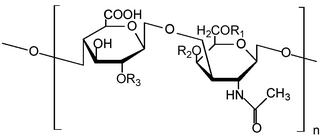
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units. The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers.
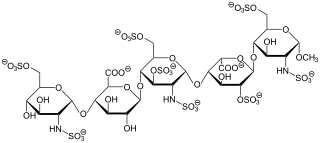
Fondaparinux is an anticoagulant medication chemically related to low molecular weight heparins. It is marketed by Viatris. A generic version developed by Alchemia is marketed within the US by Dr. Reddy's Laboratories.

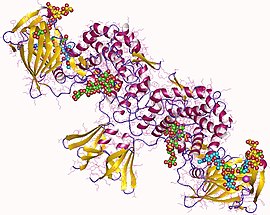
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. In this form, HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB, and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2.
In enzymology, a chondroitin-glucuronate 5-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-glucuronate 5'-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme heparin lyase catalyzes the following process:
In enzymology, a glucuronate-2-sulfatase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction of cleaving off the 2-sulfate groups of the 2-O-sulfo-D-glucuronate residues of chondroitin sulfate, heparin and heparitin sulfate.
In enzymology, a 3-galactosyl-N-acetylglucosaminide 4-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-galactosyl-N-acetylglucosaminide 3-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a galactosylgalactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycoprotein 6-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.68) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-glucuronosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyllactosaminide alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a neolactotetraosylceramide alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NDST3 gene. It catalyses the reaction:
3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate + α-D-glucosaminyl-[heparan sulfate](n) = adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate + 2 H+ + N-sulfo-α-D-glucosaminyl-[heparan sulfate](n)
Glucuronyl-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-xylosyl-proteoglycan 4IV-alpha-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronosyl-N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Rhamnopyranosyl-N-acetylglucosaminyl-diphospho-decaprenol beta-1,3/1,4-galactofuranosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-alpha-D-galactofuranose:alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-diphospho-trans,octacis-decaprenol 3-beta/4-beta-galactofuranosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction