Related Research Articles

Gila Bend, founded in 1872, is a town in Maricopa County, Arizona, United States. The town is named for an approximately 90-degree bend in the Gila River, which is near the community's current location. As of the 2020 census, the population of the town was 1,892.

Sacaton is a census-designated place (CDP) in Pinal County, Arizona, United States. The population was 3,254 at the 2020 census. It is the capital of the Gila River Indian Community.

The Akimel O'odham, also called the Pima, are a group of Native Americans living in an area consisting of what is now central and southern Arizona, as well as northwestern Mexico in the states of Sonora and Chihuahua. The majority population of the two current bands of the Akimel O'odham in the United States are based in two reservations: the Keli Akimel Oʼodham on the Gila River Indian Community (GRIC) and the On'k Akimel O'odham on the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community (SRPMIC).

The Maricopa or Piipaash are a Native American tribe, who live in the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community and Gila River Indian Community along with the Pima, a tribe with whom the Maricopa have long held a positive relationship. The Maricopa at the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community consist mostly of Xalychidom Piipaash members and are concentrated in Lehi. The Maricopa at the Gila River Indian Community are concentrated in Maricopa Colony. The Maricopa are a River Yuman group, formerly living along the banks of the Colorado River.

Gila River Indian Reservation was a reservation established in 1859 by the United States government in New Mexico Territory, to set aside the lands of the Akimel O’odham (Pima) and the Piipaash (Maricopa) people along the Gila River, in what is now Pinal County, Arizona. The self-government of the reservation as the Gila River Indian Community was established by Congress in 1939.
The Halchidhoma or Alchedoma are a Native American tribe now living mostly on the Salt River reservation, but formerly native to the area along the lower Colorado River in California and Arizona when first contacted by Europeans. In the early nineteenth century, under pressure from their hostile Mohave and Quechan neighbors, they moved to the middle Gila River, where some merged with the Maricopa, and others went on to Salt River and maintained an independent identity.
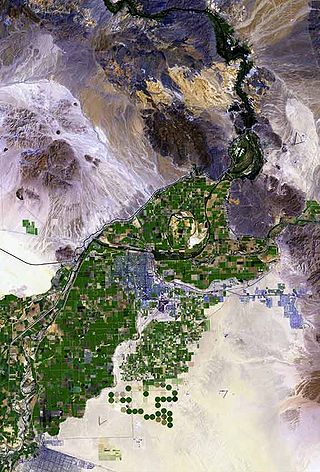
The Gila River Valley is a multi-sectioned valley of the Gila River, located primarily in Arizona. The Gila River forms in western New Mexico and flows west across southeastern, south-central, and southwestern Arizona; it changes directions as it progresses across the state, and defines specific areas and valleys. The central portion of the river flows through the southern Phoenix valley region, and the final sections in southwestern Arizona form smaller, irrigated valleys, such as Dome Valley, Mohawk Valley, and Hyder Valley.
Fort Barrett was a temporary earthwork built by the United States Army's California Column in 1862 during the American Civil War. It was located in the Pima Villages two miles from the Gila River nearby Casa Blanca, New Mexico Territory and was built around the mill of settler Ammi M. White to protect it and provide a safe location to gather food and forage from the Pima people for the advance on Tucson. The fort was named after Lieutenant James Barrett who was killed in the Battle of Picacho Peak. Following the capture of Tucson in May the construction of the post ceased, and was abandoned, except as a post for vedettes and express riders.

Casa Blanca is a census-designated place (CDP) in Pinal County, Arizona, United States, located in the Gila River Indian Community. The population was 1,388 at the 2010 census.

Pima Villages, sometimes mistakenly called the Pimos Villages in the 19th century, were the Akimel O’odham (Pima) and Pee-Posh (Maricopa) villages in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona. First, recorded by Spanish explorers in the late 17th century as living on the south side of the Gila River, they were included in the Viceroyalty of New Spain, then in Provincias of Sonora, Ostimuri y Sinaloa or New Navarre to 1823. Then from 1824 to 1830, they were part of the Estado de Occidente of Mexico and from September 1830 they were part of the state of Sonora. These were the Pima villages encountered by American fur trappers, traders, soldiers and travelers along the middle Gila River from 1830s into the later 19th century. The Mexican Cession following the Mexican American War left them part of Mexico. The 1853 Gadsden Purchase made their lands part of the United States, Territory of New Mexico. During the American Civil War, they became part of the Territory of Arizona.
Sacaton or Socatoon was a village of the Maricopa people, established above the Pima Villages, after the June 1, 1857, in the Battle of Pima Butte where it appears a few months later in the 1857 Chapman Census. Sacaton village lay on the Gila River, 3.75 miles west of modern Sacaton.

Socatoon Station was a stagecoach station of the Butterfield Overland Mail between 1858 and 1861. It was located four miles (6.4 km) east of Sacaton at a Maricopa village from which it took its name. This station was located 22 miles (35 km) east of Maricopa Wells Station, 11 miles (18 km) east of Casa Blanca Station and 13 miles (21 km) north of Oneida Station.
Arenal, "sandy place" in Spanish, also known as Aranca No.1 in the 1857 census, was one of the 19th century Pima Villages, located along the Gila River, in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona.
Hormiguerito, or Ormejera No. 2 in an 1858 census,, one of the smaller 19th century Pima Villages, located along the Gila River, in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona. Hormiguero, Spanish for "ant hill", with the diminutive "-ito", meant Little Anthill. It was among the smallest of the Pima settlements along the Gila.
El Llano, Spanish for "the plain or open space" or Buen Llano, "good plain", one of the 19th century Pima Villages, was located along the south side of the Gila River, between Sweetwater and Sacaton, in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona.
Hueso Parado, Spanish for “Standing Bone” or El Juez Tarado Spanish for "The Judge Tarado", was the largest village of the Maricopa people in the 19th century, in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona.
Agua Raiz, Spanish for "Water root" as named in the 1860 Census, it was one of the 19th century Pima Villages, located along the Gila River, near the modern site of Sacate Village, Arizona in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona.
Nugents Pass or Nugent's Pass is a gap at an elevation of 4,593 feet (1,400 m) in Cochise County, Arizona. The pass was named for John Nugent, who provided notes of his journey with a party of Forty-Niners across what became the Tucson Cutoff to Lt. John G. Parke, on expedition to identify a feasible railroad route from the Pima Villages to the Rio Grande.

Sacate is a populated place in the Middle Gila River Valley area, within Pinal County, Arizona, United States. Located 8 mi (13 km) north of Maricopa on the south side of the Gila River near Pima Butte, Sacate was an Pima village, a railroad station of the Southern Pacific Railroad, and a Catholic mission. It had originally been called Sacaton Station but the name was shortened to its current version in 1904.
Cachanillo was one of the 19th century Pima Villages, located along the Gila River, in what is now the Gila River Indian Community in Pinal County, Arizona.
References
- ↑ John P. Wilson, Peoples of the Middle Gila: A Documentary History of the Pimas and Maricopas, 1500s – 1945, Researched and Written for the Gila River Indian Community, Sacaton, Arizona, 1998 (revised July 1999) Report No. 77, Las Cruces, New Mexico, pp. 73, 140 Archived 2011-07-11 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Wilson, People of the Middle Gila, pp. 71–73.
- ↑ Wilson, People of the Middle Gila, p. 166
