
A windpump is a type of windmill which is used for pumping water.

The Darrieus wind turbine is a type of vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) used to generate electricity from wind energy. The turbine consists of a number of curved aerofoil blades mounted on a rotating shaft or framework. The curvature of the blades allows the blade to be stressed only in tension at high rotating speeds. There are several closely related wind turbines that use straight blades. This design of the turbine was patented by Georges Jean Marie Darrieus, a French aeronautical engineer; filing for the patent was October 1, 1926. There are major difficulties in protecting the Darrieus turbine from extreme wind conditions and in making it self-starting.

Savonius wind turbines are a type of vertical-axis wind turbine (VAWT), used for converting the force of the wind into torque on a rotating shaft. The turbine consists of a number of aerofoils, usually—but not always—vertically mounted on a rotating shaft or framework, either ground stationed or tethered in airborne systems.
Small wind turbines, also known as micro wind turbines, are used for microgeneration of electricity, as opposed to large commercial wind turbines, such as those found in wind farms. Small wind turbines often have passive yaw systems as opposed to active ones. They use a direct drive generator and use a tail fin to point into the wind, whereas larger turbines have geared powertrains that are actively pointed into the wind.
Marine currents can carry large amounts of water, largely driven by the tides, which are a consequence of the gravitational effects of the planetary motion of the Earth, the Moon and the Sun. Augmented flow velocities can be found where the underwater topography in straits between islands and the mainland or in shallows around headlands plays a major role in enhancing the flow velocities, resulting in appreciable kinetic energy. The sun acts as the primary driving force, causing winds and temperature differences. Because there are only small fluctuations in current speed and stream location with minimal changes in direction, ocean currents may be suitable locations for deploying energy extraction devices such as turbines. Other effects such as regional differences in temperature and salinity and the Coriolis effect due to the rotation of the earth are also major influences. The kinetic energy of marine currents can be converted in much the same way that a wind turbine extracts energy from the wind, using various types of open-flow rotors.

The Gorlov helical turbine (GHT) is a water turbine evolved from the Darrieus turbine design by altering it to have helical blades/foils. It was patented in a series of patents from September 19, 1995 to July 3, 2001 and won 2001 ASME Thomas A. Edison. GHT was invented by Alexander M. Gorlov, professor of Northeastern University.

Unconventional wind turbines are those that differ significantly from the most common types in use.

The Windstar vertical-axis turbine is a lift-type device with straight blades attached at each end to a central rotating shaft. Windstar turbines were invented by Robert Nason Thomas and developed by Wind Harvest International, Inc., formerly the Wind Harvest Company, based in Point Reyes, California. Windstar turbines are operated as Linear Array Vortex Turbine Systems (LAVTS). Each rotor unit has a dual braking system of pneumatic disc brakes and blade pitch. All Windstar models use off-the-shelf generators, gearboxes, bearings and other components.

The Quietrevolution was a brand of vertical-axis wind turbine before going into administration in 2014.
The RES Group is a global renewable energy company which has been active in the renewable energy industry for over 30 years. Its core business is to develop, construct and operate large-scale, grid-connected renewable energy projects worldwide for commercial, industrial and utility clients. RES is active in the wind and solar energy sectors and is increasingly focused on the transition to a low-carbon economy providing transmission, energy storage and demand side management expertise.

A wind turbine is a device that converts the wind's kinetic energy into electrical energy.
A windmill ship, wind energy conversion system ship or wind energy harvester ship propels itself by use of a wind turbine to drive a propeller.
IEC 61400 is an International Standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission regarding wind turbines.
QBlade is an open-source, cross-platform simulation software for wind turbine blade design and aerodynamic simulation. It comes with a user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI) based on Qt.
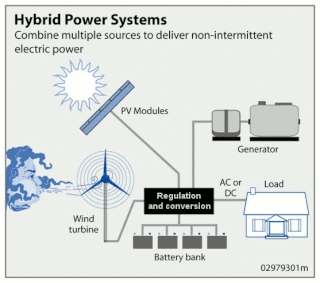
Wind hybrid power systems combines wind turbines with other storage and/or generation sources. One of the key issues with wind energy is its intermittent nature. This has led to numerous methods of storing energy.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to wind energy:

Renewable energy in Taiwan contributed to 8.7% of national electricity generation as of end of 2013. The total installed capacity of renewable energy in Taiwan by the end of 2013 was 3.76 GW. As of 2020, the Taiwan government aims for a renewable share of 20% by 2025, with coal and gas providing the other 80%.

A cyclorotor, cycloidal rotor, cycloidal propeller or cyclogiro, is a fluid propulsion device that converts shaft power into the acceleration of a fluid using a rotating axis perpendicular to the direction of fluid motion. It uses several blades with a spanwise axis parallel to the axis of rotation and perpendicular to the direction of fluid motion. These blades are cyclically pitched twice per revolution to produce force in any direction normal to the axis of rotation. Cyclorotors are used for propulsion, lift, and control on air and water vehicles. An aircraft using cyclorotors as the primary source of lift, propulsion, and control is known as a cyclogyro or cyclocopter. The patented application, used on ships with particular actuation mechanisms both mechanical or hydraulic, are named after the name of the German company Voith Turbo that produces them: Voith Schneider Propellers.

A vertical-axis wind turbine (VAWT) is a type of wind turbine where the main rotor shaft is set transverse to the wind while the main components are located at the base of the turbine. This arrangement allows the generator and gearbox to be located close to the ground, facilitating service and repair. VAWTs do not need to be pointed into the wind, which removes the need for wind-sensing and orientation mechanisms. Major drawbacks for the early designs included the significant torque variation or "ripple" during each revolution, and the large bending moments on the blades. Later designs addressed the torque ripple issue by sweeping the blades helically. Savonius vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWT) are not widespread, but their simplicity and better performance in disturbed flow-fields, compared to small horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWT) make them a good alternative for distributed generation devices in urban environment.














