As they reside only in warm water, the genus has been used as a proxy for climate change and has potential to be an indicator species for environmental change if found in novel environments.
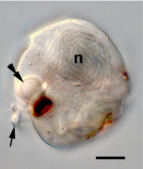
Polykrikos kofoidii is a species of phagotrophic marine pseudocolonial dinoflagellates that can capture and engulf other protist prey, including the toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium tamarense. P. kofoidii is of scientific interest due to its status as a predator of other dinoflagellates, a behavior that is significant in the control of algal blooms. It has a complex life cycle of both vegetative (asexual) and sexual reproduction complicated by its pseudocolonial structure.

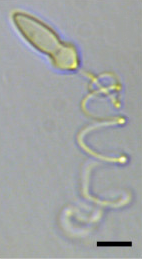
Cochlodinium polykrikoides is a species of red tide producing marine dinoflagellates known for causing fish kills around the world, and well known for fish kills in marine waters of Southeast Asia. C. polykrikoides has a wide geographic range, including North America, Central America, Western India, Southwestern Europe and Eastern Asia. Single cells of this species are ovoidal in shape, 30-50μm in length and 25-30μm in width.

An ocelloid is a subcellular structure found in the family Warnowiaceae (warnowiids), which are members of a group of unicellular organisms known as dinoflagellates. The ocelloid is analogous in structure and function to the eyes of multicellular organisms, which focus, process and detect light. The ocelloid is much more complex than the eyespot, a light-sensitive structure also found in unicellular organisms, and is in fact one of the most complex known subcellular structures. It has been described as a striking example of convergent evolution.

The Warnowiaceae are a family of athecate dinoflagellates. Members of the family are known as warnowiids. The family is best known for a light-sensitive subcellular structure known as the ocelloid, a highly complex arrangement of organelles with a structure directly analogous to the eyes of multicellular organisms. The ocelloid has been shown to be composed of multiple types of endosymbionts, namely mitochondria and at least one type of plastid.
Takayama tuberculata is a species of unarmored dinoflagellates from the genus Takayama, being closely related to T. tasmanica. It was first isolated from the Australian region of the Southern Ocean, just north of the polar front. It is medium-sized and is characterized by its long ovoid cell shape and rather long apical groove. It is considered potentially ichthyotoxic.
Karlodinium antarcticum is a species of unarmored dinoflagellates from the genus Karlodinium. It was first isolated from the Australian region of the Southern Ocean, near the polar front. It is medium-sized and is characterized by its long ovoid cell shape and rather long apical groove. It is considered potentially ichthyotoxic.
Karlodinium ballantinum is a species of unarmored dinoflagellates from the genus Karlodinium. It was first isolated from the Australian region of the Southern Ocean. It is small-sized and is characterized by its very short apical groove. It is considered potentially ichthyotoxic.
Karlodinium corrugatum is a species of unarmored dinoflagellates from the genus Karlodinium. It was first isolated from the Australian region of the Southern Ocean, just south of the polar front. It is small-sized and is characterized by having distinctive striations on the epicone surface which are parallel, and a distinctively shaped and placed ventral pore. It is considered potentially ichthyotoxic.

A piston is a complex contractile organelle found in some dinoflagellates, namely the Erythropsidinium and Greuetodinium genera of the family Warnowiaceae. This group is also well known for possessing other unusually complex subcellular structures such as the ocelloid and nematocyst. Observations of Erythropsidinium samples reveal that the length of the piston is highly variable across specimens. The piston is known to be capable of repetitive and dramatic contractile motion; although its function is unknown, roles in locomotion, prey capture, and defense have been suggested.

The Polykrikaceae are a family of athecate dinoflagellates of the order Gymnodiniales. Members of the family are known as polykrikoids. The family contains two genera: Polykrikos and Pheopolykrikos.

Erythropsidinium is a genus of dinoflagellates of the family Warnowiaceae.

Polykrikos is one of the genera of family Polykrikaceae that includes athecate pseudocolony-forming dinoflagellates. Polykrikos are characterized by a sophisticated ballistic apparatus, named the nematocyst-taeniocyst complex, which allows species to prey on a variety of organisms. Polykrikos have been found to regulate algal blooms as they feed on toxic dinoflagellates. However, there is also some data available on Polykrikos being toxic to fish.
Torodinium (ˌtɔɹoʊˈdɪniəm) is a genus of unarmored dinoflagellates and comprises two species, Torodinium robustum and the type species Torodinium teredo. The establishment of Torodinium, as well as the characterization of the majority of its morphology, occurred in 1921 and further advances since have been slow. Lack of research is largely due to its extremely fragile and easily deformed nature, which also renders fossil records implausible. The genus was originally characterized by torsion of the sulcus and a posterior cingulum. Since then, new distinctive features have been discovered including an extremely reduced hyposome, a longitudinally ribbed episome, and a canal on the dextro-lateral side. Further investigation into the function of many anatomical features is still necessary for this genus.

Cochlodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates belonging to the family Gymnodiniaceae. Over the past two decades, harmful algea blooms (HABs) caused by Cochlodinium had occurred more often and expanded from Southeast Asia to regions such as the rest of Asia, North America and Europe.
Lepidodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates belonging to the family Gymnodiniaceae. Lepidodinium is a genus of green dinoflagellates in the family Gymnodiniales. It contains two different species, Lepidodiniumchlorophorum and Lepidodinium viride. They are characterised by their green colour caused by a plastid derived from Pedinophyceae, a green algae group. This plastid has retained chlorophyll a and b, which is significant because it differs from the chlorophyll a and c usually observed in dinoflagellate peridinin plastids. They are the only known dinoflagellate genus to possess plastids derived from green algae. Lepidodinium chlorophorum is known to cause sea blooms, partially off the coast of France, which has dramatic ecological and economic consequences. Lepidodinium produces some of the highest volumes of transparent exopolymer particles of any phytoplankton, which can contribute to bivalve death and the creation of anoxic conditions in blooms, as well as playing an important role in carbon cycling in the ocean.
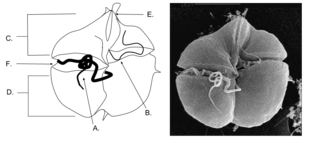
Kareniaceae is an accepted marine family of relatively small, toxic, unarmored dinoflagellates belonging to the order Gymnodiniales. Species in the Kareniaceae clade often cause harmful discolored green algea blooms (HABs) that pose a safety and health risk to humans and the surrounding regions. Such blooms also pose a risk to coastal aquaculture worldwide, especially in places like France, the Atlantic Ocean, the English Channel and the Mediterranean Sea.
Warnowia is a genus of athecate dinoflagellates, characterized by having a very sophisticated photoreceptor organelle called the ocelloid. This genus is dispersed worldwide but is scarce and difficult to find and nearly impossible to culture. As a result, the history and taxonomy of this genus are confusing at best, and many basic characteristics like its life cycle are still unknown. Still, Warnowia has drawn scientific interest as a unicellular organism with a fascinatingly complex photoreceptor system.