
Ensifer meliloti are an aerobic, Gram-negative, and diazotrophic species of bacteria. S. meliloti are motile and possess a cluster of peritrichous flagella. S. meliloti fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia for their legume symbionts, such as alfalfa. S. meliloti forms a symbiotic relationship with legumes from the genera Medicago, Melilotus and Trigonella, including the model legume Medicago truncatula. This symbiosis promotes the development of a plant organ, termed a root nodule. Because soil often contains a limited amount of nitrogen for plant use, the symbiotic relationship between S. meliloti and their legume hosts has agricultural applications. These techniques reduce the need for inorganic nitrogenous fertilizers.
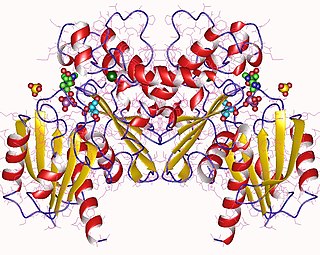
Fructokinase, also known as D-fructokinase or D-fructose (D-mannose) kinase, is an enzyme of the liver, intestine, and kidney cortex. Fructokinase is in a family of enzymes called transferases, meaning that this enzyme transfers functional groups; it is also considered a phosphotransferase since it specifically transfers a phosphate group. Fructokinase specifically catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from adenosine triphosphate to fructose as the initial step in its utilization. The main role of fructokinase is in carbohydrate metabolism, more specifically, sucrose and fructose metabolism. The reaction equation is as follows:

suhB, also known as mmgR, is a non-coding RNA found multiple times in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens genome and related alpha-proteobacteria. Other non-coding RNAs uncovered in the same analysis include speF, ybhL, metA, and serC.
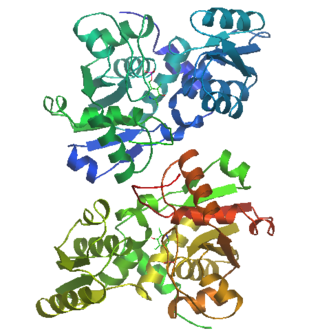
Serine racemase is the first racemase enzyme in human biology to be identified. This enzyme converts L-serine to its enantiomer form, D-serine. D-serine acts as a neuronal signaling molecule by activating NMDA receptors in the brain.

Ensifer is a genus of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (rhizobia), three of which have been sequenced.
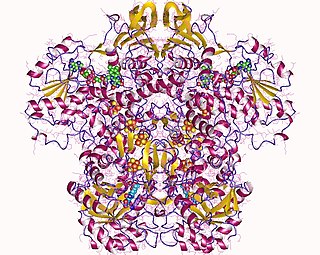
In enzymology, a dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.3.1.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

α-Methylacyl-CoA racemase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AMACR gene. AMACR catalyzes the following chemical reaction:

In enzymology, a maleate isomerase, or maleate cis-tran isomerase, is a member of the Asp/Glu racemase superfamily discovered in bacteria. It is responsible for catalyzing cis-trans isomerization of the C2-C3 double bond in maleate to produce fumarate, which is a critical intermediate in citric acid cycle. The presence of an exogenous mercaptan is required for catalysis to happen.

In enzymology, a dihydropyrimidinase (EC 3.5.2.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-amino-acid transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 E3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2E3 gene.

Carboxypeptidase A2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CPA2 gene.

Medicarpin is a pterocarpan, a derivative of isoflavonoids.

Within genetics, post-genomic research has rendered bacterial small non-coding RNAs (sRNAs) as major players in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in response to environmental stimuli. The Alphaproteobacteria includes Gram-negative microorganisms with diverse life styles; frequently involving long-term interactions with higher eukaryotes.
αr7 is a family of bacterial small non-coding RNAs with representatives in a broad group of Alphaproteobacterial species from the order Hyphomicrobiales. The first member of this family was found in a Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 locus located in the chromosome (C). Further homology and structure conservation analysis identified full-length homologs in several nitrogen-fixing symbiotic rhizobia, in the plant pathogens belonging to Agrobacterium species as well as in a broad spectrum of Brucella species. αr7 RNA species are 134-159 nucleotides (nt) long and share a well defined common secondary structure. αr7 transcripts can be catalogued as trans-acting sRNAs expressed from well-defined promoter regions of independent transcription units within intergenic regions (IGRs) of the Alphaproteobacterial genomes.
αr9 is a family of bacterial small non-coding RNAs with representatives in a broad group of α-proteobacteria from the order Hyphomicrobiales. The first member of this family (Smr9C) was found in a Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 locus located in the chromosome (C). Further homology and structure conservation analysis have identified full-length Smr9C homologs in several nitrogen-fixing symbiotic rhizobia, in the plant pathogens belonging to Agrobacterium species as well as in a broad spectrum of Brucella species. αr9C RNA species are 144-158 nt long and share a well defined common secondary structure consisting of seven conserved regions. Most of the αr9 transcripts can be catalogued as trans-acting sRNAs expressed from well-defined promoter regions of independent transcription units within intergenic regions (IGRs) of the α-proteobacterial genomes.
αr15 is a family of bacterial small non-coding RNAs with representatives in a broad group of α-proteobacteria from the order Rhizobiales. The first members of this family were found tandemly arranged in the same intergenic region (IGR) of the Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 chromosome (C). Further homology and structure conservation analysis have identified full-length Smr15C1 and Smr15C2 homologs in several nitrogen-fixing symbiotic rhizobia, in the plant pathogens belonging to Agrobacterium species as well as in a broad spectrum of Brucella species. The Smr15C1 and Smr15C2 homologs are also encoded in tandem within the same IGR region of Rhizobium and Agrobacterium species, whereas in Brucella species the αr15C loci are spread in the IGRs of Chromosome I. Moreover, this analysis also identified a third αr15 loci in extrachromosomal replicons of the mentioned nitrogen-fixing α-proteobacteria and in the Chromosome II of Brucella species. αr15 RNA species are 99-121 nt long and share a well defined common secondary structure consisting of three stem loops. The transcripts of the αr15 family can be catalogued as trans-acting sRNAs encoded by independent transcription units with recognizable promoter and transcription termination signatures within intergenic regions (IGRs) of the α-proteobacterial genomes.
αr35 is a family of bacterial small non-coding RNAs with representatives in a reduced group of Alphaproteobacteria from the order Hyphomicrobiales. The first member of this family (Smr35B) was found in a Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 locus located in the symbiotic plasmid B (pSymB). Further homology and structure conservation analysis have identified full-length SmrB35 homologs in other legume symbionts, as well as in the human and plant pathogens Brucella anthropi and Agrobacterium tumefaciens, respectively. αr35 RNA species are 139-142 nt long and share a common secondary structure consisting of two stem loops and a well conserved rho independent terminator. Most of the αr35 transcripts can be catalogued as trans-acting sRNAs expressed from well-defined promoter regions of independent transcription units within intergenic regions of the Alphaproteobacterial genomes.
αr45 is a family of bacterial small non-coding RNAs with representatives in a broad group of α-proteobacteria from the order Hyphomicrobiales. The first member of this family (Smr45C) was found in a Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 locus located in the chromosome (C). Further homology and structure conservation analysis identified homologs in several nitrogen-fixing symbiotic rhizobia, in the plant pathogens belonging to Agrobacterium species as well as in a broad spectrum of Brucella species, in Bartonella species, in several members of the Xanthobactereacea family, and in some representatives of the Beijerinckiaceae family. αr45C RNA species are 147-153 nt long and share a well defined common secondary structure. All of the αr45 transcripts can be catalogued as trans-acting sRNAs expressed from well-defined promoter regions of independent transcription units within intergenic regions (IGRs) of the α-proteobacterial genomes.
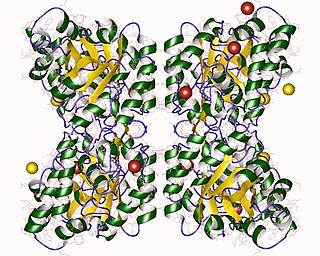
4-Hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase (EC 4.3.3.7, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydropicolinate synthetase, dihydrodipicolinic acid synthase, L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing), dapA (gene)) is an enzyme with the systematic name L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing; (4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-(2S)-dipicolinate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction














